Differential amplifier small tip modules – Teledyne LeCroy WaveLink Differential Probe Series (13-25 GHz) User Manual
Page 13
Operator's Manual
WL-HBW-A-OM-E Rev B
7
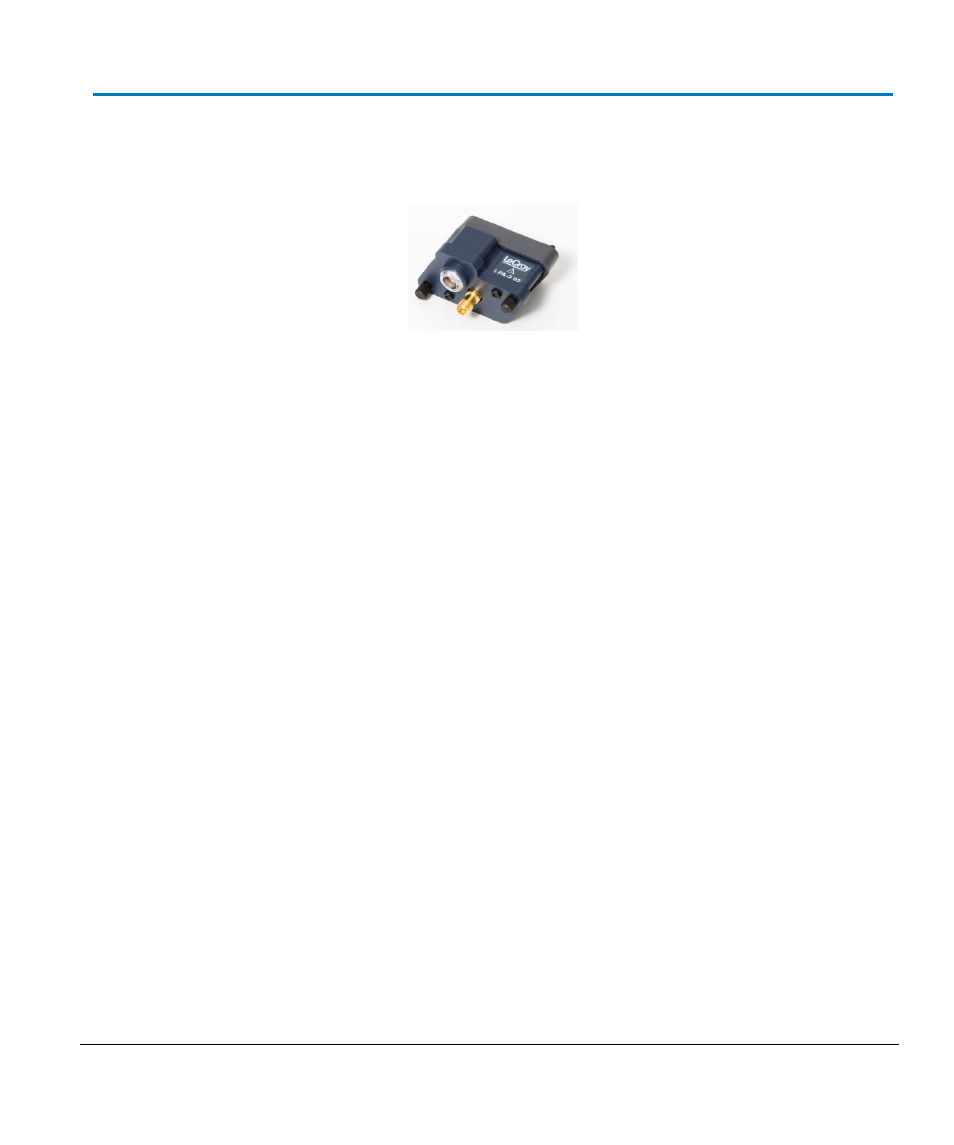
LPA-2.92 mm to ProLink Probe Adapter
This adapter provides a simple and effective method to convert a Teledyne LeCroy ProLink interface
to a Teledyne LeCroy 2.92mm interface.
Teledyne LeCroy's 2.92mm interface utilizes a 2.92mm connector for the signal, and a
LEMO connection for probe power and communication. This interface is used for >20 GHz and <=36
GHz inputs on Teledyne LeCroy oscilloscopes.
Teledyne LeCroy's ProLink interface utilizes a blind-mate adapter (BMA) connector for the signal and
6-pin connection for probe power and communication.
In order to better leverage the complete probe system amongst all possible input types, the LPA-
2.92 may be used to adapt a WL-2.92MM platform/cable assembly to a ProLink connection - saving
you from having to purchase of an additional type of Platform/Cable Assembly. This adapter is
included standard with the WL-2.92MM-CASE.
Differential Amplifier Small Tip Modules
This module contains the active amplifier circuitry and performs the important task of amplifying the
low-level signal at the probe tip for transmission to the oscilloscope via the Platform/Cable
Assembly.
For this 13-25 GHz probe series, Teledyne LeCroy utilizes advanced differential distributed (traveling
wave) amplifier architecture to achieve superior high frequency broadband performance. A
distributed amplifier uses a transmission line to provide inputs to a series of amplification stages.
Another parallel transmission line is used to sum the outputs of each amplification stage. The two
transmission lines are designed with specific delay and impedance characteristics to ensure that the
amplification stages are summed correctly. Since the amplifier gain stages add rather than multiply
(as in a typical cascade design), it is possible to achieve high gain over a wide frequency range with
very low inherent noise. This provides the added benefit of a lower probe attenuation, which
enables the oscilloscope to be operating in an input range which itself requires lower gain, and
hence will typically have lower noise. In addition, higher bandwidths can typically be achieved with
this amplifier architecture. Since a pure distributed amplifier provides insufficient low frequency
response, an additional amplifier is integrated into the assembly for this purpose.
