3 understanding tdma, Frequency time – Comtech EF Data MDX420 SkyWire Manual User Manual
Page 19
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway
Introduction
MN-MDX420 Revision 6
1–3
1.3 Understanding
TDMA
In a traditional Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) system, a transponder resource is shared
between a number of earth stations based on frequency allocations. In a FDMA system, an earth station
will continuously transmit a single carrier on specific frequency broadcasting to a single receiver or
multiple receivers at different earth stations.
In a TDMA system, a frequency allocation is shared between a number of earth stations based on time
‘slots’. Within a TDMA system, the transponder receives a sequential burst of transmissions from multiple
earth stations broadcasting out to multiple receivers. In traditional “non-skywire” TDMA systems, the time
plan for each earth station’s burst is determined by a central control system at a central location.
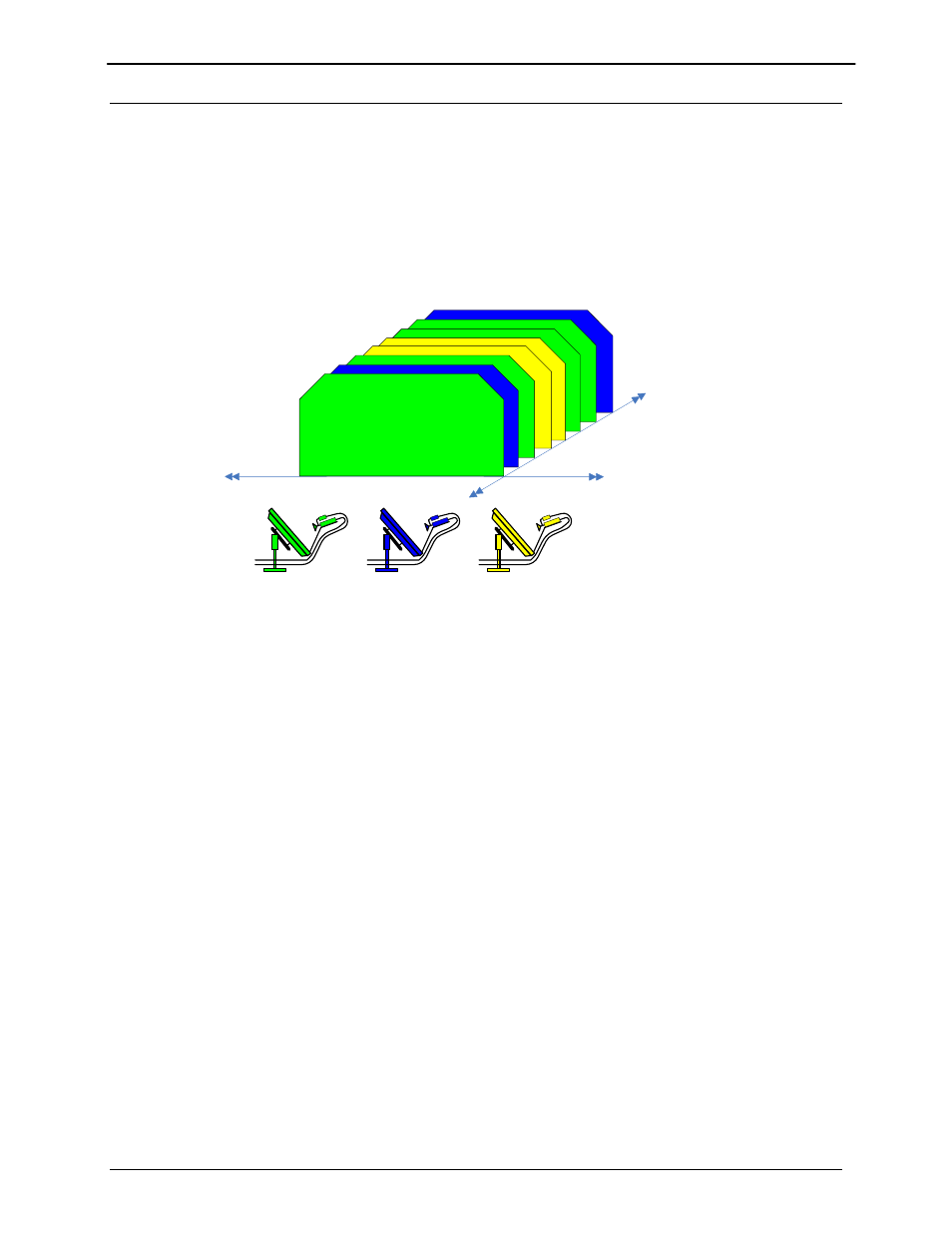
Figure 1-3 TDMA Access Example
Figure 1-3 shows an example of TDMA access of the satellite frequency allocation. In the example
above, 3 remote sites are sharing a frequency allocation with each site transmitting sequentially. As
stated above, in a TDMA platform, multiple sites “time share” their transmission on the same frequency
carrier and data rates. The aggregate transmission will be received by a hub or participating remotes
allowing each remote to determine which data they need to pass on to the local LAN. The aggregate
transmission reflects multiple bursts from all 3 earth stations transmitting their IP data over satellite to the
all sites in the network.
Frequency
Time
TX
LN
B
BU
C
RX
TX
LN
B
BU
C
RX
TX
LN
B
BU
C
RX
