Discontinuing truecopy operations – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 119
Hitachi TrueCopy for z/OS user guide 119
of the conditions that affect disk array performance and provides recommendations for addressing these
conditions.
Discontinuing TrueCopy operations
If you plan to use TC390 for nondisruptive data migration or duplication (see ”
” on page 140), you will need to configure and establish TC390 operations, allow
TC390 to synchronize the volumes, redirect application I/Os (if migrating), and then discontinue TC390
operations. When you are ready to discontinue TC390 operations, you will need to perform TC390
operations in the correct order to avoid generating error messages. For example, you cannot delete an
RCU path until you have deleted all TC390 pairs still using that path and you cannot delete a group until
you have deleted all TC390A pairs in that group.
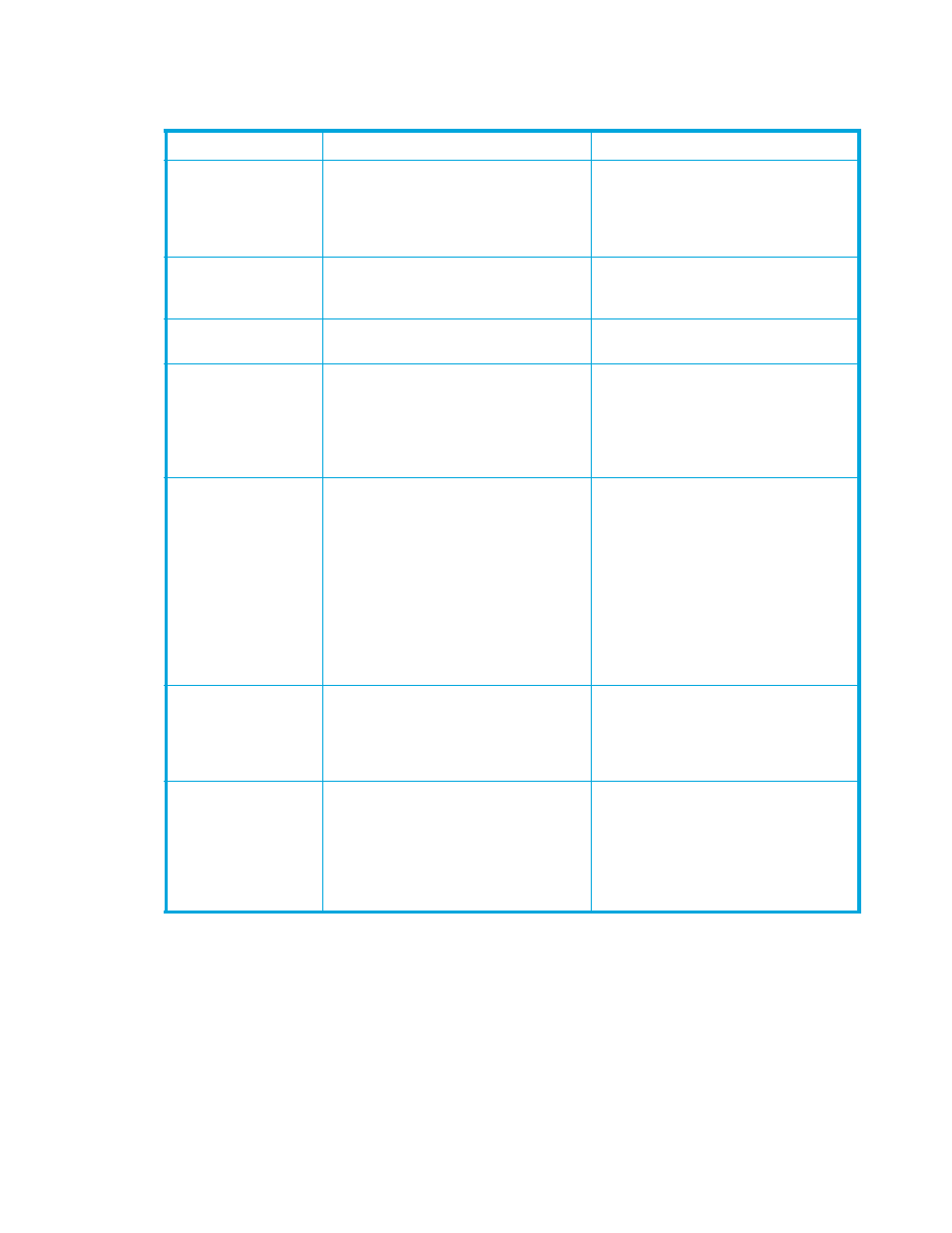
Table 24
Optimizing TrueCopy operations and XP12000/XP10000 performance
Condition
Description
Recommendation(s)
Write-intensive
workloads
Write-intensive workloads, such as SPOOL
volumes and database logging volumes,
can have a significant impact on disk
array I/O response times.
Spread write-intensive data across several
volumes to minimize queuing. Also
consider increasing the duplex write line
(DWL) of the disk array using Performance
Monitor.
Large block size
Workloads with large write block sizes,
such as DB2 deferred writes, can impact
performance.
Spread workloads with large write block
sizes across several volumes.
High host channel
demand
The demand on the MCU’s host channels
can affect performance.
Spread the workload across several disk
arrays to use additional channels.
Sequential write
operations
TC390 operations can have a negative
impact on workloads with a high
percentage of sequential write operations,
such as batch processing operations (for
example, dump/restore or sort
operations).
Avoid performing restore operations to
volumes that belong to TC390 pairs.
Instead, restore data to a scratch volume
and then establish the TC390 volume pair.
Cache size
Large cache size improves read hit
performance, which allows more disk
array resources to be devoted to write
operations. The resulting performance
improvement can offset some or all of the
performance loss due to the TC390 remote
copy operations.
TC390A and HXRC require additional
cache for sidefile data. Insufficient cache
resources can result in command retries,
SCP notifications, and puncture conditions.
Consider increasing the cache size of the
TC390 disk arrays to handle TC390A and
HXRC sidefile operations and to improve
overall disk array performance. For best
results, the cache and NVS capacity of the
main and remote disk arrays should be the
same (for TC390A the RCU sidefile
requirements are 2x that of the MCU) to
enable the remote site to function
adequately during disaster recovery.
RCU capacity
The performance of the RCUs directly
affects the performance of the MCUs. If an
RCU becomes overloaded with heavy
update activity, MCU and system
performance can also be degraded.
Distribute TC390 remote copy operations
among several remote disk arrays to avoid
overloading any one RCU.
Remote copy
connection paths
An inadequate number of Remote copy
connection paths may decrease disk array
performance. Performing TC390
Synchronous operations over long
distances can also degrade disk array
performance. TC390A is recommended
for long distances.
Make sure to install an adequate number
of Remote copy connection paths between
the main and remote disk arrays. This is
especially important for disk arrays that
contain both M-VOLs and R-VOLs.
