Print head cleaning method, Types of cleaning and order of implementation, Diagnostic cleaning – Epson SureLab D1070 Professional Minilab Printer User Manual
Page 105: Forced cleaning
SL-D1000 Series User's Guide
Using the Maintenance Tool (Mac)
105
Print Head Cleaning Method
Types of Cleaning and Order of
Implementation
There are two types of cleaning,
Forced Cleaning
,
which is cleaning the print head manually, and
Diagnostic Cleaning
, which detects clogged nozzles
and cleans the print head automatically.
First, implement
Diagnostic Cleaning
.
After that, when "Diagnostic cleaning is finished.
Clogged nozzles detected. Perform diagnostic cleaning
again.” is displayed on screen, implement
Diagnostic
Cleaning
again.
If the clogged nozzles are not cleared after repeating
Diagnostic Cleaning
three times, then do
Forced
Cleaning
set to
Power
.
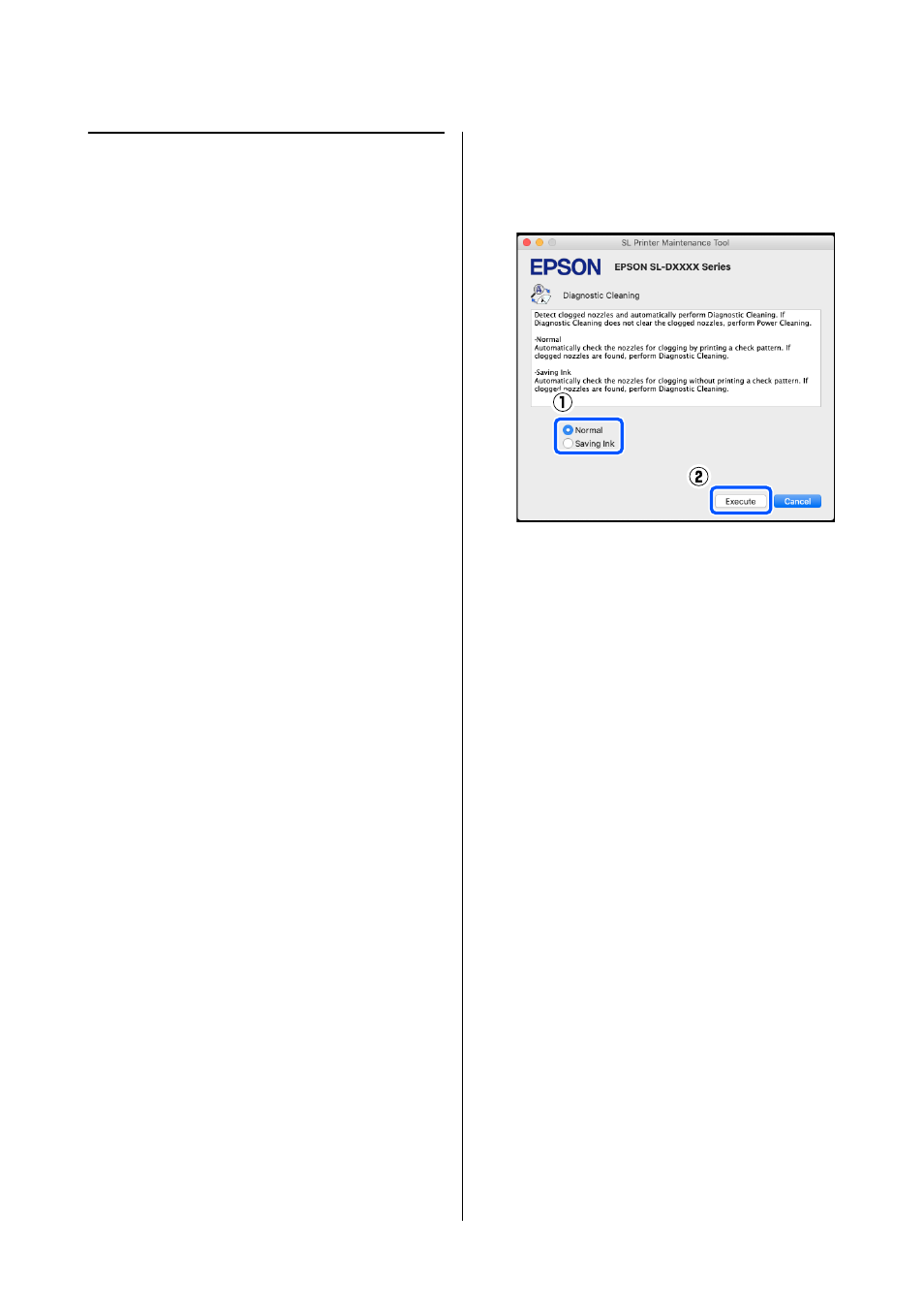
Diagnostic Cleaning
1
Click
Diagnostic Cleaning
on the main screen.
The
Diagnostic Cleaning
screen is displayed.
2
Select
Normal
or
Saving Ink
, and then click
Execute
.
Normal
prints a check pattern on roll paper and
automatically checks the status of the nozzles.
Roll paper must be loaded on the printer.
Saving Ink
does not print a check pattern and
automatically checks the state of the nozzles,
whether roll paper or cut sheets are loaded on
the printer.
The nozzle check starts and cleaning is executed
if necessary.
The time needed for cleaning varies according
to the status of the nozzles.
3
Check the results of Diagnostic Cleaning in the
message displayed on the screen.
When the message "Diagnostic cleaning
completed." is displayed, the work is complete.
When "Diagnostic cleaning is finished. Clogged
nozzles detected. Perform diagnostic cleaning
again.” is displayed, execute
Diagnostic
Cleaning
again.
If the clogged nozzles are not cleared after
repeating
Diagnostic Cleaning
three times,
then execute
Forced Cleaning
set to
Power
.
U
Forced Cleaning
1
Click
Forced Cleaning
on the main screen.
The
Forced Cleaning
screen is displayed.
2
Select
Normal
or
Power
, and then click
Execute
.
