Input frequency, Counter types, Linear counter – Rockwell Automation 1769-HSC Compact High Speed Counter Module User Manual
Page 28: Input frequency counter types
28
Rockwell Automation Publication 1769-UM006E-EN-P - July 2013
Chapter 2
Module Operation
Input Frequency
Maximum input frequency is determined by the input configuration as shown in
the table.
Counter Types
Each of the four possible counters can be configured to stop counting and set a
flag at its limits (linear counter) or to rollover and set a flag at its limits (ring
counter). A counter’s limits are programmed by the Ctr
nMaxCount and
Ctr
nMinCount words in the module’s configuration array. Both types are
described below.
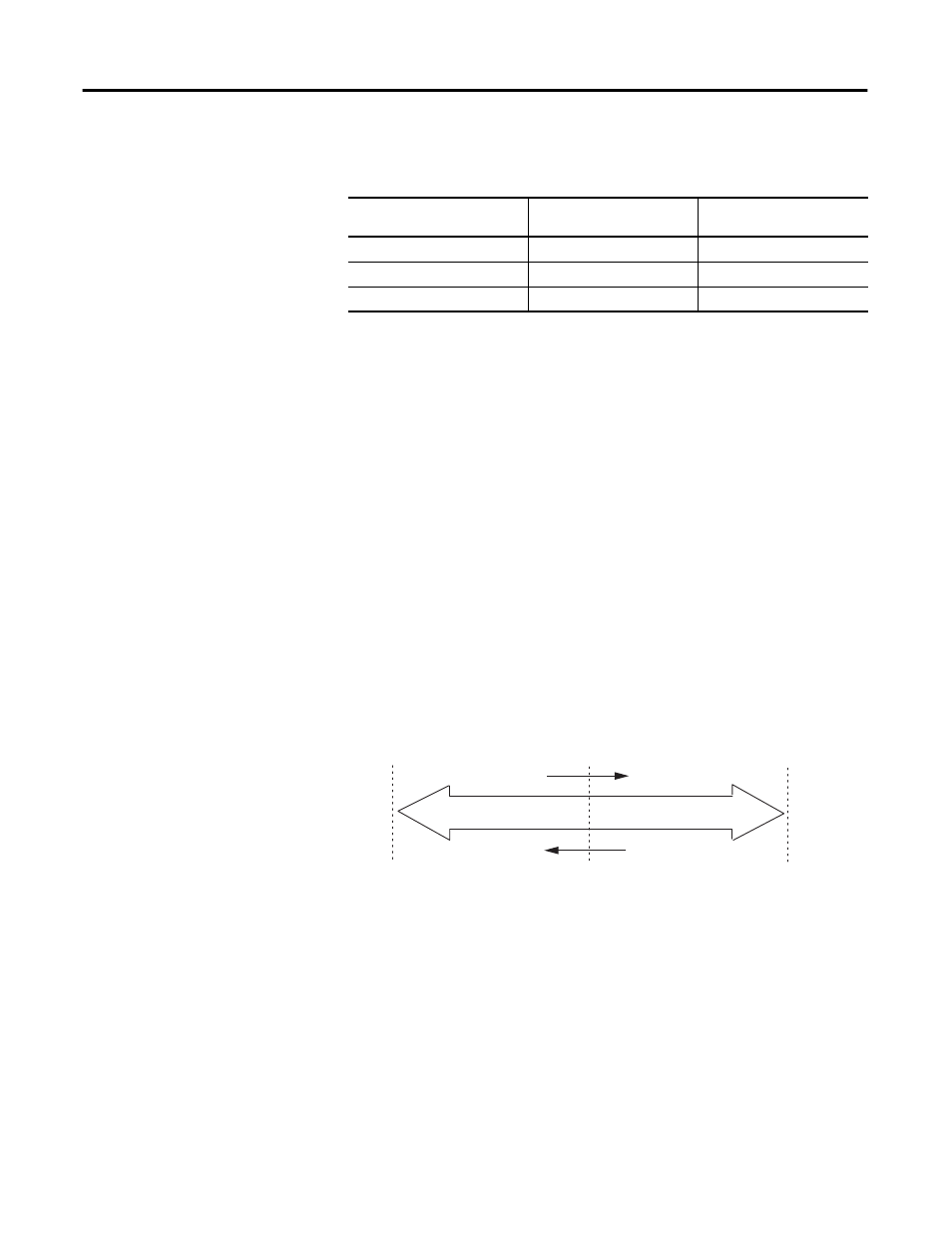
Linear Counter
Figure 7 illustrates linear counter operation. In linear operation, the current count
(Ctr[
n].CurrentCount) value remains between, or equal to, the
user-programmed minimum count (Ctr
nMinCount) and maximum count
(Ctr
nMaxCount) values. If the Ctr[n].CurrentCount value goes above (>) or
below (<) these values, the counter stops counting, and an overflow/underflow
bit is set. The overflow/underflow bits can be reset using the
Ctr
nResetCounterOverflow and CtrnResetCounterUnderflow bits.
Figure 7 - Linear Counter Diagram
Pulses are not accumulated in an overflow/underflow state. The counter begins
counting again when pulses are applied in the proper direction. For example, if
you exceed the maximum by 1000 counts, you do not need to apply 1000 counts
in the opposite direction before the counter begins counting down. The first
pulse in the opposite direction decrements the counter.
Input Configuration
Input Frequency
1769-HSC Module
Input Frequency
Packaged Controller
X4 Quadrature encoder
250 kHz
250 kHz
X2 Quadrature encoder
500 kHz
250 kHz
All other configurations
1 MHz
250 kHz
Count Up
Count Down
Counter Value
Maximum Count Value
Overflow and Hold
Minimum Count Value
Underflow and Hold
0
