Echelon FT 3150 Smart Transceiver User Manual
Page 45
FT 3120 / FT 3150 Smart Transceiver Data Book
39
I/O Timing Issues
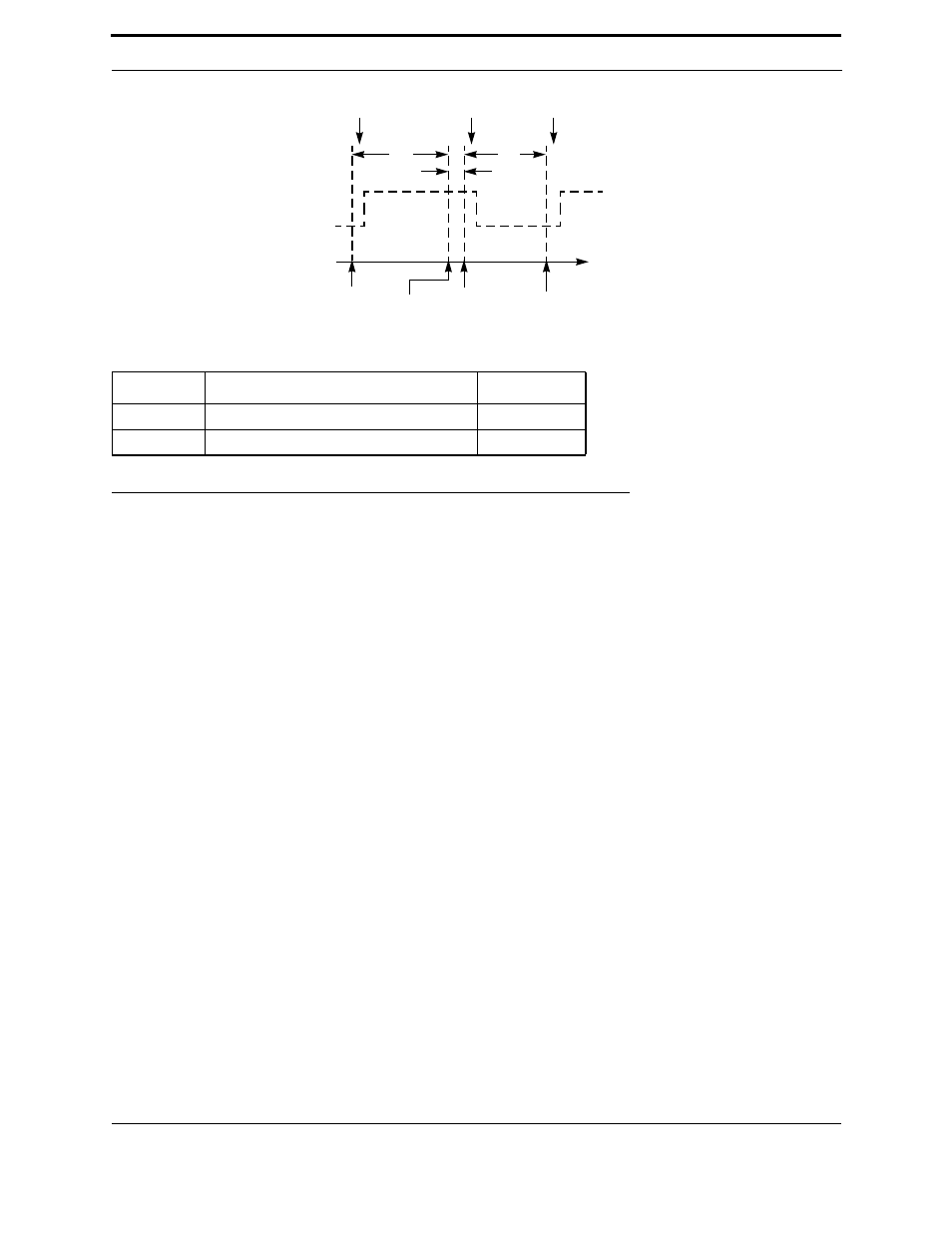
Figure 3.4 when-Clause to when-Clause and Scheduler Overhead Latency
The when-clause to when-clause latency, t
ww
, in this case includes the execution time of one io_out() function
(65 µs latency at 10MHz) and is for an event that always evaluates to TRUE. The actual t
ww
for a given application is
driven by the actual task within the when statement as well as the when event which is evaluated.
The above example not only measures the best-case minimum latency between consecutive when clauses (whose
events evaluate to TRUE), t
ww
, but also reveals that the end-of-loop overhead latency of the scheduler is t
sol
. As
shown in Figure 3.4, t
ww
is the off-time period of the output waveform and t
sol
is the on-time of the output waveform,
minus t
ww
. This shows that the scheduler overhead latency, or the scheduler end-of-loop latency, occurs just before
the execution of the last when clause in the program.
The latency associated with the return from the io_out() function is small, relative to that of the execution of the
function call itself.
NOTE: Some I/O objects suspend application processing until the task is complete. This is because they are
firmware-driven. These are bitshift, Neurowire, parallel, and serial I/O objects, I
2
C, magcard, magtrack, Touch I/O,
and Wiegand. They do not suspend network communication as this is handled by the network processor and the
media access processor.
Firmware and Hardware-Related I/O Timing Information
All I/O updates in the FT Smart Transceiver are performed by the Neuron firmware using system image function
calls.
The total latency for a given function call, from start to end, can be broken down into two separate parts. The first is
due to the processing time required before the actual hardware I/O update (read or write) occurs. The second delay is
associated with the time required to finish the current function call and return to the application program.
Overall accuracy is always related to the accuracy of the CLK1 input of the FT Smart Transceiver. Timing diagrams
are provided for all non-trivial cases to clarify the parameters given.
For more information on the operation of each of the I/O objects, refer to the Neuron C Reference Guide.
Symbol
Description
Typ @ 10MHz
t
ww
when-clause to when-clause latency
940 µs
t
sol
Scheduler overhead latency (see text)
54 µs
end-of-loop
processing
begins
TIME
t
sol
t
ww
IO_0
1st when
clause
2nd when
clause
1st when
clause
t
ww
(Not to scale)
IO_out call
IO_out call
IO_out call
