Table 58 drive capacitor absorption, Energy dissipated in motor winding resistance – Parker Hannifin 88-021610-01G User Manual
Page 179
Parker Hannifin
Appendix B External Power-Dump Resistor Selection 179
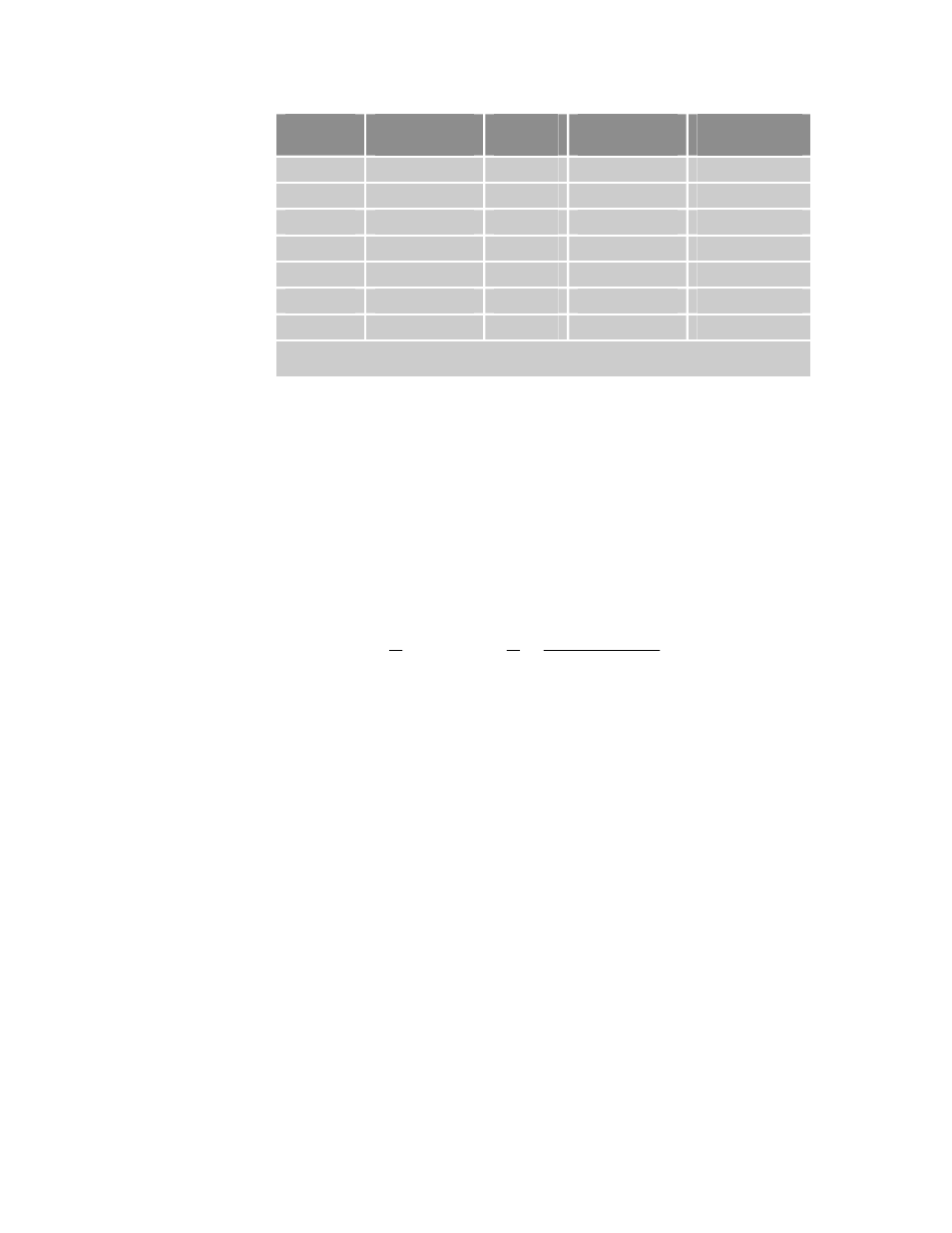
Drive
Capacitance
(uF)
V
TRIP
(VDC)
E
C
(120 VAC)
Joules
E
C
(240 VAC)
Joules
AR-01xx
440
400
28
9
AR-02xx
660
400
43
14
AR-04xx
880
400
57
19
AR-08xx
1100
400
72
24
AR-13xx
1590
400
104
35
AR-20xE
2240
400
N/A
50
AR-30xE
2240
400
N/A
50
When the voltage drops below 385 VDC, the Aries drive stops dissipating power through the
power dump resistor.
Table 58 Drive Capacitor Absorption
Energy Dissipated in Motor Winding Resistance
Some energy is dissipated in the motor windings. Because the energy is
converted to wasted heat in the motor, it is referred to as copper losses.
The energy during deceleration can be derived from the inertia, deceleration
rate, motor resistance, and motor torque constant. If some of the parameters
are not known, the energy dissipated in the motor windings (E
W
) can
conservatively be assumed zero (0).
This is based on current and motor winding resistance.
(
)
D
M
D
T
L
M
D
M
W
t
R
t
k
J
J
t
R
I
E
⋅
⋅
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
⋅
⋅
+
⋅
=
⋅
=
2
2
2
1
2
1
ω
Where
E
W
= energy dissipated in the motor windings (Joules) – copper losses
I
=
current through the windings (Amps
rms
)
R
M
= line to line motor resistance (Ohms)
t
D
=
deceleration time (Seconds)
J
M
=
rotor inertia (kg
⋅m
2
)
J
L
=
load inertia (kg
⋅m
2
)
k
T
=
motor torque constant (Nm/Amp
rms
)
ω =
rotational speed in radians per sec (1 revolution/sec =
2
⋅π⋅radians/sec)
