Echelon LNS User Manual
Page 185
LNS Programmer's Guide
171
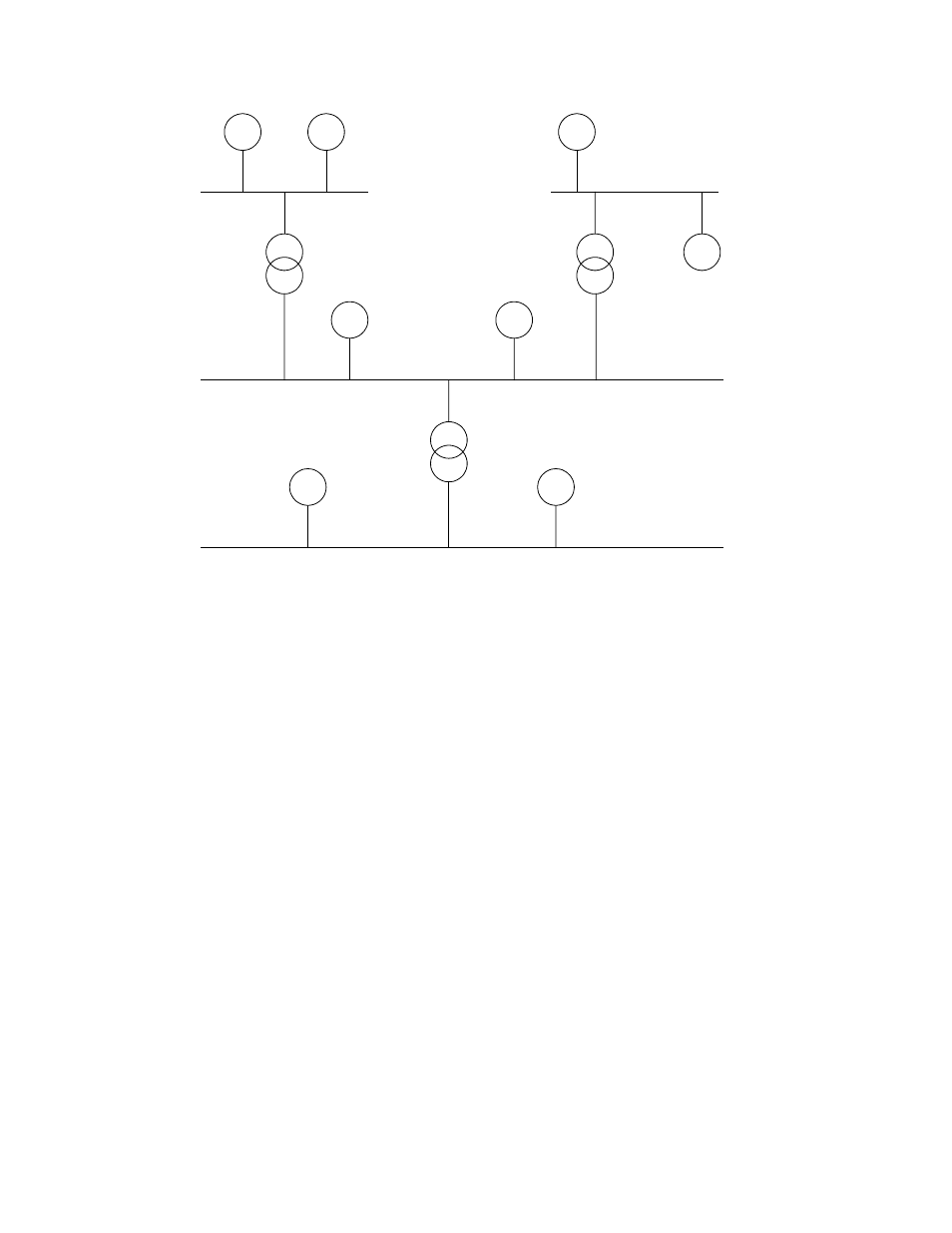
Channel 1
Channel 2
Router
Router
Channel 3
Router
Channel 4
Figure 8.1 A Network with Multiple Channels
A L
ON
W
ORKS
router can be configured as one of four router types:
• A repeater forwards all valid packets received on one channel to the other
channel, without regard for address. Repeaters extend the physical reach
of a channel, while preventing corrupted packets from causing problems.
You should not confuse a router configured as a repeater with a physical
repeater. Repeaters cannot be used in topologies with physical loops, as a
given message could be repeated endlessly in this case. Physical
repeaters, in contrast, act as simple signal boosters and noise filters to
extend the physical reach of a channel, without providing any message
routing, validation or filtering.
• A bridge forwards a valid packet received on one channel to the other
channel if the packet is sent on a domain that the bridge belongs to. In a
single domain network, a bridge functions in the same manner as a
repeater. Bridges cannot be used in topologies with physical loops, as a
given message could be repeated endlessly in this case.
• A learning router forwards packets based on internal routing tables.
These tables contain one entry for each subnet in the application domain.
Learning routers have their routing tables in volatile memory so that
after they are reset, the router forwards packets addressed to all subnets
in the application domain. Whenever a learning router receives a packet
from one of its channels, it uses the source subnet ID to learn the
network topology. It then sets the corresponding routing table entries to
indicate that the subnet in question can be discovered in the direction
from which the packet was received.
