Fluke Biomedical VT Plus HF User Manual
Page 132
VT Plus HF
Operators Manual
A-6
O
u
tlet
Inlet
V
entilator
Inspiratory Hose
Expiratory Hose
Analyzer
TEST
LU
N
G
fec002.eps
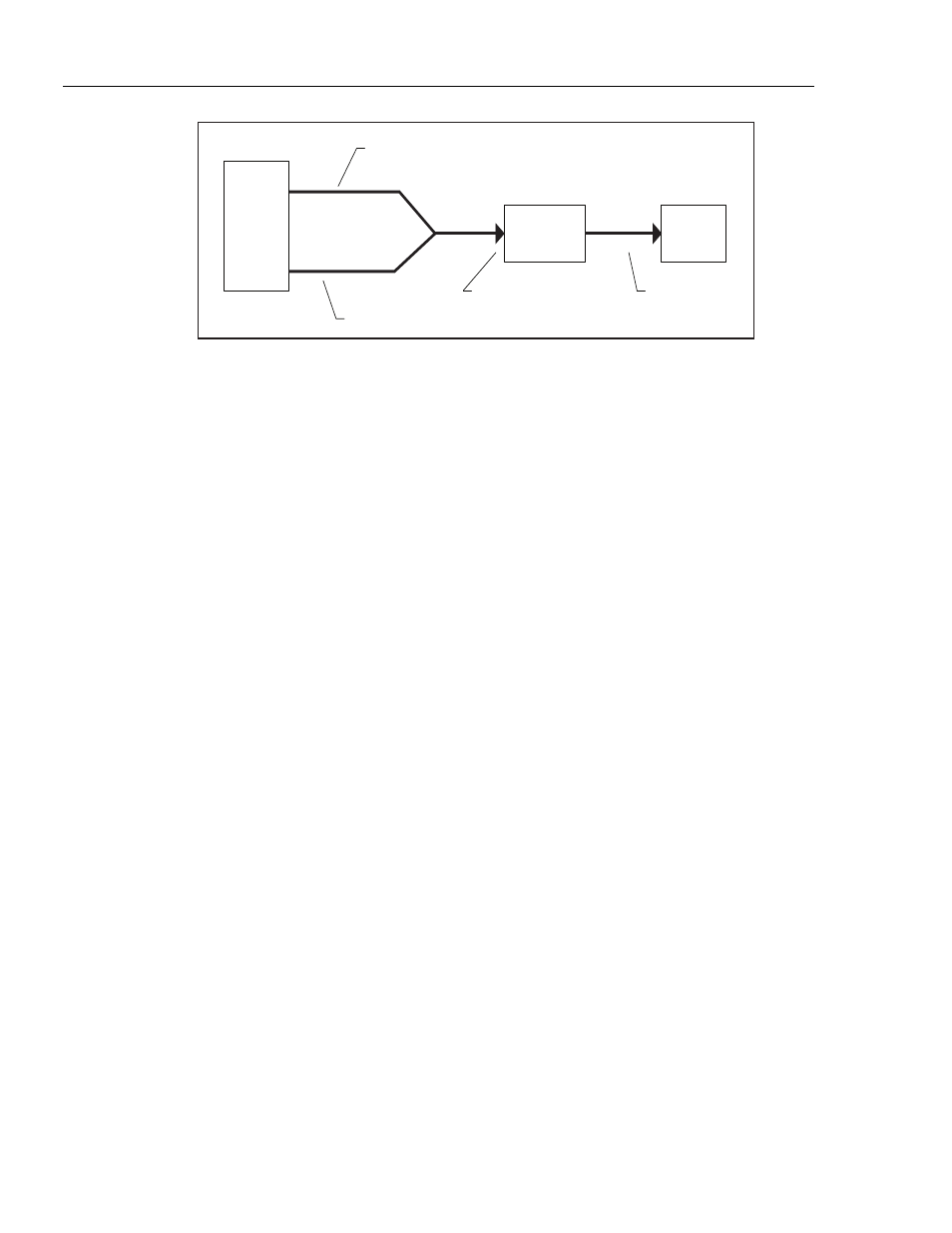
Figure A-1. Circuit Connection for the Analyzer in Bi-directional Mode
Note
When using the Analyzer with a ventilator and a test lung, the bidirectional
breath detect mode is preferred. Only use the inspiratory and expiratory
breath detect modes if measurements cannot be made in the bi-directional
mode.
Additional breath detect modes were implemented for users that are accustomed to
performing measurements with flow devices that can only measure flow in one direction.
Base Flow
In the inspiratory and expiratory limb of the breathing circuit, some ventilators may have
a bias flow when no flow is going to or from the patient (test lung). This is implemented
differently on different ventilators and is called by different names by the various
ventilator manufactures. It may be called base flow, bias flow, flow-by, blow-by, or many
other names.
In the inspiratory- or expiratory-only breath detection modes, the Analyzer can measure
the base flow present. The detection and calculation of base flow may take 30 to 60
seconds. In expiratory-only mode, detection of base flow requires a sufficient end-
expiratory period and sufficient change in pressure. The use of lower-lung compliance
settings improves performance in expiratory mode.
During expiratory-only mode, the base flow is subtracted from the flow signal for
obtaining the ventilator parameters, such as tidal volume and peak flow. During
inspiratory-only mode, the base flow is not subtracted, because the base flow is typically
turned of during the inspiratory phase on most ventilators.
