Security and authentication mechanisms, Basic message exchange process of radius – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 16
1-3
z
Server: The RADIUS server runs on the computer or workstation at the network center and
maintains information related to user authentication and network service access. It listens to
connection requests, authenticates users, and returns the processing results (for example,
rejecting or accepting the user access request) to the clients.
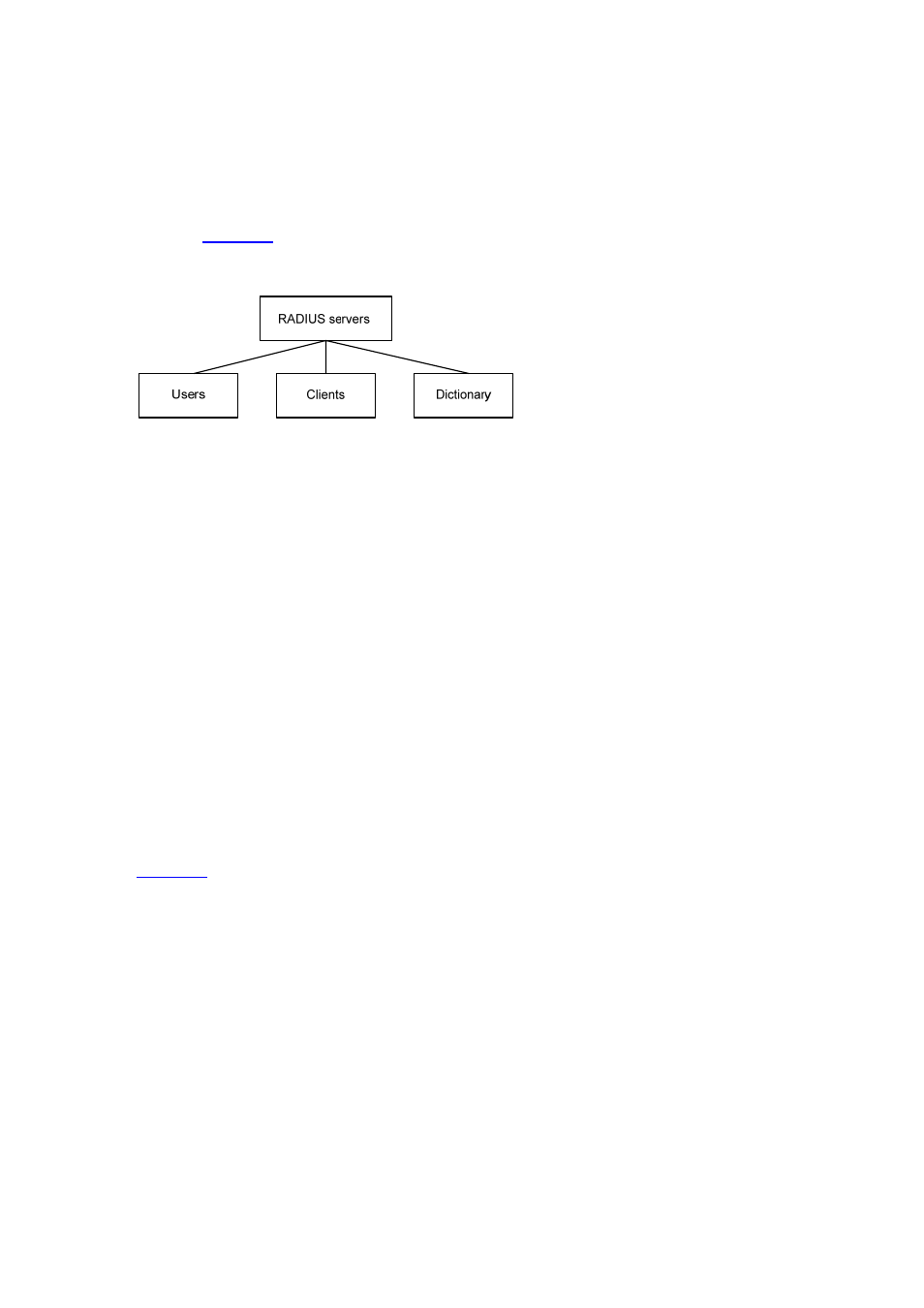
In general, the RADIUS server maintains three databases, namely, Users, Clients, and Dictionary, as
shown in
Figure 1-2 RADIUS server components
z
Users: Stores user information such as the usernames, passwords, applied protocols, and IP
addresses.
z
Clients: Stores information about RADIUS clients, such as the shared keys and IP addresses.
z
Dictionary: Stores RADIUS protocol attributes and their values.
Security and Authentication Mechanisms
Information exchanged between a RADIUS client and the RADIUS server is authenticated with a
shared key, which is never transmitted over the network. This enhances the information exchange
security. In addition, to prevent user passwords from being intercepted in non-secure networks,
RADIUS encrypts passwords before transmitting them.
A RADIUS server supports multiple user authentication methods, for example, the Password
Authentication Protocol (PAP) and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). Moreover,
a RADIUS server can act as the client of another AAA server to provide authentication proxy services.
Basic Message Exchange Process of RADIUS
illustrates the interaction of the host, the RADIUS client, and the RADIUS server.
