Gw + 1.61, M)/(x + ao – Yokogawa Single Channel Oxygen Analyzer System ZR22/ZR402 User Manual
Page 109
IM 11M13A01-02E
7-10
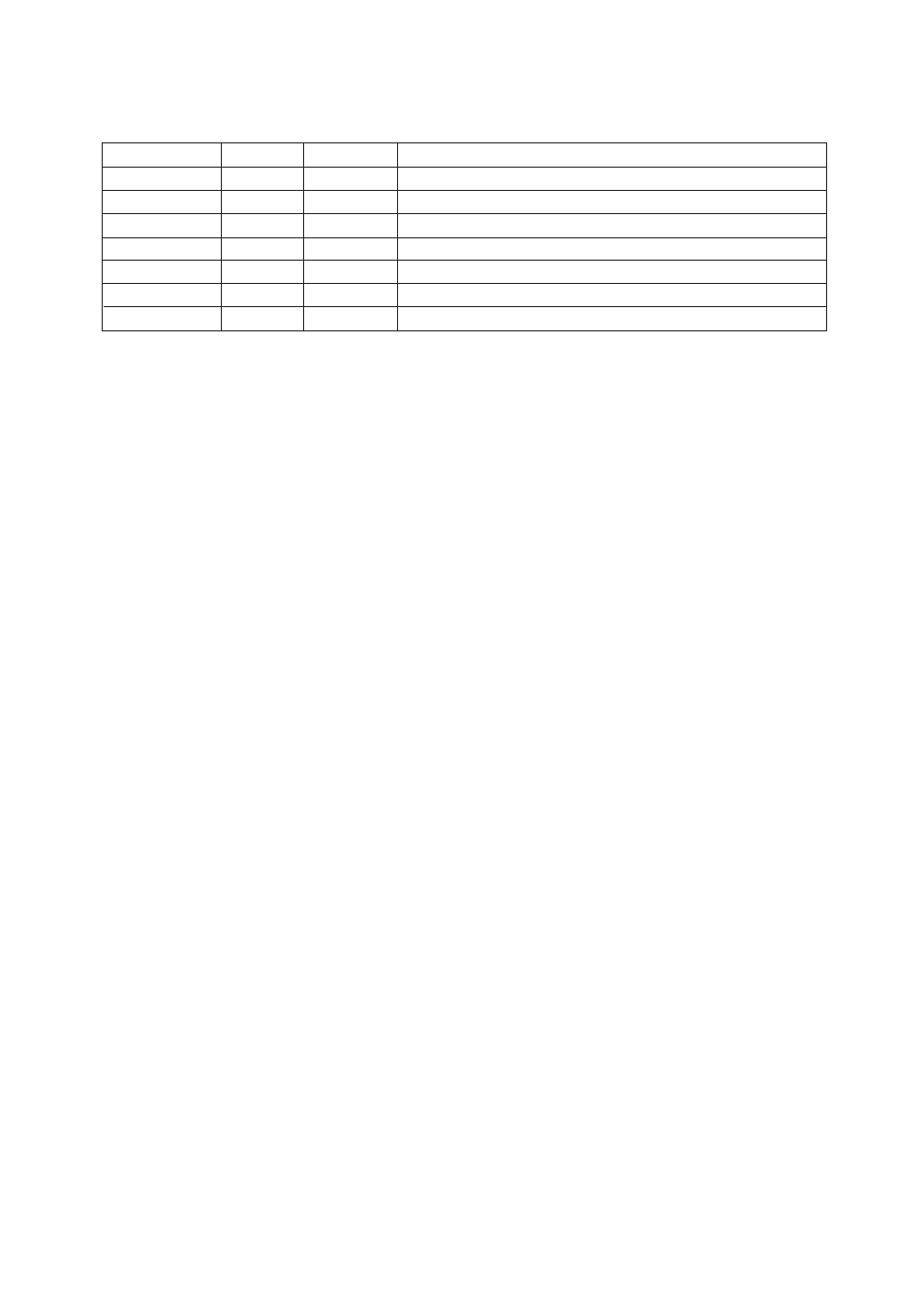
Table 7.2 Display Items
T7.2E.EPS
*1: If an analog output damping constant is set, the oxygen concentration display then includes these settings.
Item
Primary value
Secondary and
tertiary values
Oxygen concentration
Oxygen concentration during measurement
Air ratio
Current computed air ratio
Moisture quantity
Moisture quantity (%H
2
O) in the exhaust gas
Output 1 item
Oxygen concentration with the equipment set for oxygen analyzer (See *1 below.)
Output 2 item
Oxygen concentration with the equipment set for oxygen analyzer (See *1 below.)
Current output 1
Current value output from analog output 1
Current output 2
Current value output from analog output 2
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
᭺
Display
About the air ratio:
“Air ratio” is defined as the ratio of (the amount of air theoretically required to com-
pletely burn all the fuel) to (the amount of air actually supplied).
For this equipment, the air ratio will be obtained in a simplified way by measuring the
oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The air ratio may be expressed mathematically
by:
m ={1 / (21- Oxygen concentration)}
ϫ 21
If you use the air ratio data for estimating the combustion efficiency, etc., check that no
air is leaking in beforehand and that the measured value has not been affected by any
interference gas (CH
4
, CO, H
2
, etc.).
About moisture quantity:
The moisture quantity in the exhaust gas is calculated based on the parameters of the
fuel setting (refer to Section 8.6.3, “Setting Fuel” later in this manual). The moisture
content may be expressed mathematically by:
Moisture quantity = {(water vapor content per fuel unit quantity) + (water content in
air)}/ total amount of exhaust gas
= (Gw + 1.61
ϫ
Z
ϫ
Ao
ϫ
m)/(X + Ao
ϫ
m)
where,
Gw
= water vapor content in exhaust gas, m
3
/kg (m
3
)
Z
= Ambient absolute humidity, kg/kg
Ao
= Ideal air amount, m
3
/kg (m
3
)
m
= Air ratio
X
= Fuel coefficient, Nm
3
/kg or m
3
/m
3
For details on each parameter, refer to Section 8.6.3, “Setting Fuel”.
