1 egd example 1 – configuring node 1, Egd example 1 – configuring node 1 – Horner APG XL4 OCS HE-ETN300 User Manual
Page 42
CH.6
SUP0740-07
11/30/2009
Page 42 of 98
# 958
6.8.1
EGD Example 1 – Configuring Node 1
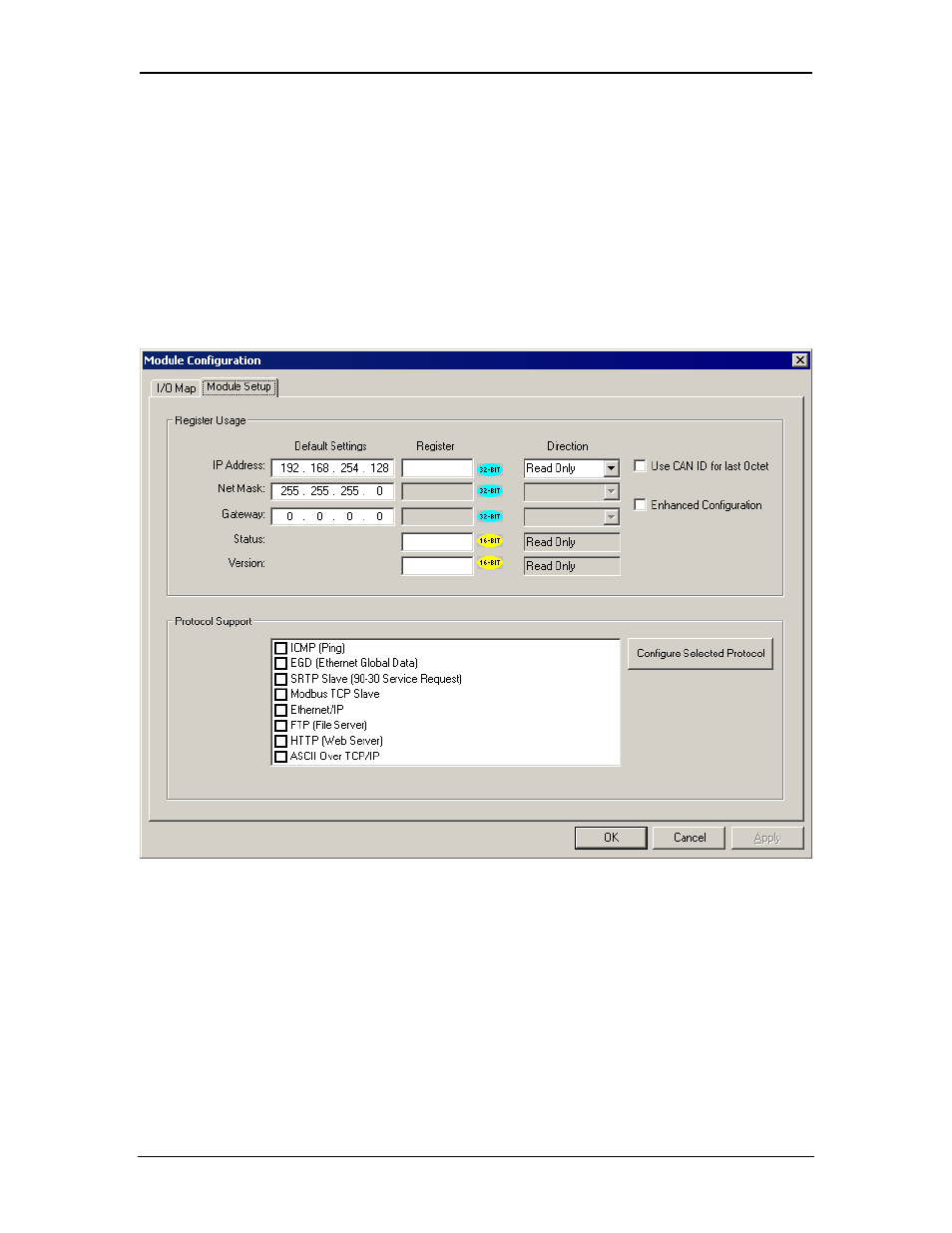
To configure Node 1 for EGD Example 1, as shown in Figure 6.6, perform the following six steps:
1. On the main Cscape screen, select New on the File menu to start a new user program. Then
open the Ethernet Module Configuration dialog (Chapter 3, Figure 3.5 [page 18]), and fill in
the parameters for Node 1, as shown in Figure 6.7 below.
In this example, Node 1 will have a Static IP Address (Section 3.2.1 [page 21]), and the %R1,
%R2 and %R3 registers will be used to report the Ethernet Module’s status, firmware version,
and IP Address (step 5 in Section 3.1). Note that since an IP Address is 32-bits long, Node
1’s IP Address (192.168.0.1) will actually be written into %R3 and %R4.
Figure 6.7– Ethernet Module Configuration - Node 1
2. Click on the Config button next to the EGD (Ethernet Global Data) checkbox to open the
Ethernet Global Data Configuration dialog (Figure 6.1 [page 32]) and click on the Add Exch
button to create a Produced Exchange. Then, fill in the parameters for Node 1, as shown in
Figure 6.8 below, and click OK.
In this example, Node 1 will transmit Exchange 1 to a specific Consumer (Node 2), instead of
to a Group of Consumers. Also, the Production Period is set to 100, which will cause Node 1
to transmit Exchange 1 every 100 mS.
