Diagnostic counters, Standard controlnet counters, Module specific counters – Rockwell Automation AutoMax ControlNet Communication Interface Module User Manual
Page 64: Figure 25 standard controlnet diagnostic counters
Page 64 AutoMax ControlNet Module
Publication number DSMBCN-UM001B-EN-P February 2003
Diagnostic Counters
The MBCN maintains two sets of diagnostic counters:
• the standard ControlNet diagnostic counters
• additional diagnostic counters specific to the MBCN
These counters can be used to monitor MBCN operation and to diagnose
problems.
The counters all roll over to 0 when they reach their maximum value.
To clear the counters, write a non-zero value to register 4. The MBCN
clears the contents of the standard ControlNet and module specific
diagnostic counters, then clears register 4 to indicate the counters have
been cleared. This register can be written to at any time.
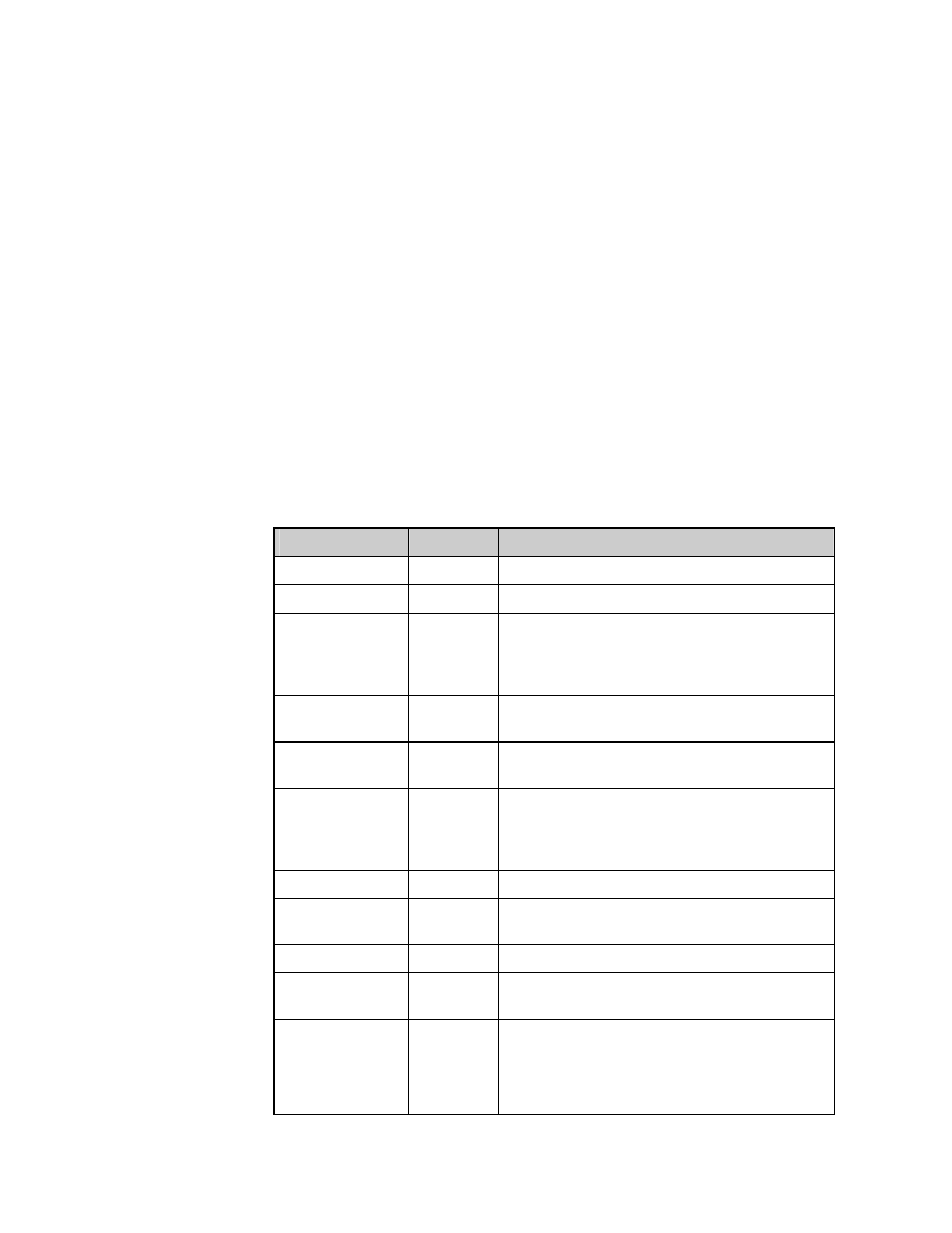
Standard ControlNet Counters
The following counters are defined in the ControlNet specification.
NOTE: Some counters are double words.
Name
Location Description
TxGood
9344-9345 Transmit Frames – Good
RxGood
9346-9347 Frame Received - Good CRC
RxBadCrc
9348
Frame Received - Bad CRC. If this is
incrementing, other error counters are
probably incrementing too. Indicates physical
problems with the network.
AFrmErrs
9349
Cable A Framing Errors. This counter
increments even if channel A is disabled
BFrmErrs
9350
Cable B Framing Errors. This counter
increments even if channel B is disabled
TxAborts
9351
Transmit Frames – Aborted. If this counter is
incrementing, other error counters are
probably incrementing too. It indicates
physical problems with the network.
HighWaters 9352
Not
Used
NutOverloads
9353
More Scheduled Data than will fit in the current
NUT. This indicates scheduling problems
SlotOverLoads
9354
More than 510 bytes in a MAC frame
Blockages
9355
Not enough Unscheduled Bandwidth to fit an
Unscheduled message
NonConcurrence
9356
The MBCN’s Implicit Token Value did not
match the network's. The MBCN has lost
synchronization with the network. The MBCN
thinks another node is transmitting out of turn.
This could be caused by physical problems
