Comtech EF Data MM200 User Manual
Page 56
User Interfaces
MM200 High-Speed Microwave Modem
4-32
TM086 - Rev. 4.1
The format and structure of the COMMSPEC message exchanges are described herein. Decimal
numbers have no suffix; hexadecimal numbers end with a lower case h suffix and binary values
have a lower case b suffix. Thus, 22 = 16h = 000010110b. The principal elements of a data
frame, in order of occurrence, are summarized as follows:
beginning of a message. The
through TBD. This field is 2 bytes long for the MM200 protocol.
that all nodes on a given control bus have a unique address that must be defined.
to which the message is sent.
- The FSN is a tag with a value from 0 through 255 that is sent
with each message. It assures sequential information framing and correct equipment
acknowledgment and data transfers.
associated with the data that follows it. Acknowledgment and error codes are returned in this
field. This field is 2 Bytes for the MM200 protocol.
<...DATA...> - The Data field contains the binary, data bytes associated with the
excluding the
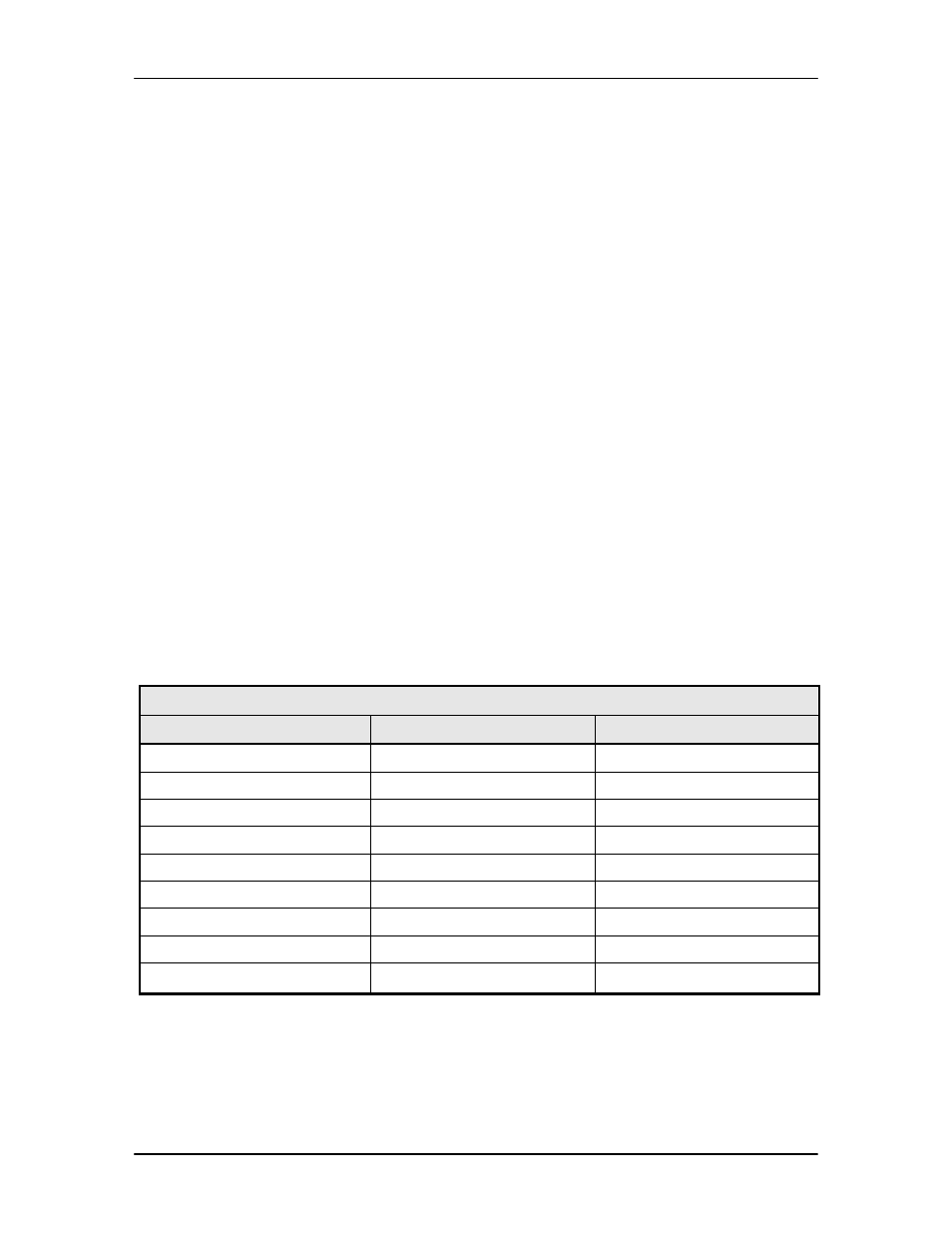
within the message. In a message block with the following parameters, the checksum is
computed as shown below in Table 4-4.
Table 4-4. Checksum Calculation Example
BYTE FIELD
DATA CONTENT
RUNNING CHECKSUM
00h = 00000000b
00000000b
02h = 00000010b
00000010b
F0h = 11110000b
11110010b
2Ah = 00101010b
00011100b
09h = 00001001b
00100101b
00h = 00000000b
00101000b
03h = 00000011b
00101000b
(Byte 1)
DFh = 11011111b
00000111b
(Byte 2)
FEh = 11111110b
00000101b
Thus, the checksum is 00000101b; which is 05h or 5 decimal. Alternative methods of
calculating the checksum for the same message frame are:
