11 isochronous operation, Isochronous operation, Figure 14 – HEIDENHAIN PROFIBUS-DP (DPV2) User Manual
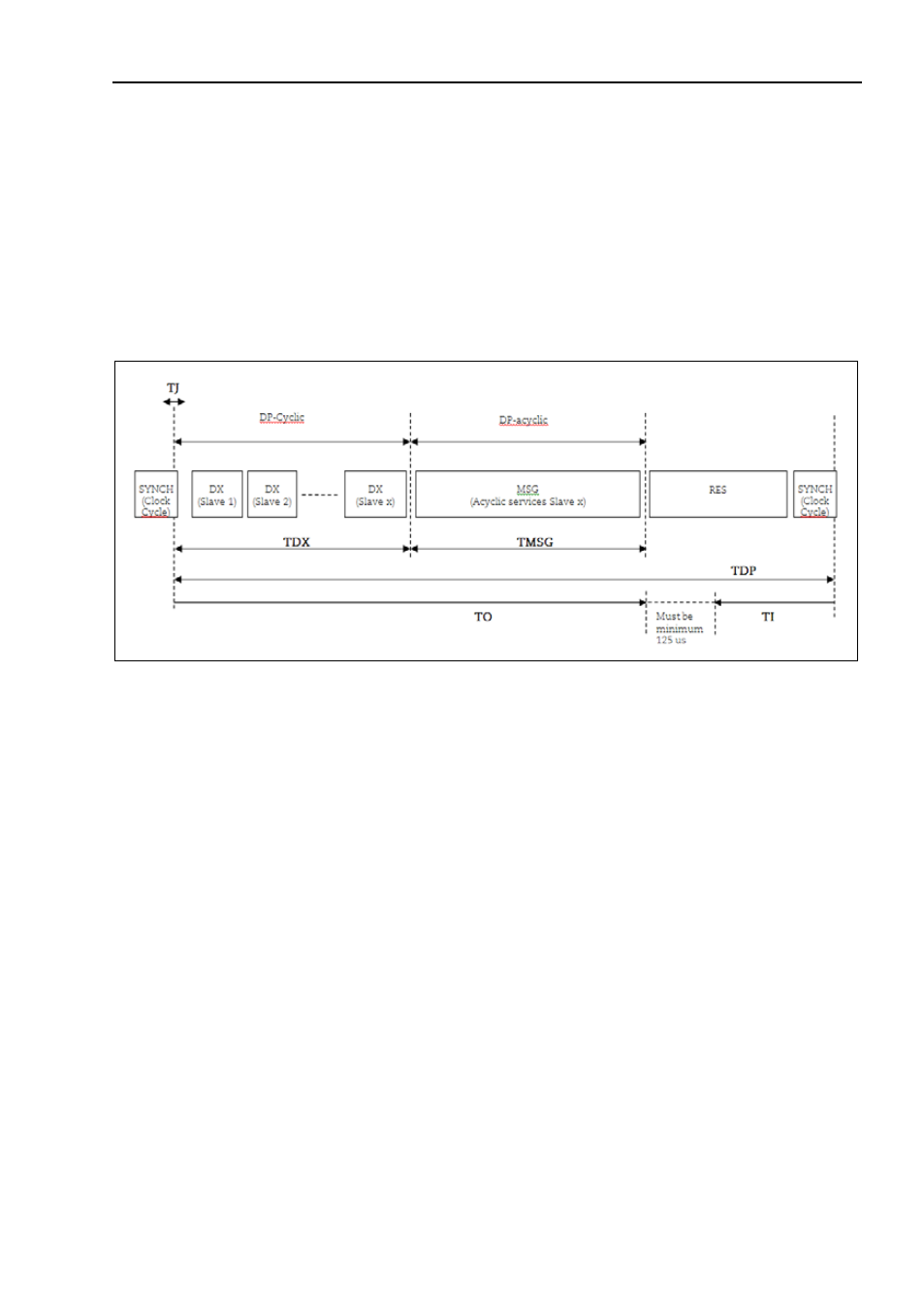
Page 49: Sequence of the dp-cycle in isochronous mode
PROFIBUS IO data description
49
5.11 Isochronous operation
Clock Synchronous Operation at PROFIBUS DP is done by using
the PROFIBUS DP-V2 Isochronous Mode. Clock cycle
synchronous operation in the PROFIBUS DP Isochronous Mode is
implemented by using an isochronous clock signal. This cyclic,
isochronous clock signal is transmitted as Global Control telegram
from the DP-master (class 1) to all PROFIBUS slaves. Thus, the
slaves supporting isochronous operation may synchronies their
applications (internal/Slave Clock) with the Master Clock.
Figure 14
Sequence of the DP-cycle in isochronous mode
TI
(Input time)
This is the time for actual value acquisition. The time TI refers to
the end of the DP-Cycle. The minimum time for TI is 375 µs for the
gateway and 125µs for the absolute encoder. There has to be a
minimum time of 125µs between TI and TO.
TO
(Output time)
Time TO refers to the start of the DP-cycle. The time TO is the
time for setpoint transfer . For the encoder and the gateway the
time TO is insignificant.
TJ
(Jitter Time)
TJ mirrors the time in which the clock jitter lasts. The clock jitter is
the shifting of the Global Control (GC) telegram with respect to
time.
TDX
(Data_Exchange Time)
This time is the sum of the transmission times of all
Data_Exchange telegrams for all slaves.
