Extron Electronics DMP 128 User Guide User Manual
Page 83
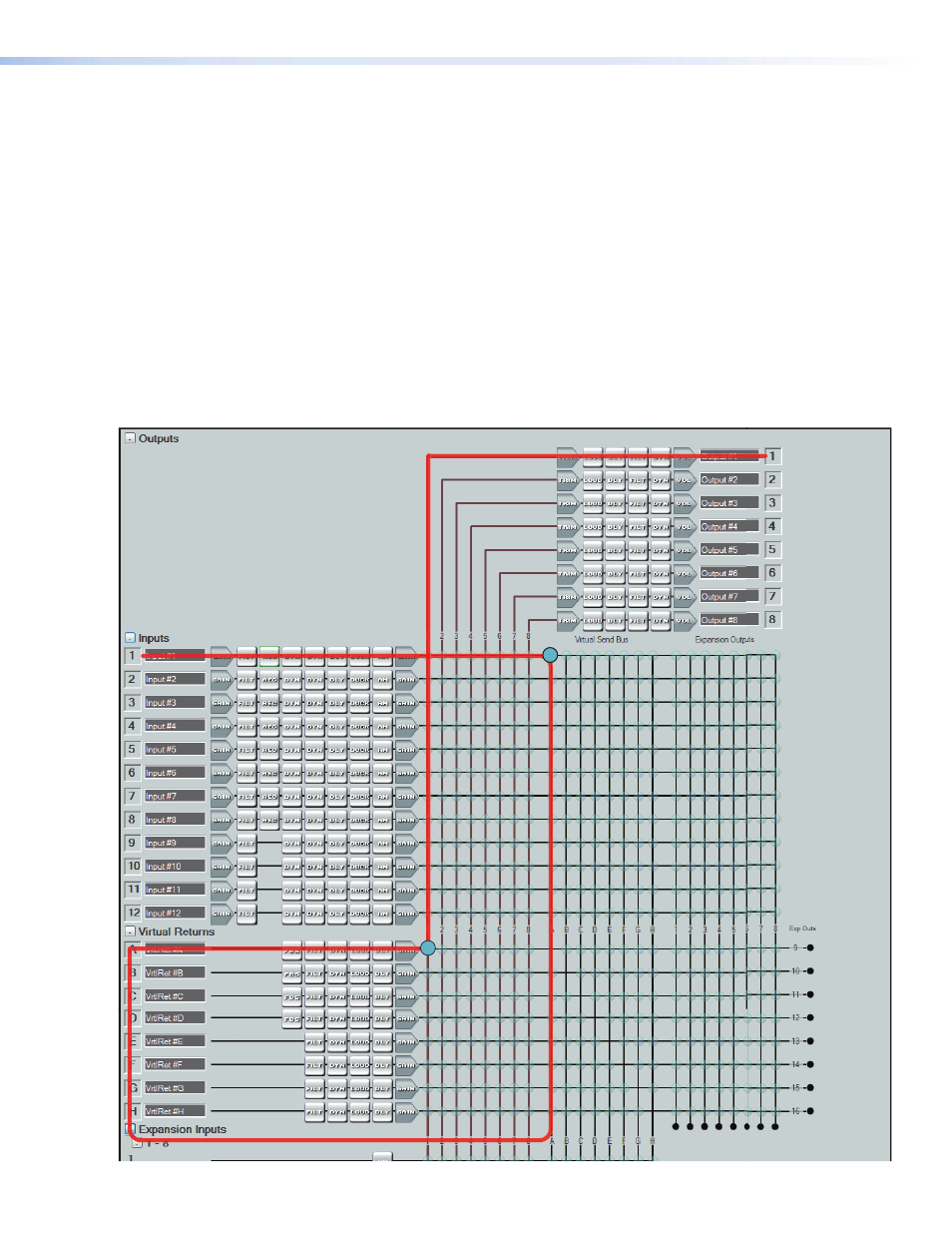
In the example in figure 46 below, input 1 is sent to the virtual send bus by muting all
eight signals on the Input 1 output mix-points and unmuting virtual send bus output 1.
The virtual bus now serves as additional signal processing for the input. The signal routes
from virtual send A through the virtual bus A signal chain before it is sent to the virtual bus
return mix-point and finally to output 1.
This configuration is useful when more than one input requires identical processing.
For example if all inputs were normalized but required a uniform gain to bring them up
to adequate output levels, rather than changing each pre-mix gain control by a similar
amount, all twelve inputs can be routed to a virtual bus (in this case virtual bus A). Then,
using the virtual bus A return gain control, a single adjustment can apply the same gain to
all twelve inputs before sending the signal to the desired output.
In other cases, when multiple mic inputs are mixed with program material, only the
program material might require loudness contouring. So the mics are routed directly to the
output but the program material input is routed to the virtual bus return where loudness
contouring is applied. The program material is then routed to the same output as the
mics.
Figure 46.
Input 1 to virtual Bus A
DMP 128 • Software Control
77
