1 performing a slave boot, 1 slave boot procedure, 1 performing a slave boot -8 – Cirrus Logic CS4953xx User Manual
Page 22: Figure 2-3. slave boot sequence -8, Figure 2-3. slave boot sequence
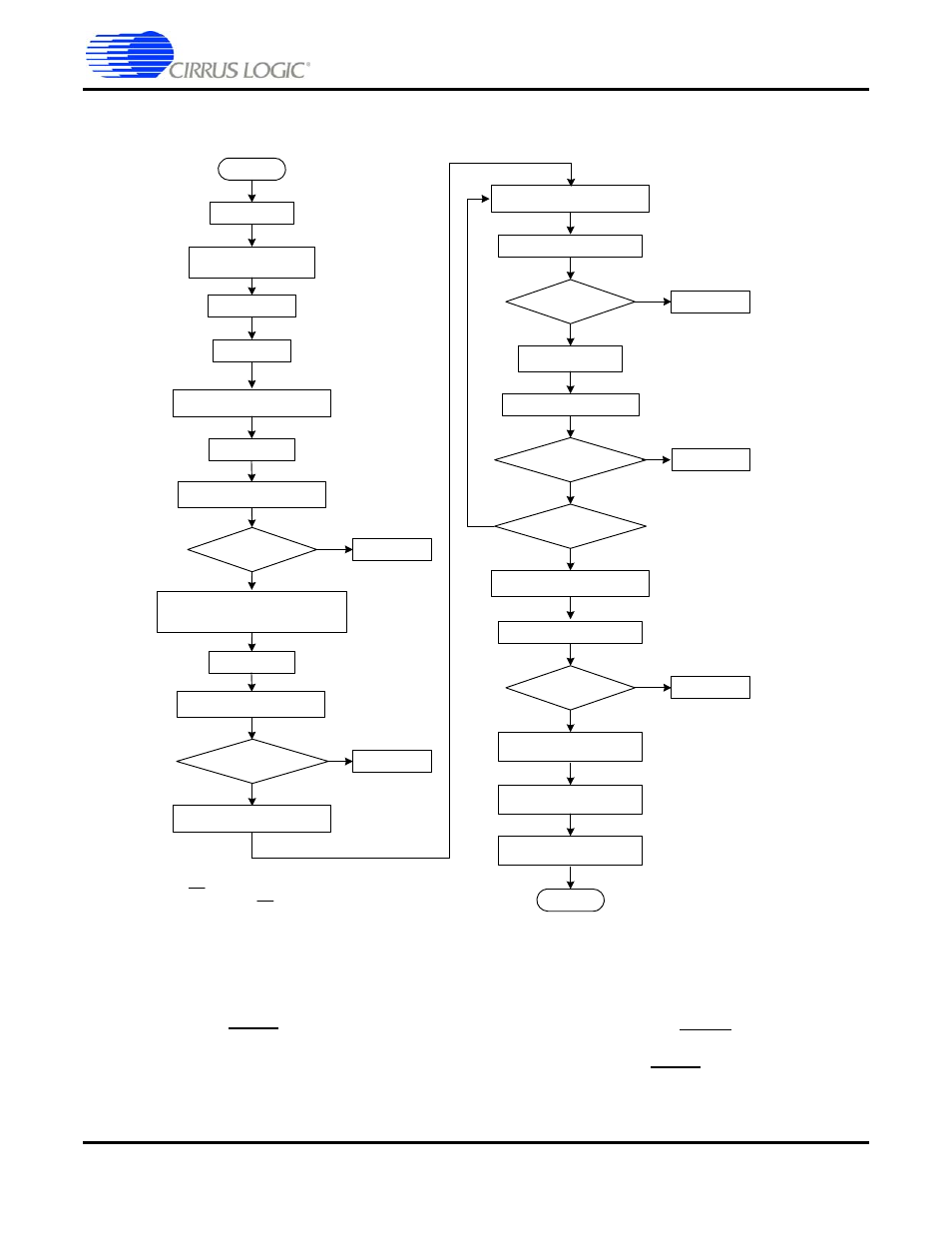
Slave Boot Procedures
CS4953xx Hardware User’s Manual
DS732UM10
Copyright 2010 Cirrus Logic, Inc
2-8
2.3.2.1 Performing a Slave Boot
shows the steps taken during a Slave boot. The procedure is discussed in
Figure 2-3. Slave Boot Sequence
2.3.2.1.1 Slave Boot Procedure
1.
Toggle RESET. A download sequence is started when the host holds the RESET pin low for the
required time. The mode pins (HS[4:0]) must be in the appropriate state to set the host
communication mode before and immediately after the rising edge of RESET. Pull-up and pull-down
resistors are typically used to set the default state of the HS[4:0] pins.
2. Wait for 50
μ
s.
WAIT 10
μ
S
WRITE_* (SLAVE_BOOT)
MSG
==BOOT_START
EXIT(ERROR)
N
Y
WAIT 10
μ
S
READ_* (MSG)
NOTE 1
EXIT(ERROR)
N
Y
MSG==
BOOT_SUCCESS
WRITE_*
(SOFT_RESET_DSP_A)
READ_* (MSG)
NOTE 1
WRITE_* (BOOT_ ASSIST_A.ULD FILE)
Or (boot_assist_xtal_div2_a*.uld)
RESET# (HIGH)
WAIT 50
μ
S
START
RESET# (LOW)
SET HS[3:0] PINS FOR
OPERATIONAL MODE
NOTE 1. Read four bytes from the DSP.
IRQ will not drop for this read sequence.
NOTE 2. Obey IRQ for all reads from
this point forward.
MSG
==BOOT_START
WRITE_*(SLAVE_BOOT)
READ_*(MSG)
NOTE 2
EXIT (ERROR)
N
Y
MSG==
BOOT_SUCCESS
EXIT(ERROR)
N
Y
READ_* (MSG)
WRITE_*(.ULD FILE)
MSG ==APP_START
WRITE_* (SOFT_RESET)
READ_* (MSG)
EXIT (ERROR)
N
Y
MORE .ULD FILES?
Y
N
DONE
SEND HARDWARE
CONFIGURATIONS
SEND FIRMWARE
CONFIGURATIONS
WRITE_* (KICKSTART)
* is replaced with SCP, I2C, etc.
depending on the communication
protocol used.
