Altera Stratix V Avalon-ST User Manual
Page 104
Note: You can also use the Configuration Space signals to read Configuration Space registers. For more
information, refer to Transaction Layer Configuration Space Signals.
When a LMI write has a timing conflict with configuration TLP access, the configuration TLP accesses
have higher priority. LMI writes are held and executed when configuration TLP accesses are no longer
pending. An acknowledge signal is sent back to the Application Layer when the execution is complete.
All LMI reads are also held and executed when no configuration TLP requests are pending. The LMI
interface supports two operations: local read and local write. The timing for these operations complies
with the Avalon-MM protocol described in the Avalon Interface Specifications. LMI reads can be issued at
any time to obtain the contents of any Configuration Space register. LMI write operations are not
recommended for use during normal operation. The Configuration Space registers are written by requests
received from the PCI Express link and there may be unintended consequences of conflicting updates
from the link and the LMI interface. LMI Write operations are provided for AER header logging, and
debugging purposes only.
• In Root Port mode, do not access the Configuration Space using TLPs and the LMI bus simultane‐
ously.
Table 5-15: LMI Interface
Signal
Direction
Description
lmi_dout[31:0]
Output Data outputs.
lmi_rden
Input
Read enable input.
lmi_wren
Input
Write enable input.
lmi_ack
Output Write execution done/read data valid.
lmi_addr[11:0]
Input
Address inputs, [1:0] not used.
lmi_din[31:0]
Input
Data inputs.
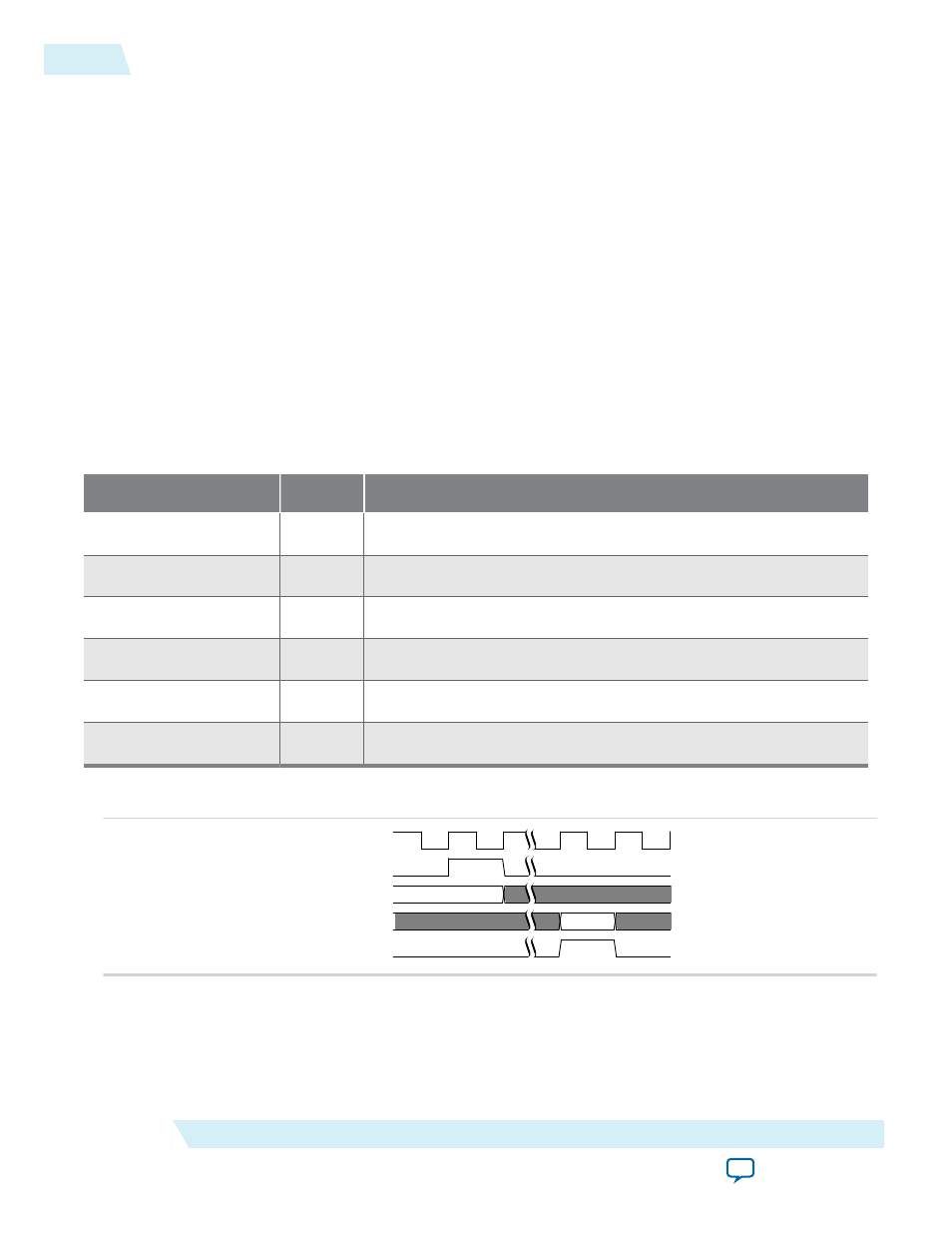
Figure 5-36: LMI Read
pld_clk
lmi_rden
lmi_addr[11:0]
lmi_dout[31:0]
lmi_ack
5-52
LMI Signals
UG-01097_avst
2014.12.15
Altera Corporation
Interfaces and Signal Descriptions
