Eap over radius, Eap-message, Message-authenticator – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 95: 1x authentication triggering, Unsolicited triggering of a client
5-5
z
Identifier: Used to match request and response messages.
z
Length: Length of the EAP packet, including the Code, Identifier, Length, and Data fields, in
bytes.
z
Data: Content of the EAP packet. This field is zero or more bytes and its format is
determined by the Code field.
EAP over RADIUS
Two attributes of RADIUS are intended for supporting EAP authentication: EAP-Message and
Message-Authenticator. For information about RADIUS packet format, see AAA Configuration
in the Security Configuration Guide.
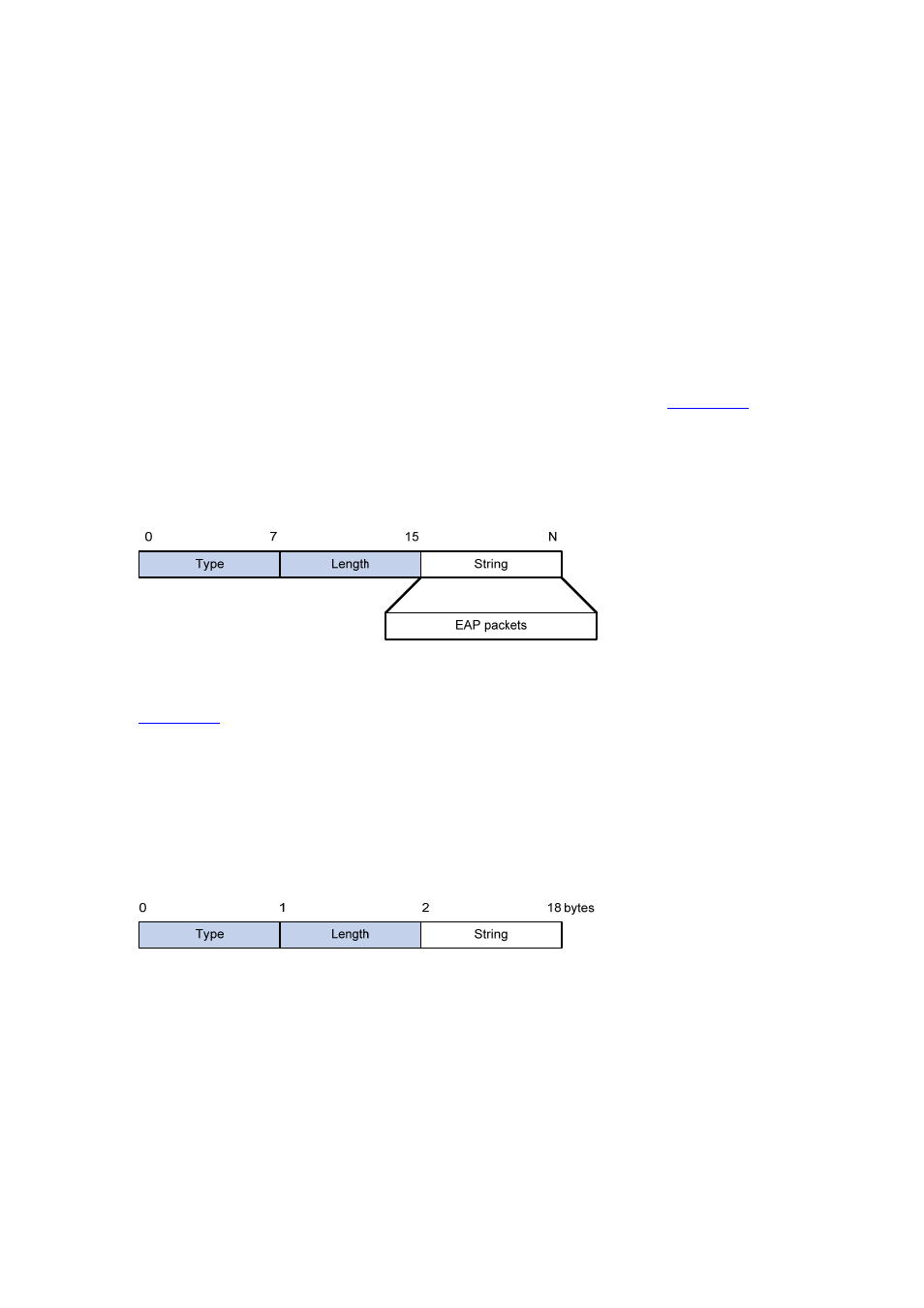
EAP-Message
The EAP-Message attribute is used to encapsulate EAP packets.
shows its
encapsulation format. The value of the Type field is 79. The String field can be up to 253 bytes.
If the EAP packet is longer than 253 bytes, it can be fragmented and encapsulated into multiple
EAP-Message attributes.
Figure 5-5 Encapsulation format of the EAP-Message attribute
Message-Authenticator
shows the encapsulation format of the Message-Authenticator attribute. The
Message-Authenticator attribute is used to prevent access requests from being snooped during
EAP authentication. It must be included in any packet with the EAP-Message attribute and it is
used to check packet integrity. If the integrity checksum of a packet calculated by the receiver is
not consistent with the Message-Authenticator attribute value in the packet, the packet will be
considered invalid and get discarded.
Figure 5-6 Encapsulation format of the Message-Authenticator attribute
802.1X Authentication Triggering
802.1X authentication can be initiated by either a client or the device.
Unsolicited triggering of a client
A client can initiate authentication by sending an EAPOL-Start packet to the device. The
destination address of the packet is 01-80-C2-00-00-03, the multicast address specified by the
IEEE 802.1X protocol.
