Section 2. internal data storage – Campbell Scientific CR23X Micrologger User Manual
Page 51
2-1
SECTION 2. INTERNAL DATA STORAGE
2.1 FINAL STORAGE AREAS, OUTPUT
ARRAYS, AND MEMORY POINTERS
Final Storage is the memory where final
processed data are stored. Final Storage data
are transferred to your computer or external
storage peripheral.
The size of Final Storage is expressed in terms of
memory locations or bytes. A low resolution data
point (4 decimal characters) occupies one
memory location (2 bytes), whereas a high
resolution data point (5 decimal characters)
requires two memory locations (4 bytes). Table
1.5-1 shows the default allocation of memory
locations to Program, Input, Intermediate, and the
two Final Storage areas. The
A
Mode is
used to reallocate memory or erase Final Storage
(Section 1.5).
The default size of Final Storage with standard
memory is 586,568 low resolution memory
locations.
Final Storage can be divided into two parts:
Final Storage Area 1 and Final Storage Area 2.
Final Storage Area 1 is the default storage area
and the only one used if the operator does not
specifically allocate memory to Area 2.
Two Final Storage Areas may be used to:
1.
Output different data to different devices.
2.
Separate archive data from real time display
data. In other words, you can record a short
time history of real time data and separately
record long term, archive data.
3.
Record both high speed data (fast recording
interval) and slow data without having the
high speed data write over the slow data.
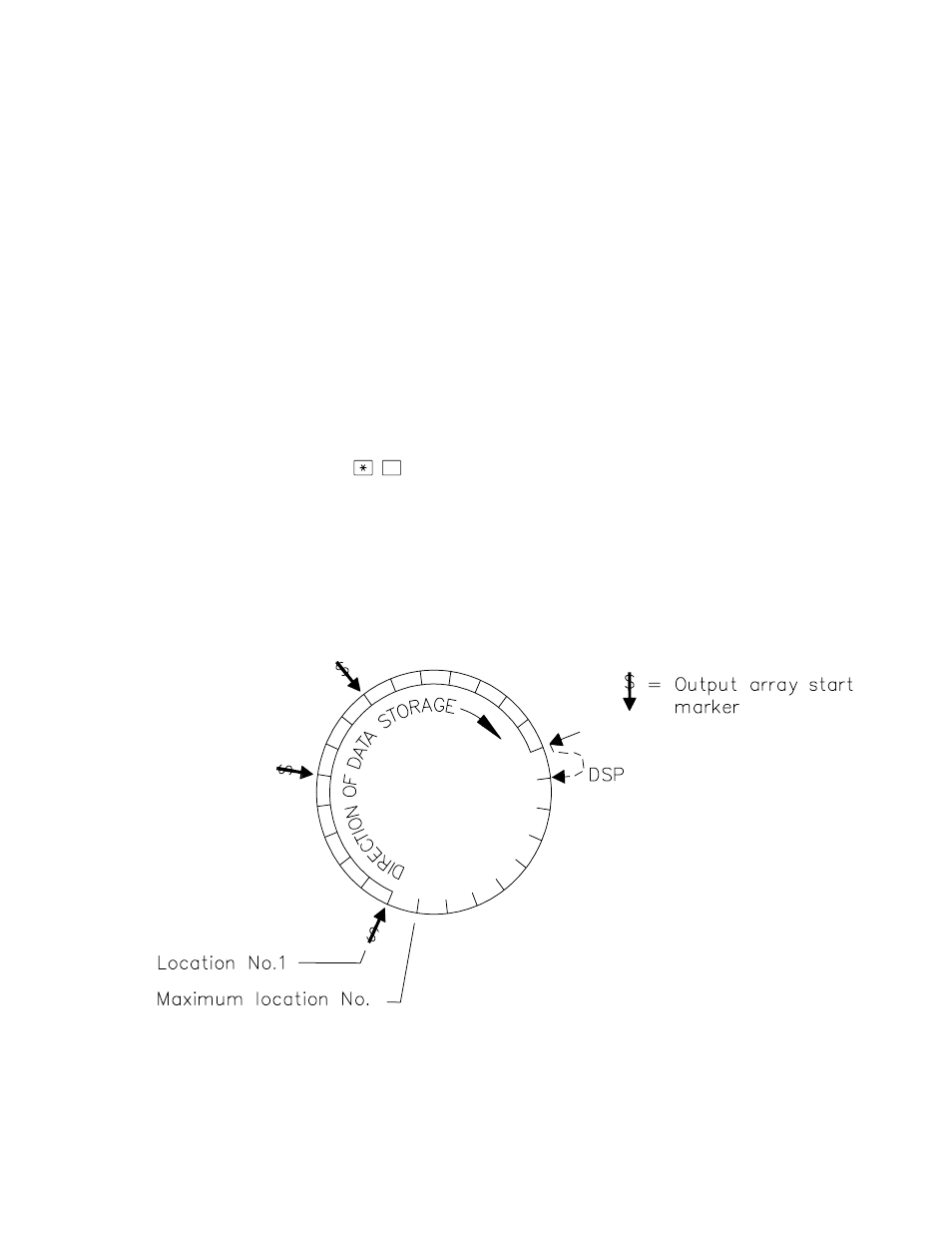
Each Final Storage Area can be represented as
ring memory (Figure 2.1-1) on which the newest
data are written over the oldest data.
The Data Storage Pointer (DSP) is used to
determine where to store each new data point in
the Final Storage area. The DSP advances to
the next available memory location after each
new data point is stored.
FIGURE 2.1-1. Ring Memory Representation of Final Data Storage
