Dynasonics TFX Ultra Transit Time Flow Meters User Manual
Page 19
Step 2 – Transducer Spacing
The transmitter can be used with five different transducer types: DTTN, DTTL, DTTH, DTTS and DTTC. Meters that utilize
the DTTN, DTTL or DTTH, transducer sets consist of two separate sensors that function as both ultrasonic transmitters and
receivers. DTTS and DTTC transducers integrate both the transmitter and receiver into one assembly that fixes the separation
of the piezoelectric crystals. DTTN, DTTL and DTTH transducers are clamped on the outside of a closed pipe at a specific
distance from each other.
The DTTN, DTTL and DTTH transducers can be mounted in:
• W-Mount where the sound traverses the pipe four times. This mounting method produces the best relative travel
time values but the weakest signal strength.
• V-Mount where the sound traverses the pipe twice. V-Mount is a compromise between travel time and
signal strength.
• Z-Mount where the transducers are mounted on opposite sides of the pipe and the sound crosses the pipe once.
Z-Mount will yield the best signal strength but the smallest relative travel time.
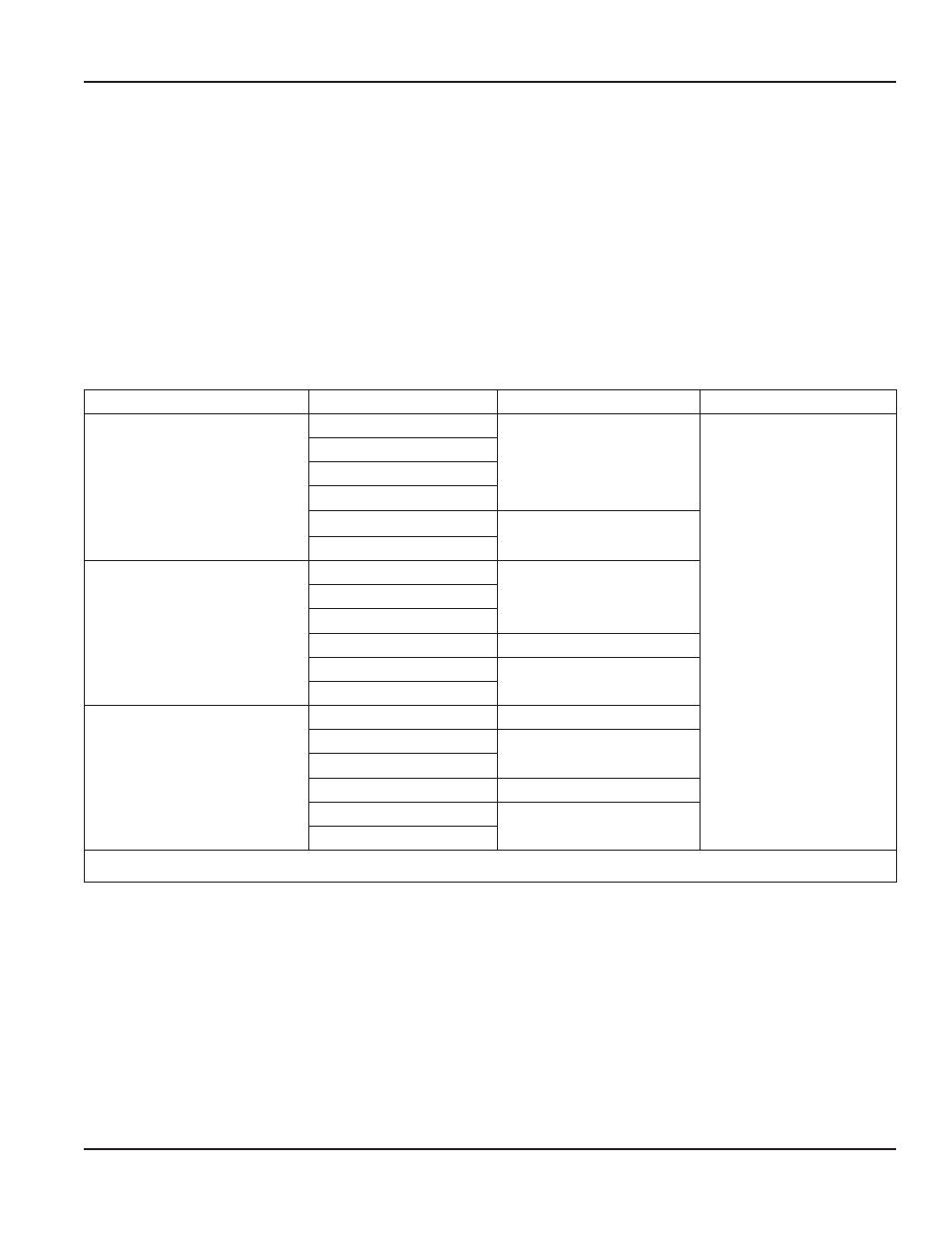
Transducer Mounting Mode
Pipe Material
Pipe Size
Liquid Composition
W-Mount
Plastic (all types)
2…4 in. (50…100 mm)
Low TSS; non-aerated
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Copper
Ductile Iron
Not recommended
Cast Iron
V-Mount
Plastic (all types)
4…12 in. (100…300 mm)
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Copper
4…30 in. (100…750 mm)
Ductile Iron
2…12 in. (50…300 mm)
Cast Iron
Z-Mount
Plastic (all types)
> 30 in. (> 750 mm)
Carbon Steel
> 12 in. (> 300 mm)
Stainless Steel
Copper
> 30 in. (> 750 mm)
Ductile Iron
> 12 in. (> 300 mm)
Cast Iron
TSS = Total Suspended Solids
Table 2: Transducer mounting modes — DTTN, DTTL, and DTTH
For further details, reference
Figure 9
. The appropriate mounting configuration is based on pipe and liquid characteristics.
Selection of the proper transducer mounting method is not entirely predictable and many times is an iterative process.
Table 2
contains recommended mounting configurations for common applications. These recommended configurations may
need to be modified for specific applications if such things as aeration, suspended solids, out of round piping or poor piping
conditions are present. Use of the flow meter diagnostics in determining the optimum transducer mounting is covered later
in this section.
TRANSDUCER INSTALLATION
Page 19
March 2014
