Rockwell Automation 1772-LS_LSP,D17726.8.6 PROG/OPER MANUAL-MINI PLC-2/05 User Manual
Page 50
Scan Theory
Chapter 5
5Ć3
On power-up, the processor begins the scan sequence with the I/O scan. Data
from output image table is written to the output modules. Data from the input
modules is read into the input image table.
Next, the processor scans the program statement by statement:
1.
For each condition, the processor checks, or “reads,” the image table to see
if the condition has been met.
2.
If the set of conditions has been met, the processor writes a one into the bit
location in the output image table corresponding to the output terminal to
be energized. On the other hand, if the set of conditions has not been met,
the processor writes a zero into that bit location, indicating that the output
terminal should not be energized.
Important: When your processor is in the remote test mode, all outputs are
held off. When your processor is in the run/program mode, all outputs are
controlled by the user program.
Average scan time is the average amount of time it takes the processor to
monitor and update input and outputs, and to execute instructions in the
program. The scan is performed serially; first the I/O image table is updated,
(other parts of the data table are not scanned), then the user program is scanned.
There are two ways to measure average scan time:
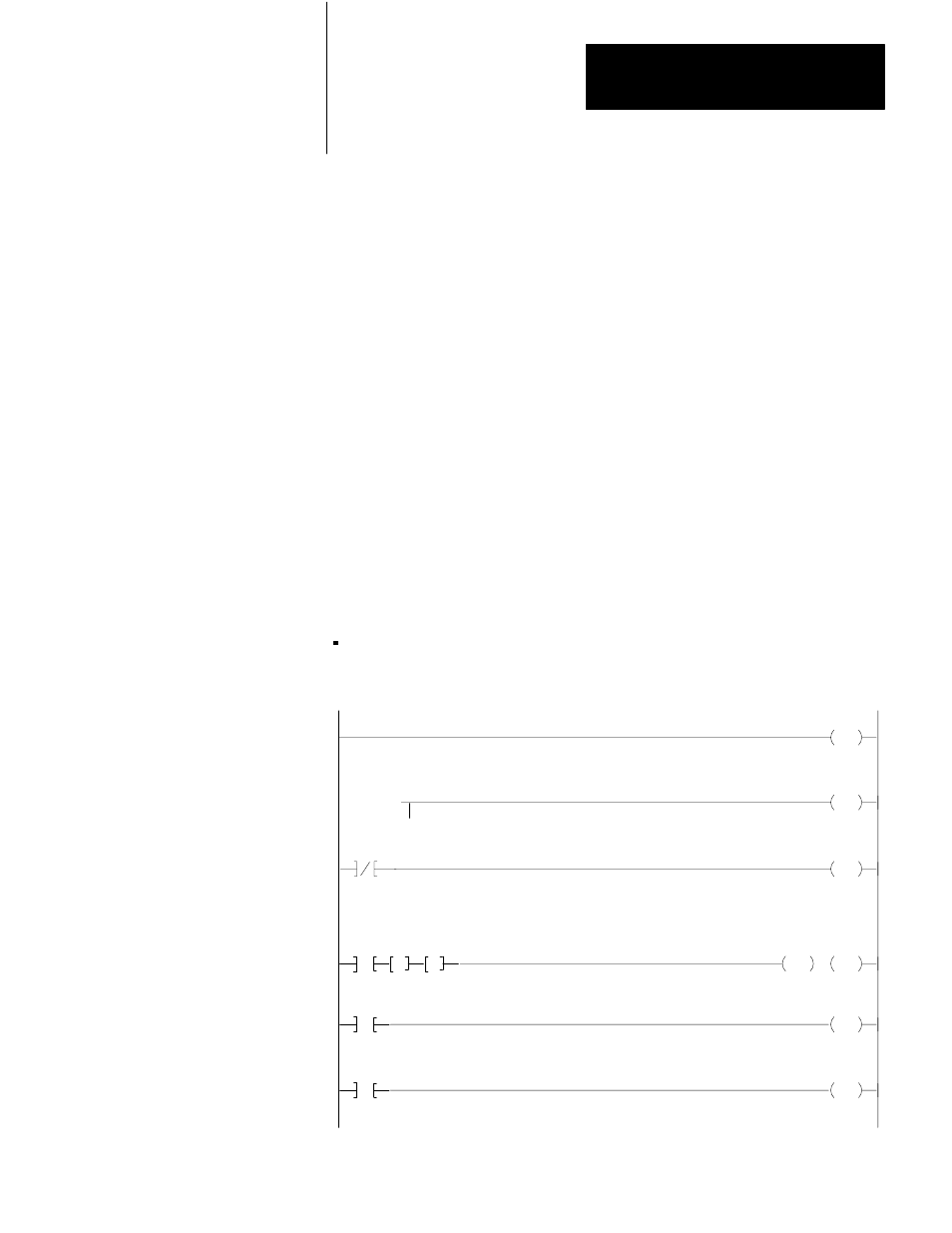
Append the rungs in Figure 5.2 to your program.
Figure 5.2
Average Scan Time
031
14
CTU
031
PR 999
031
14
CTU
031
PR 999
RTO
032
0.1
032
000
Store
010
G
G
:
Store
000
AC 000
AC 000
PR 999
AC 000
1
031
14
RTR
032
PR 999
:
Store
000 .
2
3
AC 000
031
14
RTR
032
PR 999
AC 000
Rung 1
Rung 2
Rung 3
Rung 4
Rung 5
Rung 6
Average Scan Time
