Specifications – Parker Hannifin Dynaserv G2 User Manual
Page 149
11-14
Specifications
11
N
R
= 4 (rps)
I
1
= I
3
= 9 (A)
I
2
= 3 (A)
t
1
= t
2
= t
3
= 1/4t
CY
When calculating from the above setting example,
4
1
2
1
1
η
B
= 2 ( 4 t
CY
+ 4 t
CY
+ 4 t
CY
) × 5t
CY
Ч 100
2
= 5 Ч 100 = 40
81
9
81
1
η
C
= ( 4 t
CY
+ 4 t
CY
+ 4 t
CY
) × 225t
CY
× 100
17100
= 900 = 19
When substituting the above into equation (3),
40 + 2.6
×19 = 98 < 103
Therefore, the result satisfies the equation, and the setting is deemed to be correct.
(2) Restrictions on the driver
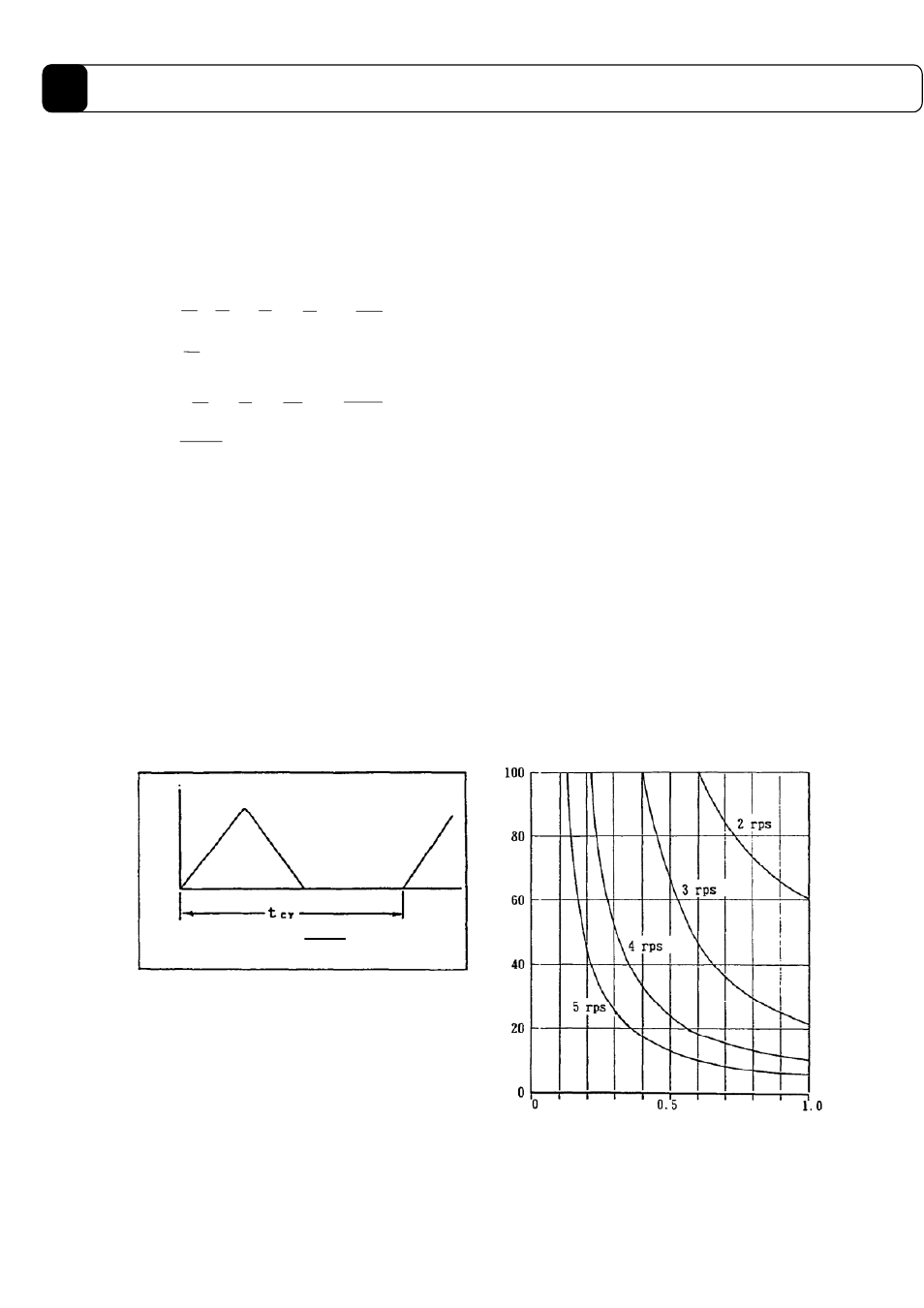
The repeat frequency caused by the driver is restricted by the heat generation of the driver’s built-in regenerative
resistor. If a repeated operation is performed using the pattern as shown in Figure 11.3, the repeat frequency, as
shown in Figure 11.4, is restricted by the load inertia using the number of revolutions as a parameter.
If the load inertia exceeds 1 kgm
2
, or if it is necessary to use on DYNASERV DR5000B series (DR5030B,
5050B, 5070B) outside of the limits, please contact
Compumotor's Applications Dept.
(Figure 11.4)
(Figure 11.3)
Repeat frequency times/min
Load inertia [kgm
2
]
Velocity
Maximum velocity
Repeat frequency =
[times/min]
60
t
CY
Time
