Managing public keys, Configuration task list – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 110
99
Managing public keys
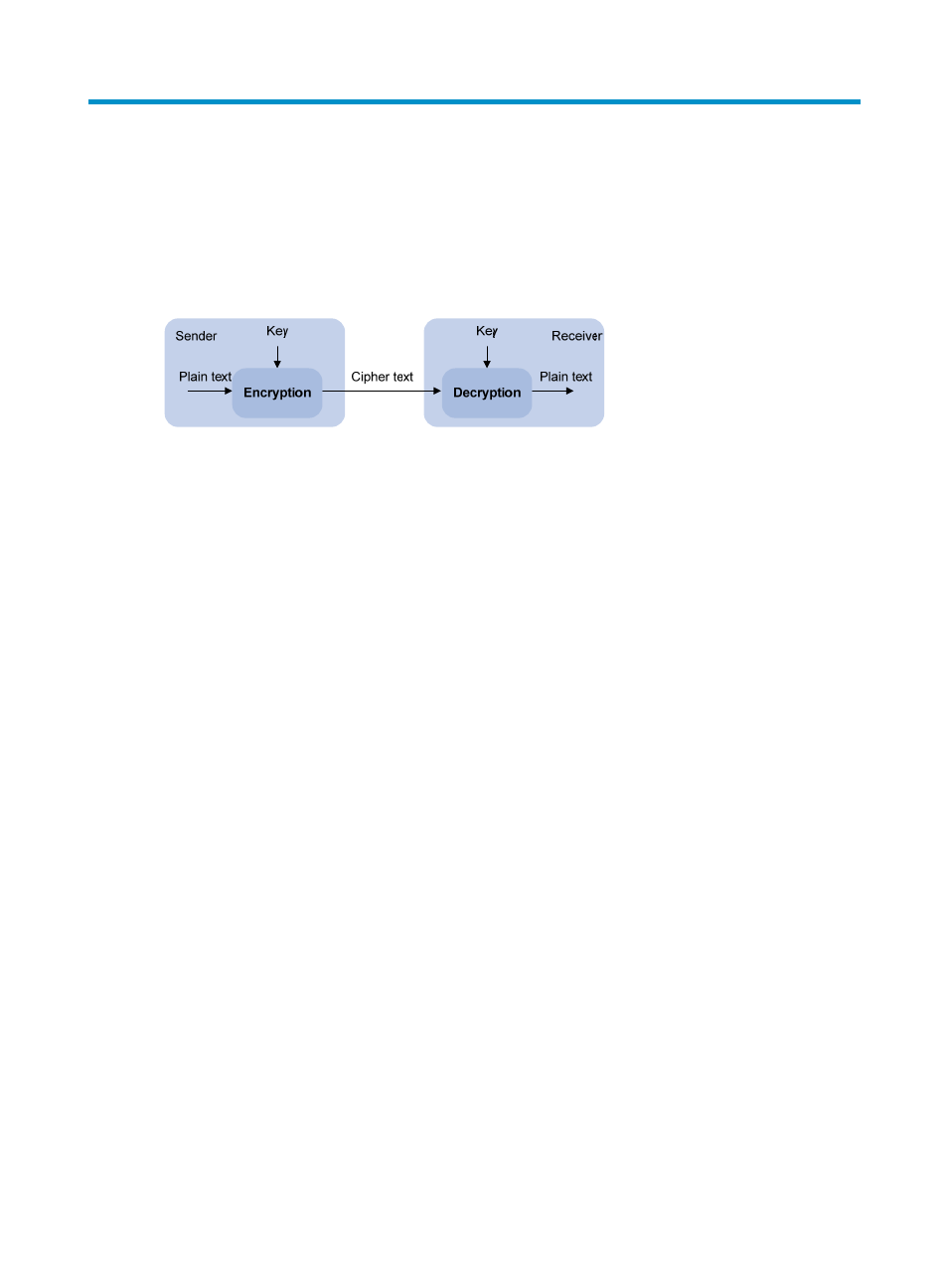
To protect data confidentiality during transmission, the data sender uses an algorithm and a key to
encrypt the plain text data before sending the data out. The receiver uses the same algorithm with the
help of a key to decrypt the data, as shown in
Figure 36 Encryption and decryption
The keys that participate in the conversion between plain text and cipher text can be the same or different,
dividing the encryption and decryption algorithms into the following types:
•
Symmetric key algorithm—The keys for encryption and decryption are the same.
•
Asymmetric key algorithm—The keys for encryption and decryption are different. One is the public
key, and the other is the private key. The information encrypted with the public key can only be
decrypted with the corresponding private key, and vice versa. The private key is kept secret, and the
public key may be distributed widely. The private key cannot be practically derived from the public
key. Asymmetric key algorithms include RSA.
The asymmetric key algorithm RSA can be used for the following purposes:
•
To encrypt and decrypt data—Any public key receiver can use the public key to encrypt information,
but only the private key owner can decrypt the information. This mechanism ensures confidentiality.
•
To authenticate a sender—Also called "digital signature." The key owner uses the private key to
"sign" information to be sent, and the receiver decrypts the information with the sender's public key
to verify information authenticity.
Asymmetric key algorithms are widely used in various applications. For example, SSH, SSL, and PKI use
the algorithms for digital signature. For information about SSH, SSL, and PKI, see "Configuring SSH,"
"Configuring SSL," and "Configuring PKI."
Public keys can be configured only at the CLI.
Configuration task list
Public key configuration tasks enable you to manage the local asymmetric key pairs and configure the
peer host public keys on the local device. By completing these tasks, the local device is ready to work
with applications such as SSH and SSL to implement data encryption/decryption, or digital signature.
Complete these tasks to configure public keys:
