Cache and nonvolatile storage (nvs) – HP XP Continuous Access Software User Manual
Page 45
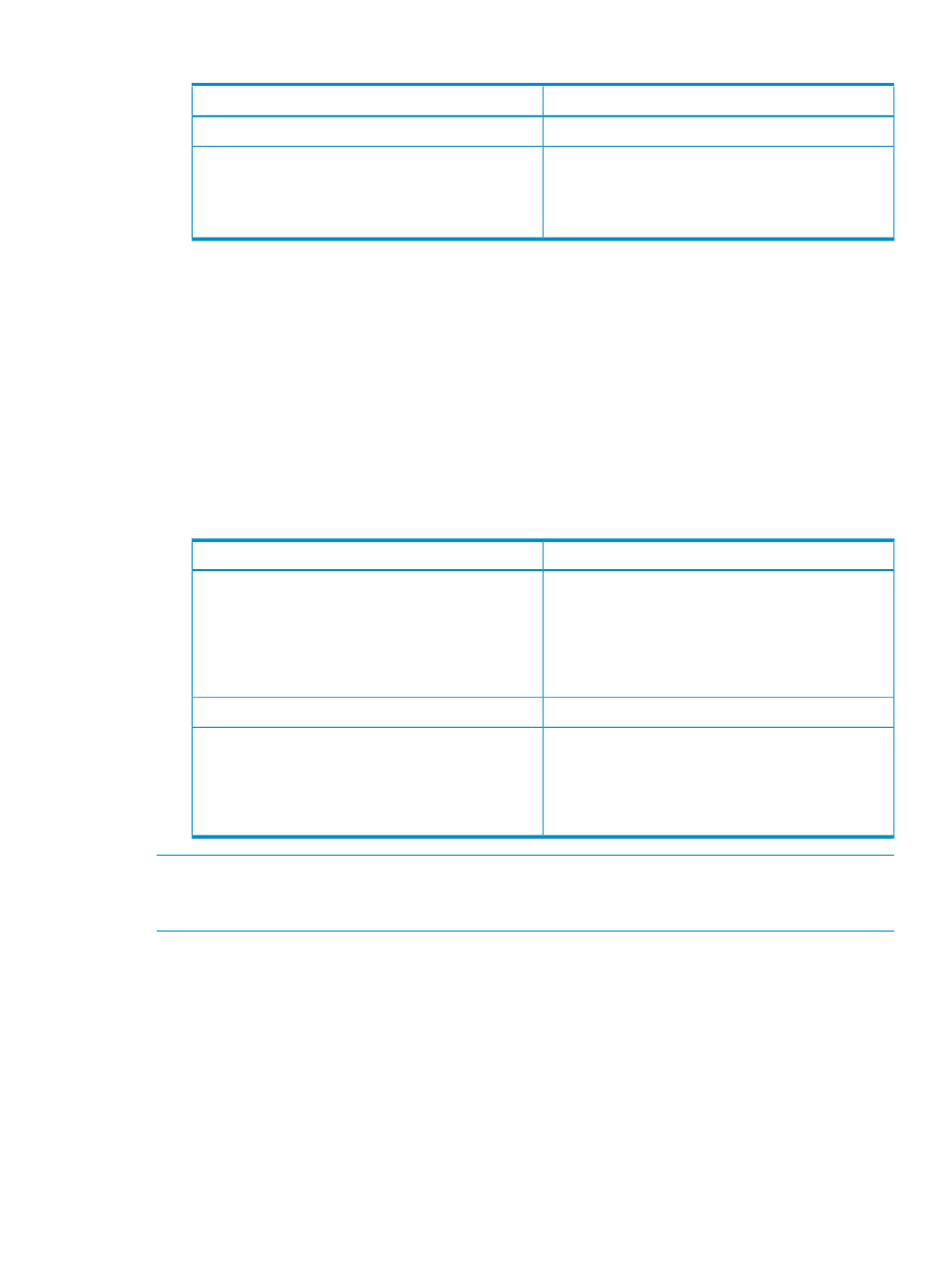
Table 13 Journal group specifications (continued)
Support specifications
Item
Up to 16
Number of journal volumes in a journal group
Up to 4 (ID No.: 0 to 3)
NOTE:
If XP Continuous Access Synchronous uses
No. 0, No. 1 to No. 3 are available for XP Continuous
Access Journal.
Number of Mirror IDs
1
Only the HP service engineer can install shared memory options and apply High Performance mode. If necessary,
contact your HP account support representative.
The same number of journal volumes is not required in the master and restore journal groups
that are paired.
A mirror ID is required for a configuration that will be supported in the future within a 3-data
center (3DC) configuration. Each pair relationship in a journal group is called a “Mirror.” The
Mirror ID identifies two or more mirrors for one journal group. The same Mirror ID is applied
for the data volume pair. See
Combining XP Continuous Access Journal with XP Continuous
Access (3DC cascading configuration)
for more information.
•
describes the relationship between data volumes, journal volumes, and
data and journal volumes in a journal group.
Table 14 Volume specifications in journal groups
Support specification
Item
Journal volumes and data volumes in the same journal
group can belong to different CLPRs. It is recommended
journal volumes should belong to the same CLPR. Also
it is recommended data volumes should belong to the
same CLPR.
NOTE:
Only OPEN-V can be used for journal volumes.
Emulation type
Same or different capacity is available.
Volume capacity
Journal and data volumes in the same journal group
must belong to the same CLPR.
NOTE:
A primary journal group and the corresponding
secondary journal group need not belong to the same
CLPR.
CLPR
NOTE:
When XP Continuous Access Journal and Hitachi Universal Replicator for z/OS coexist
in the same local array, each journal group must contain either XP Continuous Access Journal pairs
or Hitachi Universal Replicator for z/OS pairs (not both).
Accessing XP Continuous Access Journal primary and secondary data volumes
To ensure maximum data integrity during normal XP Continuous Access Journal operations, the
secondary array rejects all write operations issued by a host to an XP Continuous Access Journal
secondary data volume. If you need a write operation to an XP Continuous Access Journal secondary
data volume, you must set the secondary data volume's write option (see
). When resuming (Pairresync) the split pair, the secondary array sends the secondary
data volume's track bitmap to the primary array to ensure proper pair resynchronization.
Cache and nonvolatile storage (NVS)
Cache and nonvolatile storage (NVS) must be operable for the primary and secondary arrays of
an XP Continuous Access Journal data volume pair. If not, the XP Continuous Access Journal
Requirements and restrictions for XP Continuous Access Journal
45
