6 multicast, Multicast overview – PLANET FGSW-2840 User Manual
Page 137
User’s Manual of FGSW-2840 / FGSW-4840S
4.6 Multicast
Multicast Overview
In the network, packets are sent in three modes: unicast, broadcast and multicast. In unicast, the source server sends separate
copy information to each receiver. When a large number of users require this information, the server must send many pieces of
information with the same content to the users. Therefore, large bandwidth will be occupied. In broadcast, the system transmits
information to all users in a network. Any user in the network can receive the information, no matter the information is needed or
not.
Point-to-multipoint multimedia business, such as video conferences and VoD (video-on-demand), plays an important part in the
information transmission field. Suppose a point to multi-point service is required, unicast is suitable for networks with sparsely
users, whereas broadcast is suitable for networks with densely distributed users. When the number of users requiring this
information is not certain, unicast and broadcast deliver a low efficiency. Multicast solves this problem. It can deliver a high
efficiency to send data in the point to multi-point service, which can save large bandwidth and reduce the network load. In
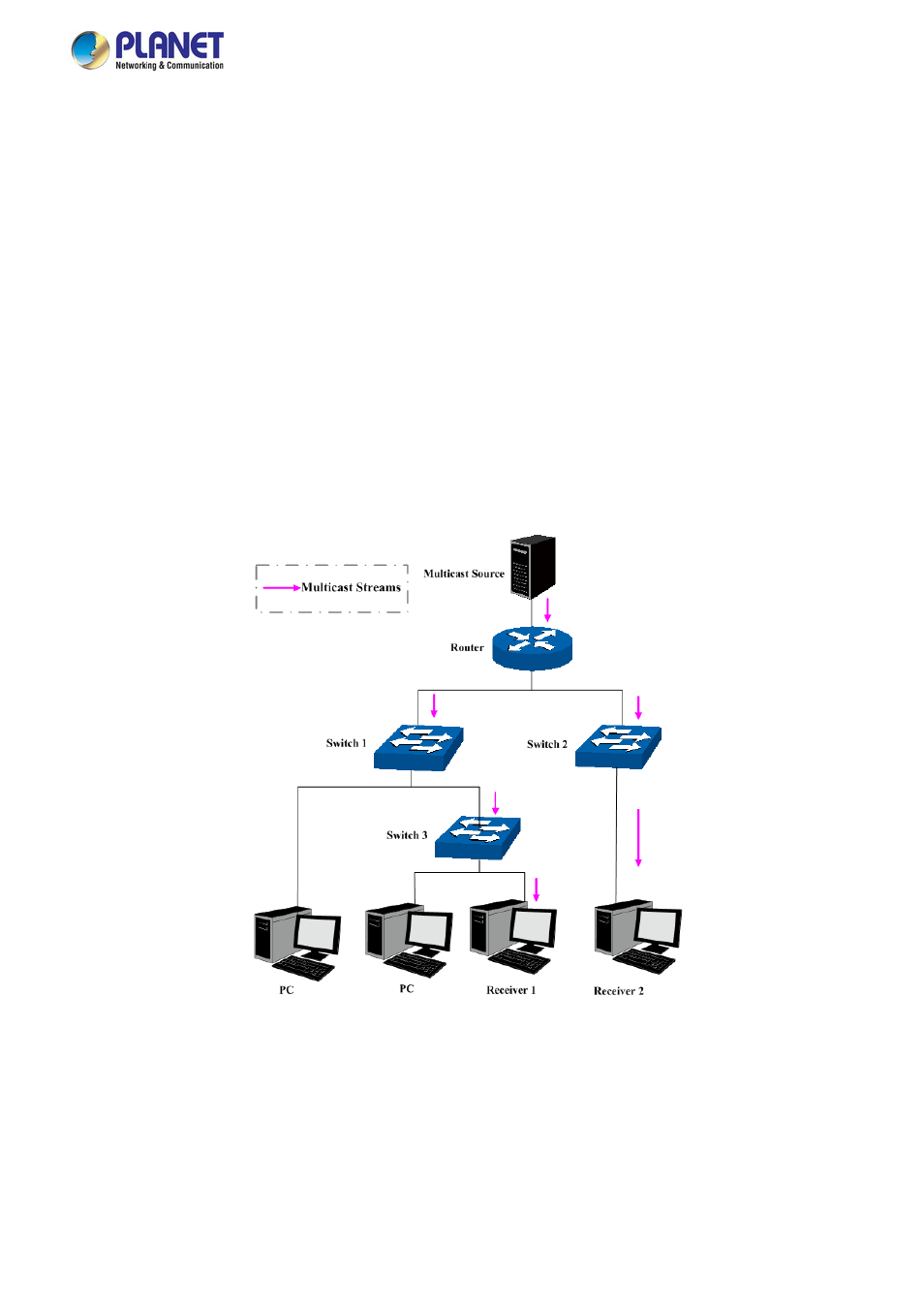
multicast, the packets are transmitted in the following way as shown in
Figure 4-6-1.
Figure 4-6-1:
Information Transmission in the Multicast Mode
Features of multicast:
1.
The number of receivers is not certain. Usually point-to-multipoint transmission is needed;
2.
Multiple users receiving the same information form a multicast group. The multicast information sender just need to
send the information to the network device once;
3.
Each user can join and leave the multicast group at any time;
4.
Real time is highly demanded and certain packets drop is allowed.
137
