1 offset voltage measurement – Campbell Scientific CR23X Micrologger User Manual
Page 202
SECTION 13. CR23X MEASUREMENTS
13-2
FIGURE 13.1-1. Fast 50 and 60 Hz Noise Rejection
450 uS
250 uS fast
260 uS
Reset Integrator
16.67 mS 60 Hz Reject
20.00 mS 50 Hz Reject
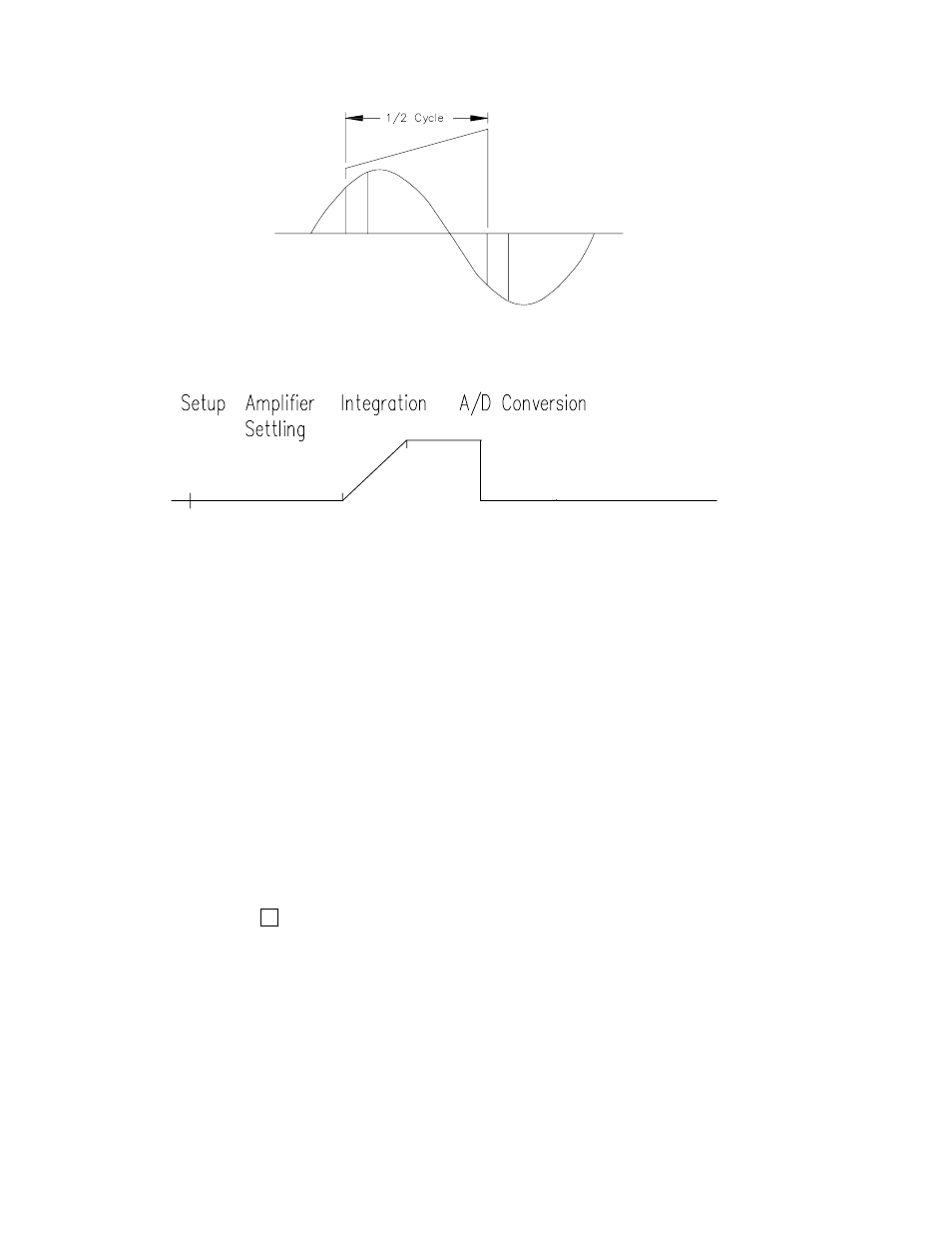
FIGURE 13.1-2. Timing of Single-Ended Measurement
13.1.1 OFFSET VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
A single-ended measurement on the
±
10 mV and
±
50 mV ranges takes longer than on other input
ranges because an offset measurement prior to
every scan is performed. Offset measurements
are performed in background on all other input
ranges. Measurement time can be reduced on
the
±
10 and
±
50 mV ranges by using the "--"
option (e.g., 11--, 12--, 21--, 22--, 31--, 32--). The
"--" option causes offset measurements for the
±
10 mV and
±
50 mV ranges to be performed in
the background. The "--" option, however, is
used at the expense of compensation for rapid
changes in offset voltage. The "--" option is
selected by pressing the
C
key after entering the
numeric value on the CR23X key pad.
13.2 SINGLE-ENDED AND
DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE
MEASUREMENTS
The timing and sequence of a single-ended
measurement is shown in Figure 13.2-1. A
single-ended measurement is made on a single
input which is referenced to ground. A single
integration is performed for each measurement.
A differential measurement measures the
difference in voltage between two inputs. The
measurement sequence on a differential
measurement involves two integrations. First
with the high input referenced to the low, then
with the inputs reversed (Figure 13.2-2).
The CR23X computes the differential voltage by
averaging the magnitude of the results from the
two integrations and using the polarity from the
first. An exception to this is the differential
measurement in Instruction 8 which makes only
one integration.
Because a single-ended measurement is
referenced to CR23X ground, any difference in
ground potential between the sensor and the
CR23X will result in an error in the
measurement. For example, if the measuring
junction of a copper-constantan thermocouple,
used to measure soil temperature, is not
insulated and the potential of earth ground is 1
mV greater at the sensor than at the point
where the CR23X is grounded, the measured
voltage would be 1 mV greater than the
thermocouple output or approximately 25
°
C
high.
