2 spi write protocol, 3 performing a serial spi read, Figure 2-3. spi write flow diagram -5 – Cirrus Logic CS4970x4 User Manual
Page 51
2-5
Copyright 2013 Cirrus Logic, Inc.
DS810UM6
SPI Port
CS4953x4/CS4970x4 System Designer’s Guide
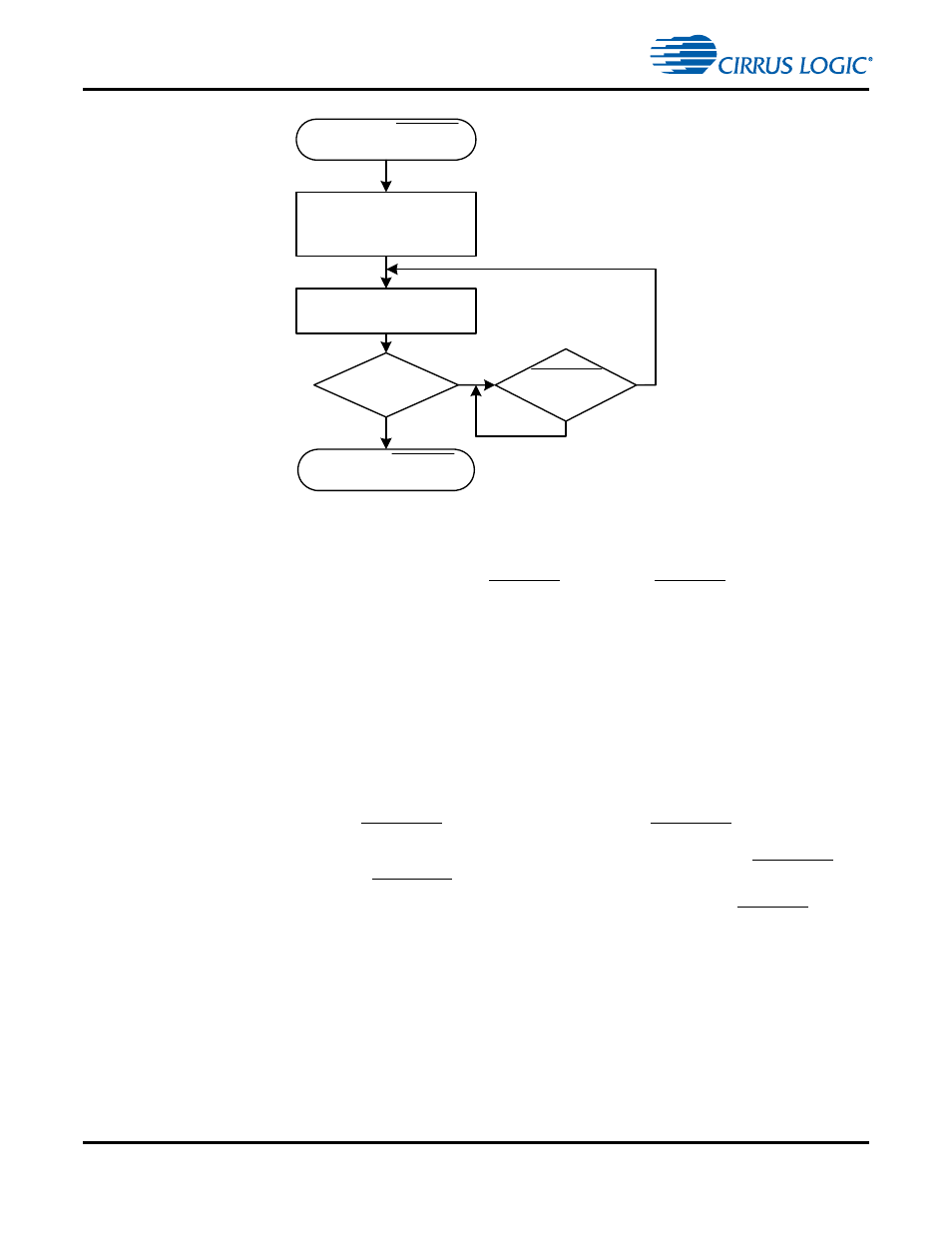
Figure 2-3. SPI Write Flow Diagram
2.4.3.2 SPI Write Protocol
1.
A SPI transfer is initiated when the chip select SCP1_CS is driven low. SCP1_CS driven low indicates
that CS4953x4/CS4970x4 is in SPI Slave mode.
2. This is followed by a 7-bit address and the read/write bit set low for a write. So, the Master should
send 0x80. The 0x80 byte represents the 7-bit SPI address 1000000b, and the least significant bit set
to ‘0’, designates a write.
3. The Master should then clock the 4-byte data word into the Slave device, most-significant bit first, one
byte at a time. The data byte is transferred to the CS4953x4/CS4970x4 DSP (Slave) on the falling
edge of the eighth serial clock. For this reason, the serial clock should be held low so that eight
transitions from low-to-high-to-low will occur for each byte.
4. If the Master has no more data words to write to the CS4953x4/CS4970x4, then proceed to Step 6. If
the Master has more data words to write to the CS4953x4/CS4970x4, then proceed to Step 5.
5. The Master should poll the SCP1_BSY signal until it goes high. If the SCP1_BSY signal is low, it
indicates that the CS4953x4/CS4970x4 is busy performing some task that requires halting the serial
control port. Once the CS4953x4/CS4970x4 is able to receive more data words, the SCP1_BSY
signal will go high. Once the SCP1_BSY signal is high, proceed to Step 3.
6. The Master finishes the SPI write transaction by driving the CS4953x4/CS4970x4 SCP1_CS signal
high.
2.4.3.3 Performing a Serial SPI Read
Information provided in this section is intended as a functional description indicating how an external
device (Master) performs an SPI read from the CS4953x4/CS4970x4 (Slave). The system designer must
ensure that all timing constraints of the SPI read cycle are met (see the CS4953x4/CS4970x4 datasheet
for timing specifications).
When performing a SPI read, the same protocol is used whether reading a single byte or multiple bytes.
From a hardware perspective, it makes no difference whether communication is a single byte or multiple
SPI START: SCP1_CS
(LOW)
WRITE ADDRESS BYTE
0x80
MORE DATA?
Y
N
WRITE 4 DATA BYTES
SPI STOP: SCP1_CS
(HIGH)
SCP1_BSY
(LOW)?
N
Y
