Figure 4-1, Disk migration – HP Integrity NonStop J-Series User Manual
Page 75
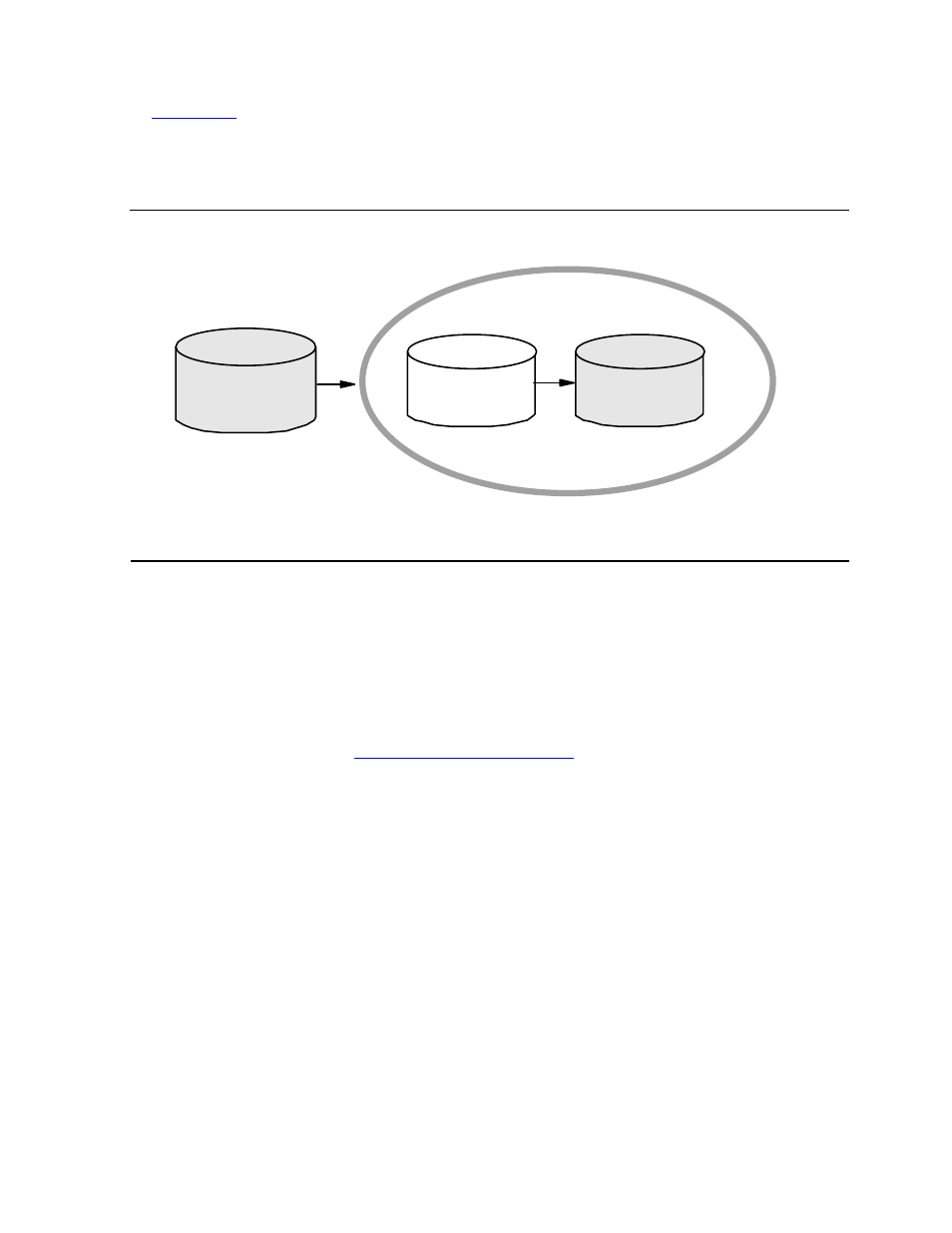
Migration Guidelines
HP NonStop Storage Management Foundation User's Guide—523562-007
4-3
The SMCONVRT Utility
In
, $DATA is the physical volume that is subsequently renamed $DATAP
upon completion of the process. The pool name $POOL is used in this illustration to
serve as the name of the pool in which the volume is included when the process
finishes.
The following steps must be taken to migrate files on $DATA to a virtual disk:
1. If the volume is a TMF data volume, issue “TMFCOM DISABLE DATAVOL $DATA.”
2. If the volume is a TMF data volume, issue “TMFCOM DELETE DATAVOL $DATA.”
3. For D-series versions, issue a PUP DOWN $DATA command. For G-series
versions, issue an SCF STOP $DATA command.
4. Use SMCONVRT (see
SMCONVRT $DATA $DATAP $POOL1
Proceed with migration of Physical Disk $DATA ? (Y/N): y
Enter ANT catalog location for new VDP $DATA: $CAT
Enter PENDOPS catalog location for new VDP $DATA: $CAT
Enter cache size for new VDP $DATA: 30000
Enter ANT capacity in bytes for new VDP $DATA: 1000000
Enter start down flag value for new VDP $DATA: 0
5. For D-series versions, issue a PUP UP $DATAP command. For G-series versions,
issue an SCF START $DATAP command.
6. If the volume is a TMF data volume, issue “TMFCOM ADD DATAVOL $DATAP.”
Figure 4-1. Disk Migration
002
CDT
.CDD
$DATA
(Physical Volume
Before Migration)
$DATA
(Virtual Disk)
$DATAP
(Physical Volume)
$POOL (Storage Pool)
