Installing and configuring routers – Echelon LNS User Manual
Page 188
LNS Programmer's Guide
174
which are connected by a permanent bridge.
3. The final rule allows for redundant routing when using configured
routers. Redundant router topologies provide fault tolerance by providing
more than one routing path from one channel to another. They are also
required when all devices on a given channel may not be able to hear one
another (referred to as an ear shot problem), e.g. on a radio frequency
channel.
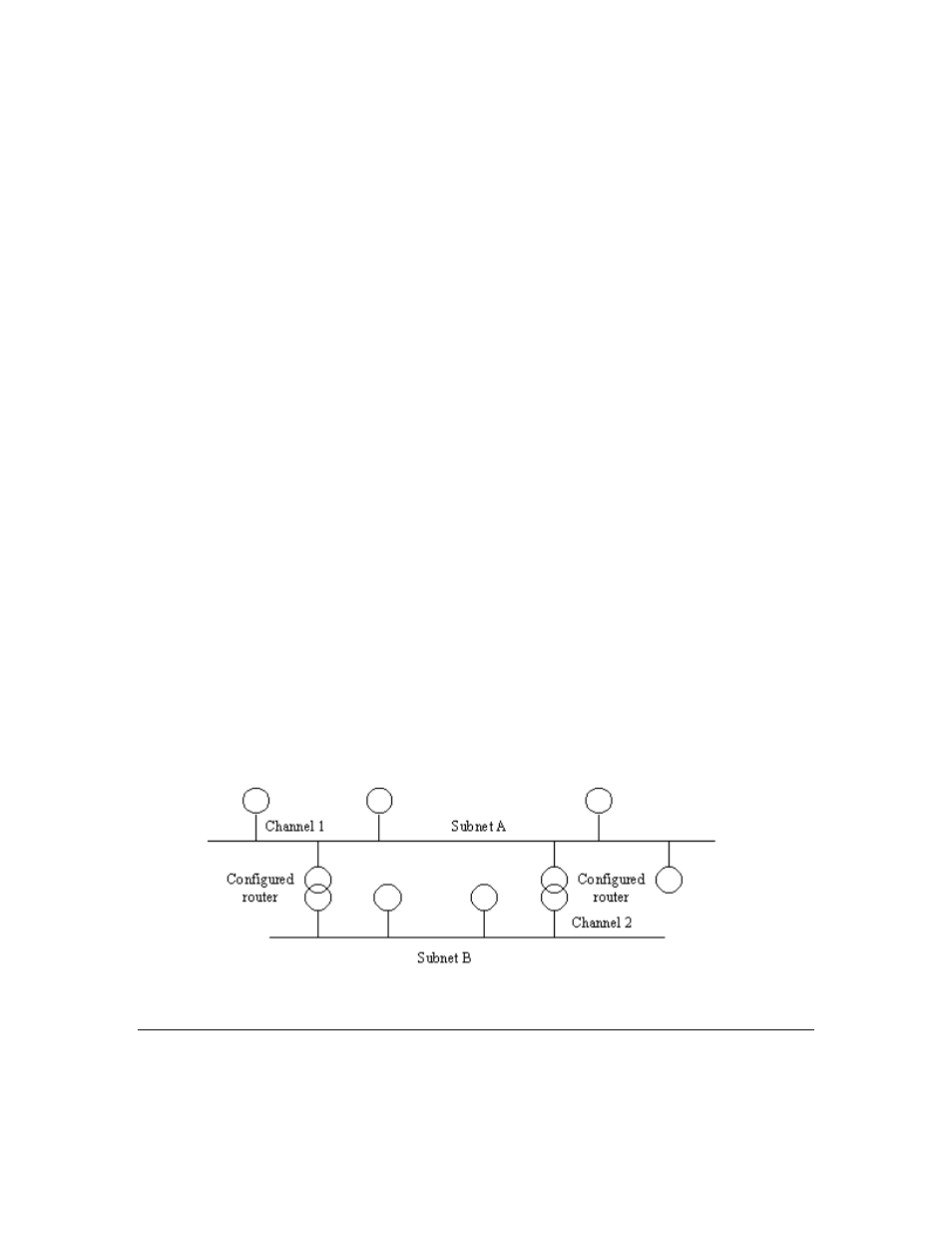
An example of a redundant routing topology is shown in Figure 8.3 below.
Both routers can forward packets originating on Subnet A and destined
for Subnet B. Any open circuit in either Channel 1 or Channel 2 still
leaves the network logically connected.
The redundant routing topology provides a backup means of
communication through redundant paths in the form of routers and the
resulting redundant packets. For every packet sent from a device on
Channel 1, Subnet A to a device on Channel 2, Subnet B, two packets will
be delivered (one packet from each of the configured routers). This will
occur for every point at which a backup router exists. Furthermore,
acknowledgments are multiplied.
For example, consider a network consisting of 3 channels that employs
redundant routers between each channel. Sending a single acknowledged
message that spans all three channels will result in 2 acknowledged
messages on the second channel, and 4 on the third channel. Each of
these four messages will be acknowledged, resulting in 8
acknowledgements on the second channel and 16 on the first channel.
This situation worsens when authenticated messaging is used, since an
authenticated transaction consists of 4 separate messages (the initial
message, a challenge, a reply, and an acknowledgment). In the example
given above, a single acknowledged authenticated message would result
in 4 acknowledged messages on the third channel, 16 challenges on the
first channel, 64 replies on the third channel and 256 acknowledgments
on the first channel. Echelon recommends that you limit the number of
redundant routers created by the user, and warn the end user of the
effects of setting up redundant routers.
Figure 8.3 Redundant Routing Topology
Installing and Configuring Routers
When installing and configuring routers, your application can treat routers in much the
same way as application devices, using the steps described in Chapters 5 and 6 of this
