Mstp configuration – Comtrol ES7510 User Manual
Page 73
RocketLinx ES7510 User Guide: 2000544 Rev. B
MSTP Configuration - 73
Configuration Using the Web Interface
MSTP Configuration
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) is a direct extension of RSTP. It can provide an independent
spanning tree for different VLANs. It simplifies network management, creates a faster convergence than
RSTP by limiting the size of each region, and prevents VLAN members from being segmented from the rest of
the group (as sometimes occurs with IEEE 802.1D STP).
While using MSTP, there are some new concepts of network architecture. A switch may belong to different
groups, act as root or designate switch, or generate BPDU packets for the network to maintain the forwarding
table of the spanning tree. MSTP can also provide load balancing between switches.
One VLAN can be mapped to a Multiple Spanning Tree Instance (MSTI). The maximum number of instances
that the ES7510 supports is 16, with a range from 0-15. The MSTP builds a separate Multiple Spanning Tree
(MST) for each instance to maintain connectivity among each of the assigned VLAN groups. An Internal
Spanning Tree (IST) is used to connect all the MSTP switches within an MST region. An MST Region may
contain multiple MSTP instances.
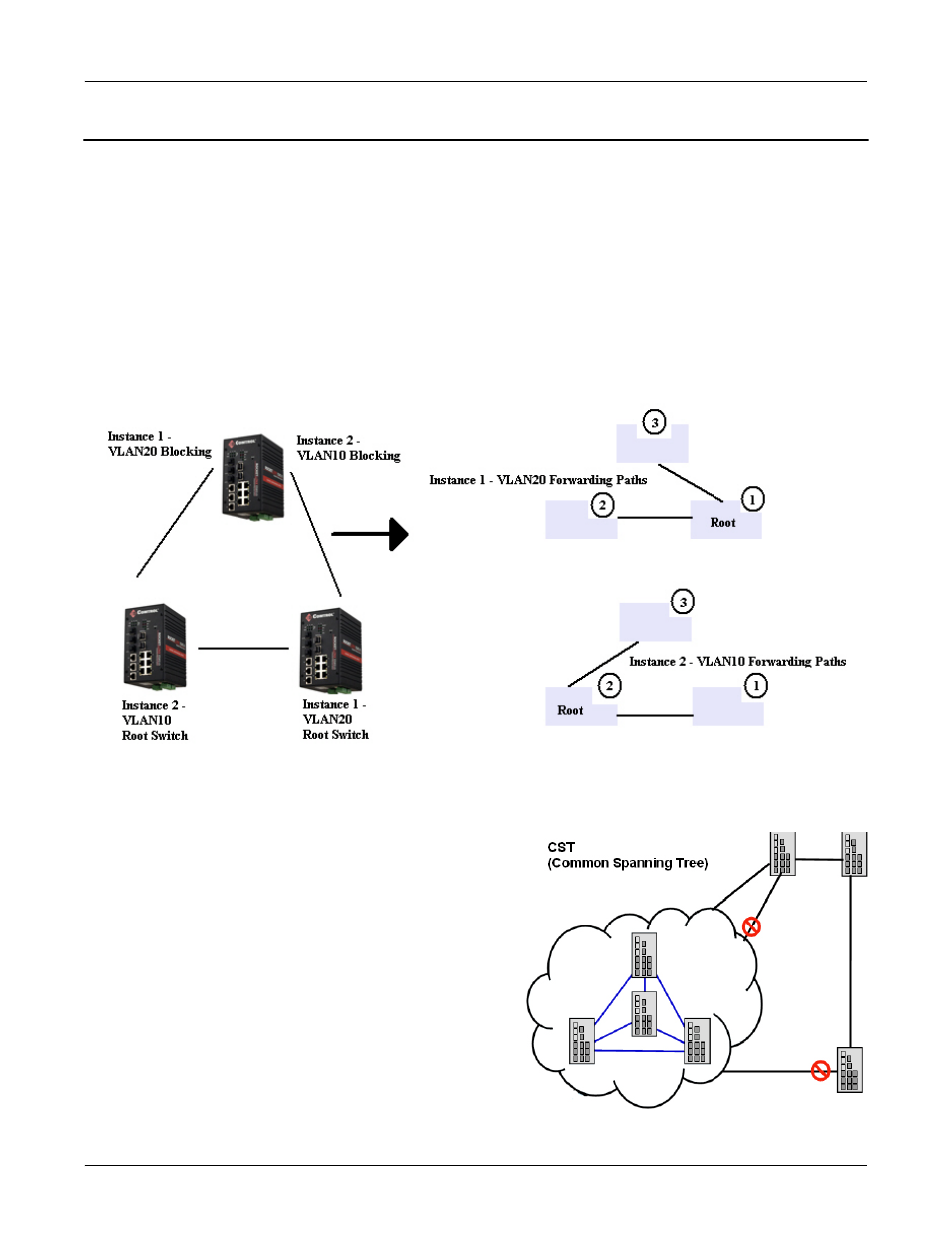
The following figure shows a MSTP instance with two VLANs. Each instance has a root node and forwarding
paths.
A Common Spanning Tree (CST) interconnects all adjacent MST regions and acts as a virtual bridge node for
communications with STP or RSTP nodes in the global network. MSTP connects all bridges and LAN
segments with a single Common Internal Spanning Tree (CIST). The CIST is formed as a result of the
running spanning tree algorithm between switches that support the STP, RSTP, or MSTP protocols.
The following diagram shows a CST attached to a larger
network. In this network, a Region may have different
instances and its own forwarding path and table, however,
the CST acts as a single bridge.
