Rockwell Automation 1772-LS_LSP,D17726.8.6 PROG/OPER MANUAL-MINI PLC-2/05 User Manual
Page 54
Relay-type Instructions
Chapter 6
6Ć2
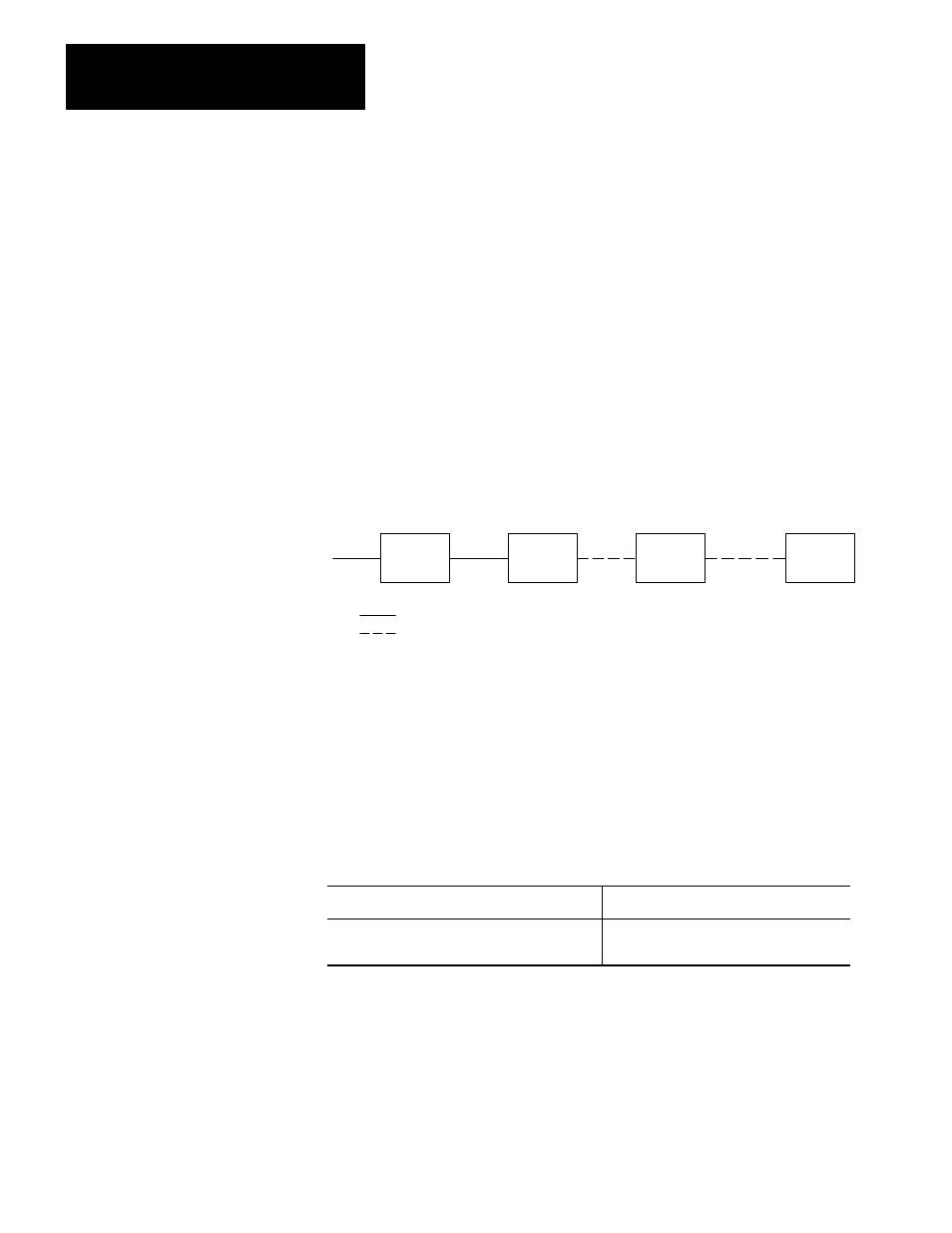
C1 = Input switch 1. When the switch is on, this condition is true. This switch
turns on a conveyer belt.
C2 = Input sensor 1. When the sensor is off, this condition is true. This sensor
detects if the temperature in the factory is below 40
o
C.
C3 = Input sensor 2. When the sensor is on, this condition is true. This sensor
detects the presence of a part of the conveyer belt.
A = The part will be drilled. = The path of conditions is continuous, that is, all
conditions are true.
When C1, C2, and C3 are true, then a continuous path is made to a particular
action. In this case, the continuous path causes the part to be drilled. When the
path of conditions is continuous, we say that the rung is true. When the path of
conditions is not continuous, we say the rung is false.
C1
True
C2
False
C3
True
A
True
False
Here the path of conditions is not continuous because condition 2 is false.
Therefore, the action A is not performed. We say the rung is false.
Set vs. Reset
As a review, if the device goes on, then we say the corresponding bit in data
table is set to a 1. If the device goes off, we say the corresponding bit in data
table is reset to a 0. (From this point on, set means the on-condition or 1. Reset
means the off-condition or 0.)
If the device is:
Then a bit in memory is
on
set
off
reset
Addresses
The processor scans the status of inputs and controls output devices. It does not
go to the input or output terminals to see if outputs are on or off. Rather, it
checks the status of the input and output devices by scanning corresponding bits
in the input and output image area of the data table. The processor uses
addresses to refer to words and bits in the data table.
