PLANET FGSW-2840 User Manual
Page 138
User’s Manual of FGSW-2840 / FGSW-4840S
Multicast Address
1. Multicast
IP
Address:
As specified by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), Class D IP addresses are used as destination addresses of
multicast packets. The multicast IP addresses range from 224.0.0.0~239.255.255.255. The following table displays the range
and description of several special multicast IP addresses.
Multicast IP address range
Description
224.0.0.0~224.0.0.255
Reserved multicast addresses for routing protocols and other
network protocols
224.0.1.0~224.0.1.255
Addresses for video conferencing
239.0.0.0~239.255.255.255
Local management multicast addresses, which are used in the
local network only
Table 4-6-1
: Range of the Special Multicast IP
2. Multicast
MAC
Address:
When a unicast packet is transmitted in an Ethernet network, the destination MAC address is the MAC address of the receiver.
When a multicast packet is transmitted in an Ethernet network, the destination is not a receiver but a group with uncertain
number of members, so a multicast MAC address, a logical MAC address, is needed to be used as the destination address.
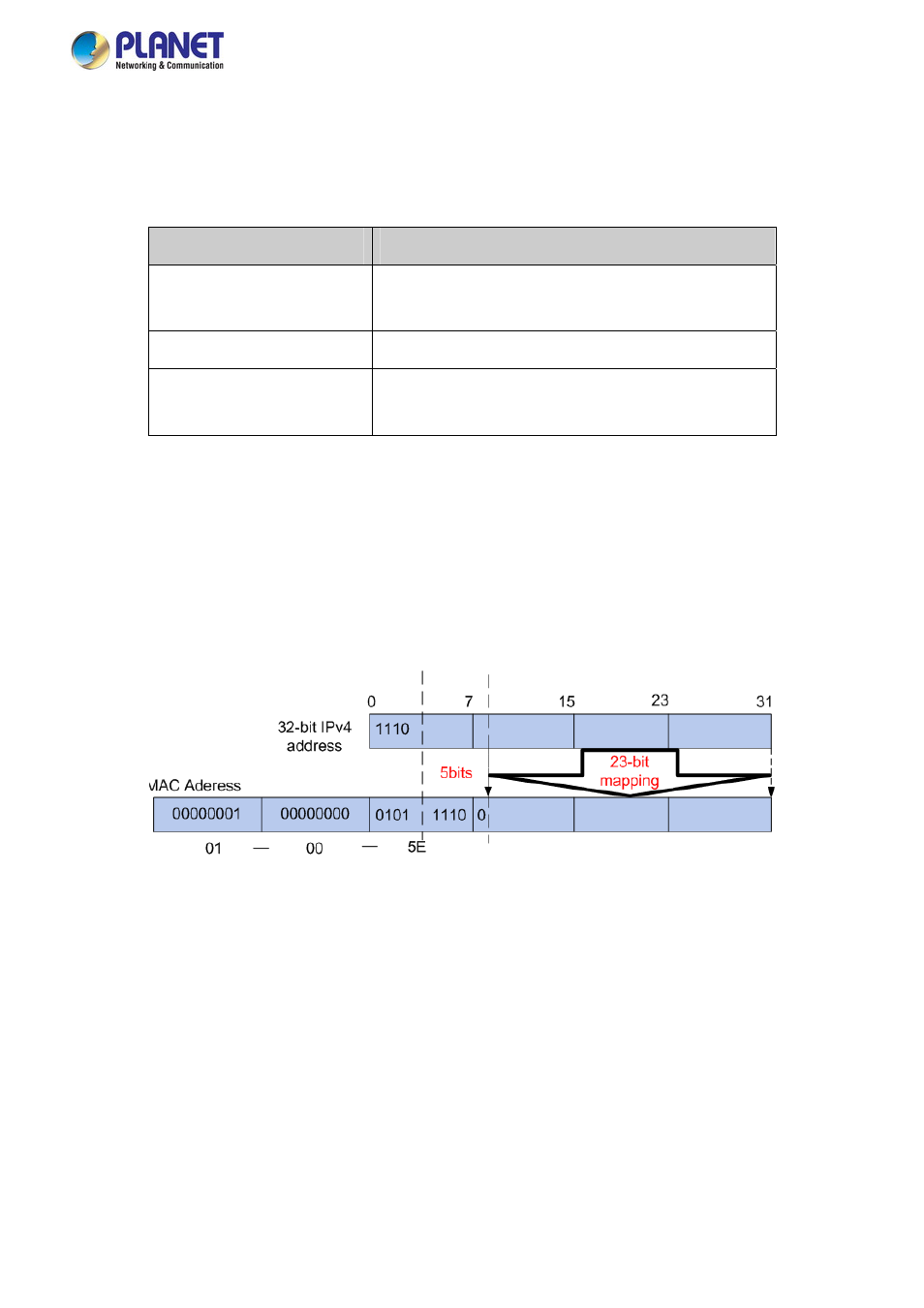
As stipulated by IANA, the high-order 24 bits of a multicast MAC address begins with 01-00-5E while the low-order 23 bits of a
multicast MAC address are the low-order 23 bits of the multicast IP address. The mapping relationship is described as
Figure
4-6-2.
Figure 4-6-2:
Mapping Relationship between Multicast IP Address and Multicast MAC Address
The high-order 4 bits of the IP multicast address are 1110, identifying the multicast group. Only 23 bits of the remaining
low-order 28 bits are mapped to a multicast MAC address. In that way, 5 bits of the IP multicast address is not utilized. As a
result, 32 IP multicast addresses are mapped to the same MAC addresses.
Multicast Address Table
The Managed Switch is forwarding multicast packets based on the multicast address table. As the transmission of multicast
packets can not span the VLAN, the first part of the multicast address table is VLAN ID, based on which the received multicast
packets are forwarded in the VLAN owning the receiving port. The multicast address table is not mapped to an egress port but a
group port list. When forwarding a multicast packet, the Managed Switch looks up the multicast address table based on the
destination multicast address of the multicast packet. If the corresponding entry can not be found in the table, the Managed
Switch will broadcast the packet in the VLAN owning the receiving port. If the corresponding entry can be found in the table, it
138
