Circular path c around circle center cc, Circular path cr with defined radius, Circle c – HEIDENHAIN TNC 320 (340 551-02) User Manual
Page 132: Circular arc cr, Circular arc with a certain radius, 4 p a th cont ours—car te sian coor dinat e s
132
6 Programming: Programming Contours
6.4 P
a
th Cont
ours—Car
te
sian Coor
dinat
e
s
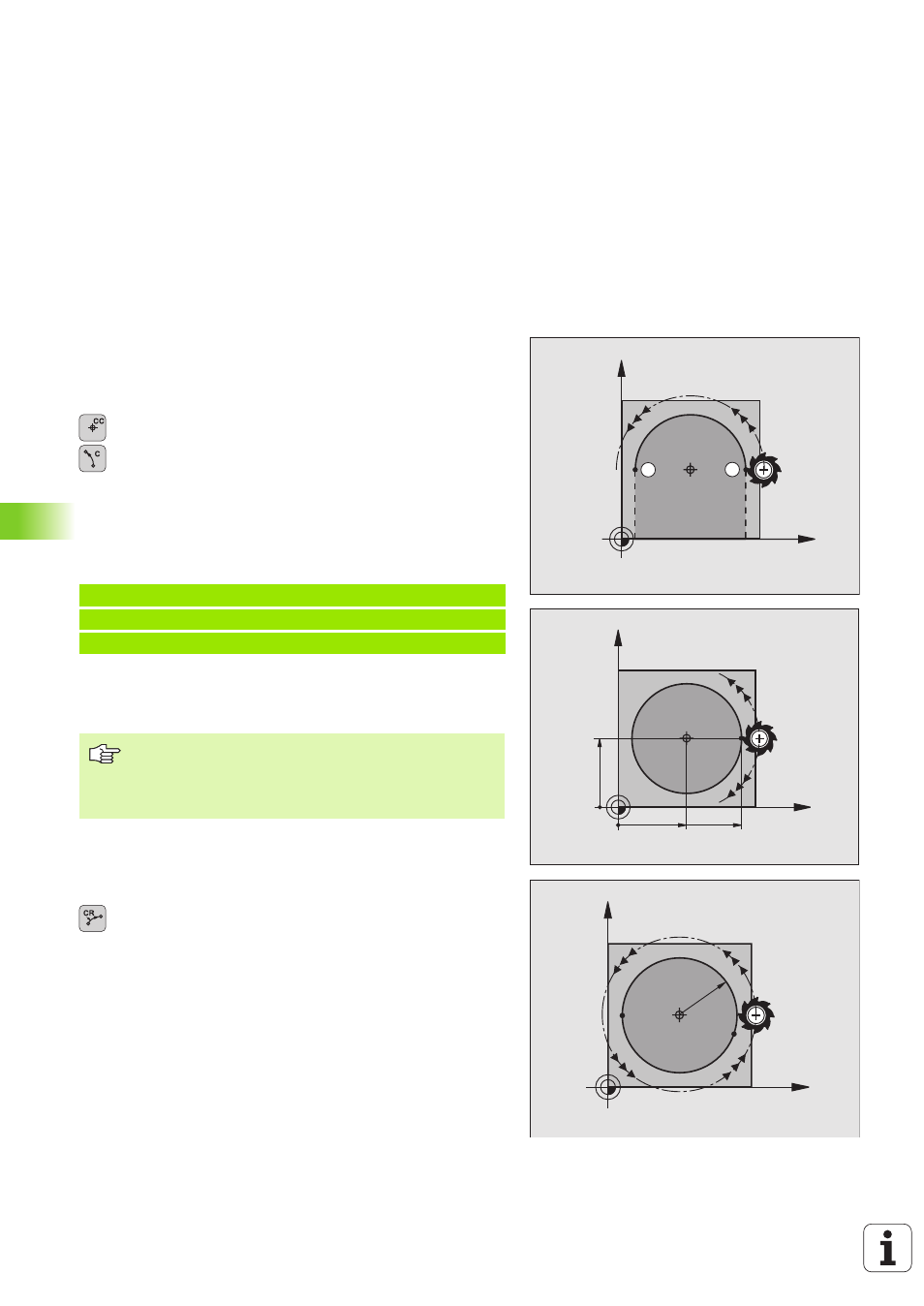
Circular path C around circle center CC
Before programming a circular path C, you must first enter the circle
center CC. The last programmed tool position before the C block is
used as the circle starting point.
8
Move the tool to the circle starting point.
8
Coordinates
of the circle center
8
Coordinates
of the arc end point
8
Direction of rotation DR
Further entries, if necessary:
8
Feed rate F
8
Miscellaneous function M
Example NC blocks
Full circle
For the end point, enter the same point that you used for the starting
point.
Circular path CR with defined radius
The tool moves on a circular path with the radius R.
8
Coordinates
of the arc end point
8
Radius R
Note: The algebraic sign determines the size of the
arc!
8
Direction of rotation DR
Note: The algebraic sign determines whether the arc
is concave or convex!
Further entries, if necessary:
8
Miscellaneous function M
8
Feed rate F
Full circle
For a full circle, program two CR blocks in succession:
The end point of the first semicircle is the starting point of the second.
The end point of the second semicircle is the starting point of the first.
5 CC X+25 Y+25
6 L X+45 Y+25 RR F200 M3
7 C X+45 Y+25 DR+
The starting and end points of the arc must lie on the
circle.
Input tolerance: up to 0.016 mm (selected through the
“circleDeviation” machine parameter).
S
E
X
Y
CC
X
Y
25
45
25
CC
DR+
DR–
X
Y
CC
S
1
=E
2
E
1
=S
2
R
