Trigger latency & jitter – Measurement Computing StrainBook/616 User Manual
Page 93
Trigger Latency & Jitter
Trigger latency and jitter depend on the trigger source and the acquisition mode:
Trigger latency is the duration between the valid trigger and the start of the acquisition.
Trigger jitter is the variation of the latency, how much time the latency can vary from trigger to
trigger.
As discussed, StrainBook has post-trigger and pre/post-trigger acquisition modes. Post-trigger modes
(N-shot, N-shot with re-arm, and infinite-post-trigger) collect scans only after the trigger has occurred.
They are different from the pre/post-trigger mode that collects scans both before and after the trigger.
This difference affects the trigger latency and jitter.
In a post-trigger mode, StrainBook is not scanning while waiting for the trigger. Thus, it is free to respond
to the trigger as soon as it occurs. This minimizes the trigger latency and jitter.
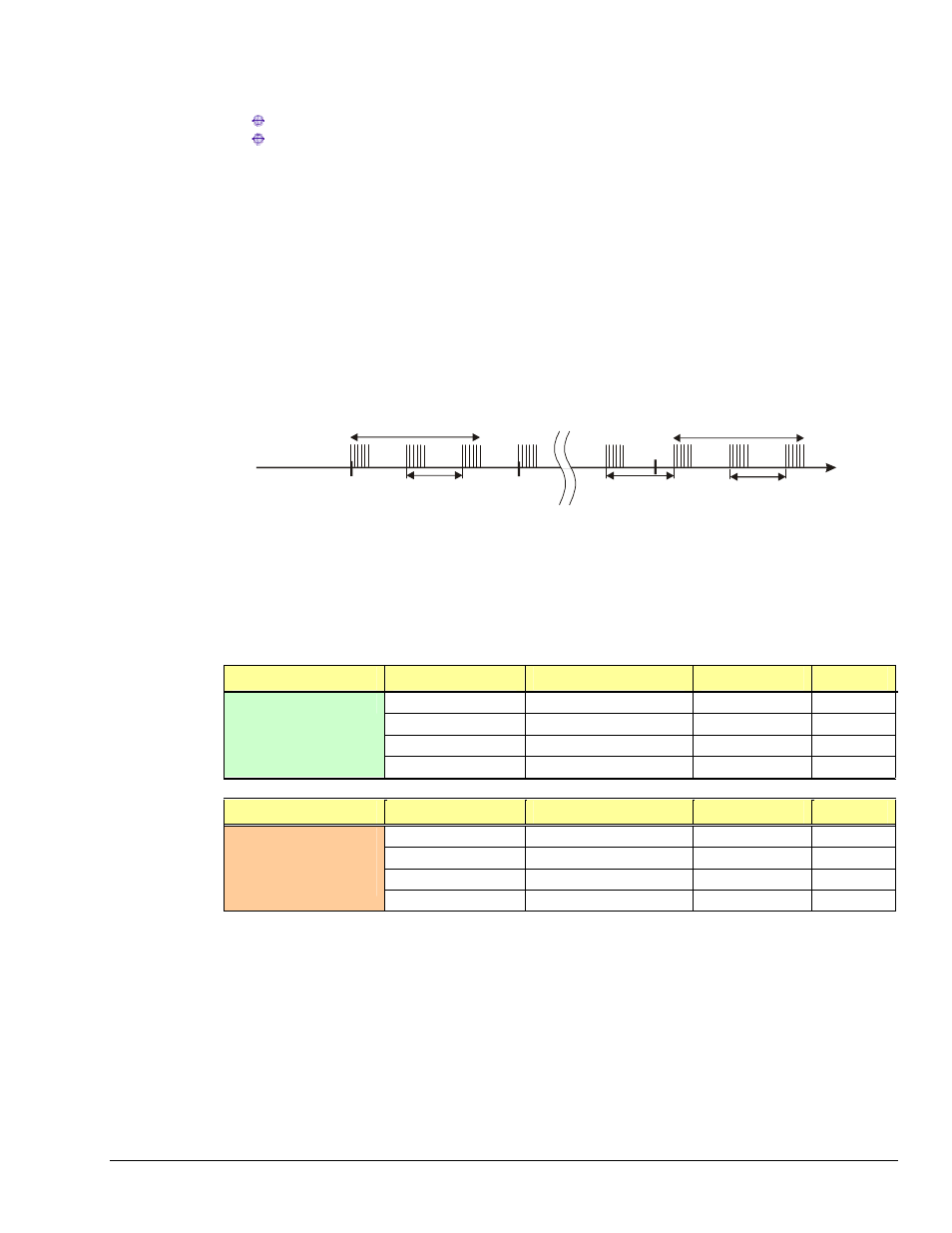
In the pre/post-trigger mode, pre-trigger data is being collected while StrainBook waits for the trigger, and
StrainBook will not respond to a trigger, until after the current scan is complete. The pre-trigger scan
period separates the first scan after the trigger from the last scan before the trigger. All the scans (up
through the one immediately following the trigger) are collected at the pre-trigger rate; and all subsequent
scans are collected at the post-trigger rate. This preserves the integrity of the acquisition timebase as
shown in the figure below:
Start
No acquisitions
before start
Pre-Trigger
Scan Period
Pre-Trigger Scan Count
Pre/Post-Trigger Acquisition
Time
Trigger
Armed
Trigger
Pre-Trigger
Scan Period
Post-Trigger
Scan Period
Post-Trigger Scan Count
The time needed to complete the final pre-trigger scan is part of the trigger latency; and so, in the pre/post-
trigger mode, the trigger latency may be greatly increased.
Not only do the trigger latency and jitter depend on the pre- versus post-trigger type of acquisition, they
also depend on the trigger source, i.e., software, digital (TTL), multi-channel, digital pattern. The
following table gives the trigger latency and jitter for each of the different trigger sources and acquisition
modes:
Acquisition Type
Trigger Source
Max. Trigger Latency
Trigger Jitter
Notes
Software
100 µs + T
100 µs + T
a, c
Digital (TTL)
200 ns + T
50 ns + T
c
Multi-Channel
2 * T - NS µs
T
c, d
Pre-Trigger
Digital Pattern
300 ns + T
50 ns + T
Acquisition Type
Trigger Source
Max. Trigger Latency
Trigger Jitter
Notes
Software
100 µs
100 µs
a
Digital (TTL)
200 ns
50 ns
Multi-Channel
2 * NC + 3 µs
NC +2 µs
b
Post-Trigger
N-Shot,
N-Shot with re-arm, or
infinite-post-trigger
Digital Pattern
300 ns
50 ns
Notes:
a) Software trigger latency and jitter depend greatly on the host computer's speed, operating system, and
printer-port protocol. Most systems should take much less than 100 µs.
b) NC is the number of channel samples used for multi-channel triggering, from 1 to 64, as specified by the trigger
configuration.
c) T is the pre-trigger scan period.
d) NS is the number of samples in a scan including, if present, the first "dummy" sample, from 1 to 128.
StrainBook/616
977694
Triggers 7-5
