Texas Instruments MSP430x4xx User Manual
Page 92
Instruction Set
3-58
RISC 16−Bit CPU
* RLA[.W]
Rotate left arithmetically
* RLA.B
Rotate left arithmetically
Syntax
RLA
dst
or
RLA.W
dst
RLA.B
dst
Operation
C <− MSB <− MSB−1 .... LSB+1 <− LSB <− 0
Emulation
ADD
dst,dst
ADD.B
dst,dst
Description
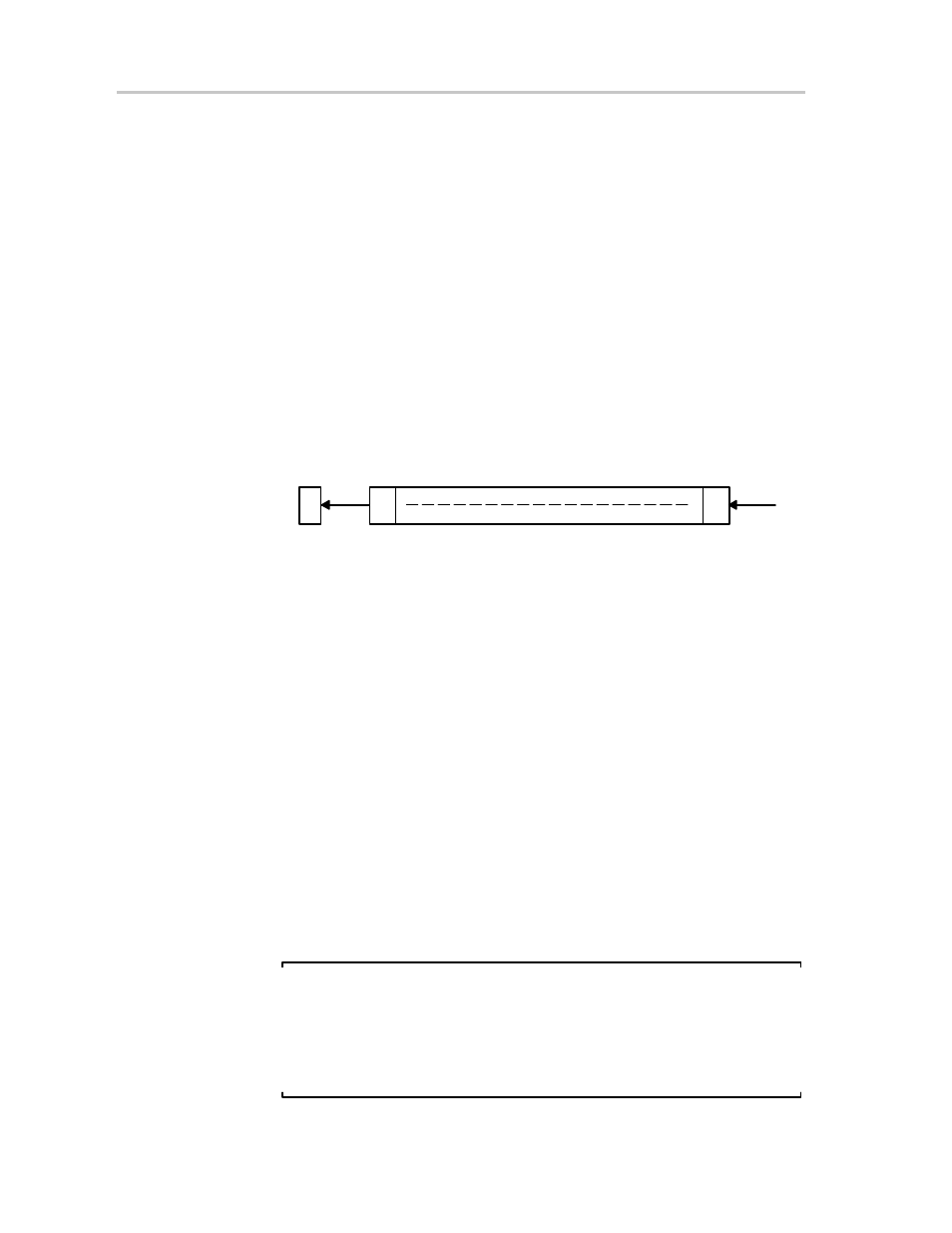
The destination operand is shifted left one position as shown in Figure 3−14.
The MSB is shifted into the carry bit (C) and the LSB is filled with 0. The RLA
instruction acts as a signed multiplication by 2.
An overflow occurs if dst
≥
04000h and dst < 0C000h before operation is
performed: the result has changed sign.
Figure 3−14. Destination Operand—Arithmetic Shift Left
15
0
7
0
C
Byte
Word
0
An overflow occurs if dst
≥
040h and dst < 0C0h before the operation is
performed: the result has changed sign.
Status Bits
N: Set if result is negative, reset if positive
Z: Set if result is zero, reset otherwise
C: Loaded from the MSB
V: Set if an arithmetic overflow occurs:
the initial value is 04000h
≤
dst < 0C000h; reset otherwise
Set if an arithmetic overflow occurs:
the initial value is 040h
≤
dst < 0C0h; reset otherwise
Mode Bits
OSCOFF, CPUOFF, and GIE are not affected.
Example
R7 is multiplied by 2.
RLA
R7
; Shift left R7 (
×
2)
Example
The low byte of R7 is multiplied by 4.
RLA.B
R7
; Shift left low byte of R7 (
×
2)
RLA.B
R7
; Shift left low byte of R7 (
×
4)
Note:
RLA Substitution
The assembler does not recognize the instruction:
RLA
@R5+
nor
RLA.B @R5+.
It must be substituted by:
ADD
@R5+,−2(R5)
or
ADD.B @R5+,−1(R5).
