Analog connectivity – Torso Electronics T-1 16-Track Algorithmic Desktop Sequencer User Manual
Page 195
195
The T-1 Notebook : Reference & Guide
NOTES
Analog Connectivity
9
1
Pitch
V/Oct - 1 Volt per Octave
Note: Frequency to the perception of pitch is logarithmic
V
o
lt
s
4
3
2
5
0
Velocity
Modulation
Voltage ranges may vary between devices and formats
V
o
lt
s
3.75
2.5
1.25
5
A1
55Hz
0
A2
110Hz
32
A3
220Hz
64
A4
440Hz
95
A5
880Hz
127
V-Trig
0 to +5V
S-Trig
+5V to 0V
Time
Time
0
V
o
lt
s
+5
0
V
o
lt
s
+5
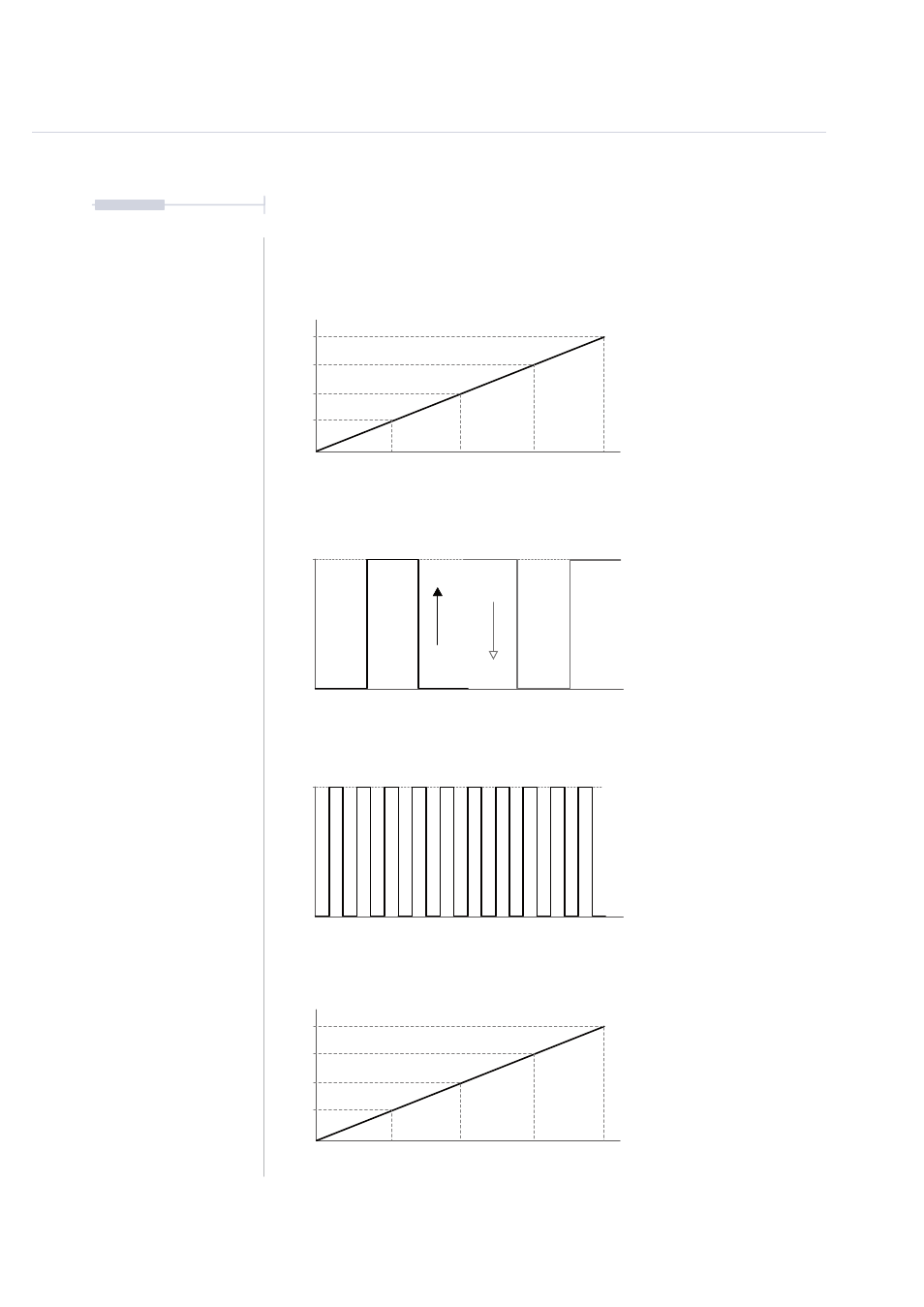
Example CV Concepts and Applications.
Diagrams and values for Illustrative purposes only. Actual behaviour will be based on specific devices.
Pitch
Volts per Octave is a common
approach to controlling pitch of an
analog device, especially in Eurorack.
Occasionally this may also follow an
alternative Hz / Volt format, used by
Korg and Yamaha.
Range
Control Voltages can also modulate
various parameters. These may be %
ranges, absolute values, offsets etc. T-
1 has a configuration option for
velocity. While this is based on the
velocity of notes it can be used to
modulate any analog parameter.
Trig
A trigger is a short voltage pulse that
activates an event. A gate is similar but
usually a longer, controlled length. A
trigger is often used for note on, off
and switch functions. V-Trig is the most
common, 0-5 rise to trigger. S-Trig
activates on a falling 5-0 voltage level.
Clock
An analog clock operates on a series
of pulses to synchronise devices.
Pulses are normally measured Pulses
per Quarter Note - PPQN. T-1 has
adjustable settings for analog clock
rates and pulse width to help match up
to devices. Analog clock is the highest
order in the clock hierarchy.
Trigger
Clock
