Avalon-st packets to pci express tlps – Altera Arria V GZ Avalon-ST User Manual
Page 76
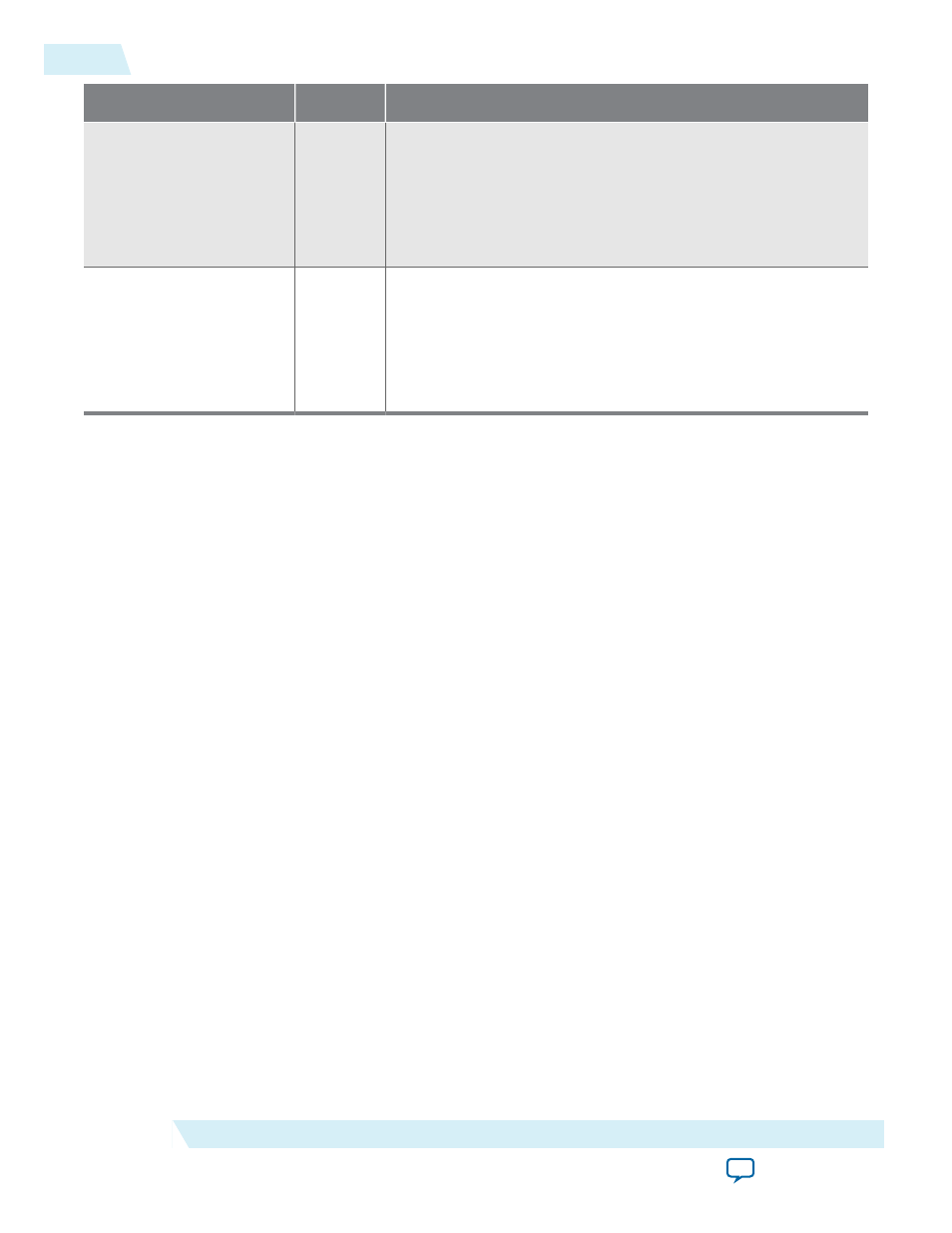
Signal
Direction
Description
ko_cpl_spc_
header[7:0]
Output
The Application Layer can use this signal to build circuitry to
prevent RX buffer overflow for completion headers. Endpoints
must advertise infinite space for completion headers; however,
RX buffer space is finite.
ko_cpl_spc_header
is a static signal
that indicates the total number of completion headers that can be
stored in the RX buffer.
ko_cpl_spc_data[11:0]
Output
The Application Layer can use this signal to build circuitry to
prevent RX buffer overflow for completion data. Endpoints must
advertise infinite space for completion data; however, RX buffer
space is finite.
ko_cpl_spc_data
is a static signal that reflects the
total number of 16 byte completion data units that can be stored
in the completion RX buffer.
Related Information
•
Data Alignment and Timing for the 64-Bit Avalon-ST TX Interface
•
Data Alignment and Timing for the 128-Bit Avalon-ST TX Interface
on page 5-27
•
Data Alignment and Timing for the 256-Bit Avalon-ST TX Interface
on page 5-30
Avalon-ST Packets to PCI Express TLPs
The following figures illustrate the mappings between Avalon-ST packets and PCI Express TLPs. These
mappings apply to all types of TLPs, including posted, non-posted, and completion TLPs. Message TLPs
use the mappings shown for four dword headers. TLP data is always address-aligned on the Avalon-ST
interface whether or not the lower dwords of the header contains a valid address, as may be the case with
TLP type (message request with data payload).
For additional information about TLP packet headers, refer to Appendix A, Transaction Layer Packet
(TLP) Header Formats and Section 2.2.1 Common Packet Header Fields in the PCI Express Base Specifica‐
tion .
Related Information
5-24
Avalon-ST Packets to PCI Express TLPs
UG-01127_avst
2014.12.15
Altera Corporation
Interfaces and Signal Descriptions
