Vertical speed indicator (vsi), Vertical deviation, Flight instruments – Garmin G1000 Piper PA-46 Meridian User Manual
Page 75
190-00763-01 Rev. A
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Piper PA-46 Meridian
61
FLIGHT INSTRUMENTS
SY
STEM
O
VER
VIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EICAS
AUDIO P
ANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANA
GEMENT
HAZARD
AV
OID
ANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL
FEA
TURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
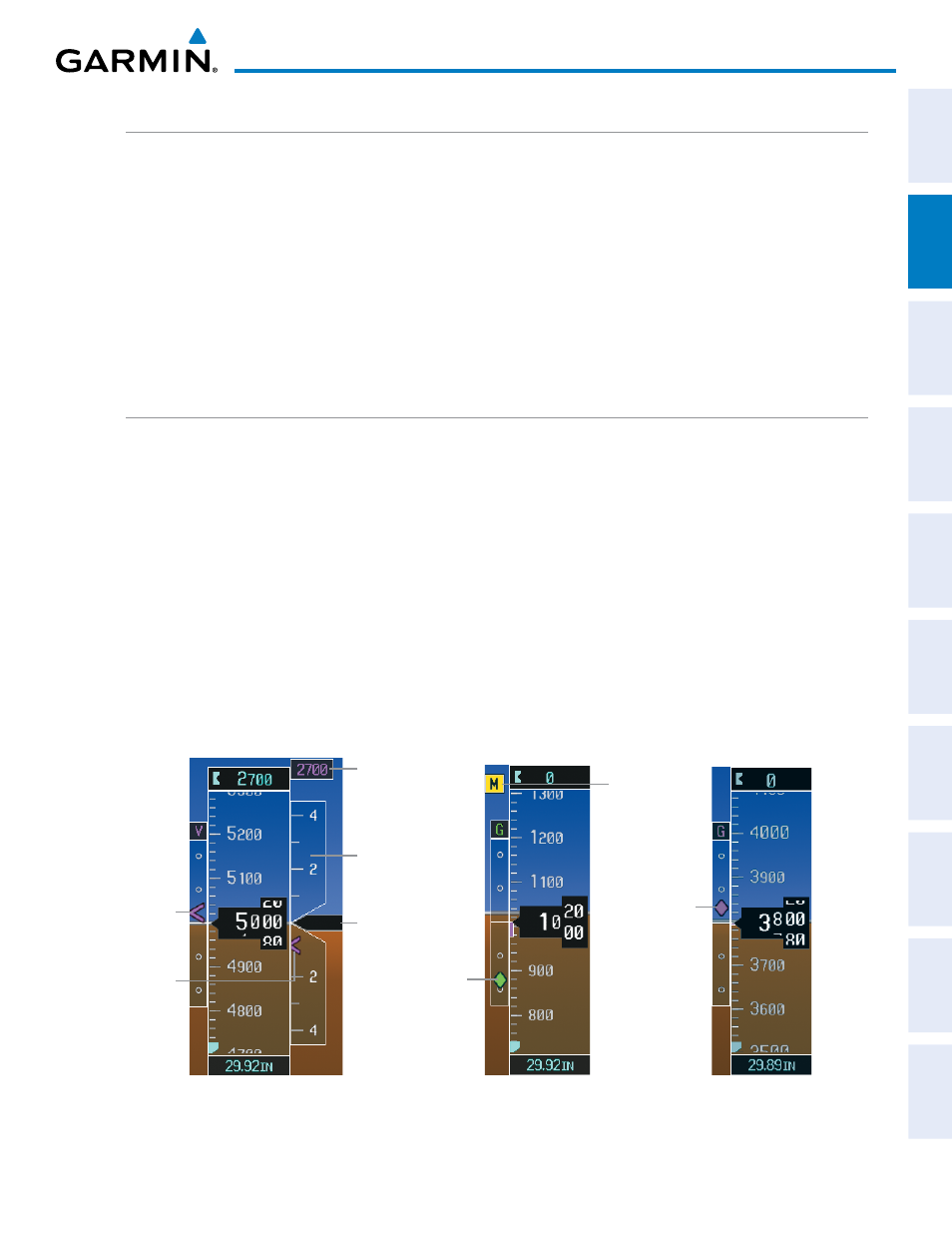
VERTICAL SPEED INDICATOR (VSI)
The Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI; Figure 2-13) displays the aircraft vertical speed with numeric labels and
tick marks at 2000 and 4000 fpm in each direction on the non-moving tape. Minor tick marks are at intervals
of 1000 fpm. The current vertical speed is displayed in the pointer, which also points to that speed on the
non-moving tape. Digits appear in the pointer when the climb or descent rate is greater than 100 fpm. If the
rate of ascent/descent exceeds 4000 fpm, the pointer appears at the corresponding edge of the tape and the rate
appears inside the pointer.
A magenta chevron bug is displayed as the Required Vertical Speed Indication (RVSI; see Figure 2-13) for
reaching a VNV Target Altitude once the “TOD [Top of Descent] within 1 minute” alert has been generated. See
the Flight Management and AFCS sections for details on VNV features, and refer to Section 2.4, Supplemental
Flight Data, for more information about VNV indications on the PFD.
VERTICAL DEVIATION
The Vertical Deviation Indicator (VDI; Figure 2-13) uses a magenta chevron to indicate the baro-VNV vertical
deviation when Vertical Navigation (VNV) is being used; the VDI appears in conjunction with the “TOD within
1 minute” alert. Full-scale deflection (two dots) is 1000 feet. The VDI is removed from the display if vertical
deviation becomes invalid. See the Flight Management and AFCS sections for details on VNV features, and refer
to Section 2.2, Supplemental Flight Data, for more information about VNV indications on the PFD.
The Glideslope Indicator (Figure 2-14) appears to the left of the Altimeter whenever an ILS frequency is
tuned in the active NAV field. A green diamond acts as the Glideslope Indicator, like a glideslope needle on a
conventional indicator. If a localizer frequency is tuned and there is no glideslope, “NO GS” is annunciated.
The glidepath is analogous to the glideslope for GPS approaches supporting WAAS vertical guidance (LNAV+V,
LNAV/VNAV, LPV) and is generated by the system to reduce pilot workload during approach. When an approach
of this type is loaded into the flight plan and GPS is the selected navigation source, the Glidepath Indicator
(Figure 2-15) appears as a magenta diamond. If the approach type downgrades past the final approach fix
(FAF), “NO GP” is annunciated.
Glidepath
Indicator
Figure 2-15 Glidepath Indicator
Glideslope
Indicator
Marker
Beacon
Annunciation
Figure 2-14 Glideslope Indicator
Vertical
Speed
Indicator
Vertical
Speed
Pointer
Required
Vertical
Speed
VNV
Target
Altitude
Vertical
Deviation
Indicator
Figure 2-13 Vertical Speed and
Deviation Indicators (VSI and VDI)
