Signal tracing – Elecraft K1 User Manual
Page 87
5
Signal Tracing
You can solve nearly all problems yourself by signal tracing using an RF probe
and signal source, such as the ones shown here.
RF Probe
The RF probe shown in Figure 1 converts RF signals to DC so they can be
measured using a DMM.
.01µF
1N34A
probe
4.7Mohm
C1
D1
R1
E1
tip
12-36" (30-90 cm)
1
2
J1
To DMM
E2
ground
COAX,
Figure 1
The probe tip (E1) should be no longer than 3” (see any ARRL Handbook for
ideas), and you should not touch the tip while taking measurements. Use an
alligator clip at E2, with a 4” (13 cm) lead.
Note: With this RF probe, DC voltage readings on your DMM will be
approximately equal to the signal voltage in Vrms (root-mean-square).
However, the error in the reading is quite significant for small signals (typ.
–50% at 50 mVrms). The signal tracing procedures take this error into account.
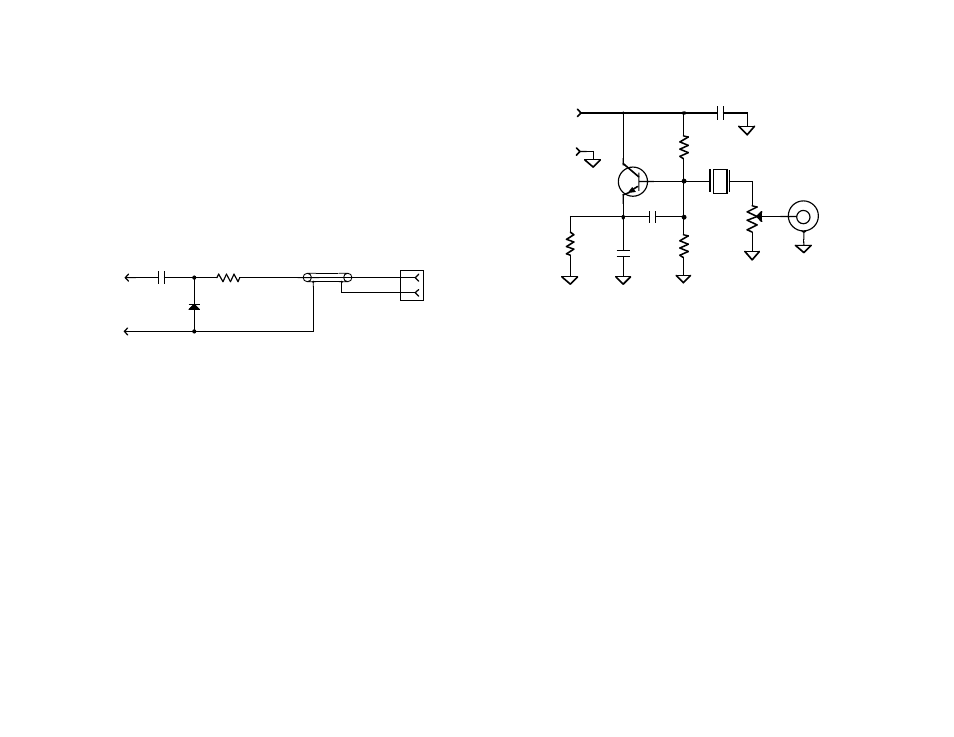
Crystal Oscillator
The simple crystal oscillator shown in Figure 2 can be used in lieu of a
commercial signal generator. It will run on voltages as low as 8 V, but 12 V or
higher is recommended.
The components are not critical, and can vary 20% with little variation in
performance. Nearly any NPN RF transistor will work in the circuit. Crystal X1
should be chosen for the band in use. The potentiometer can be any small
trimmer or panel mount unit, but should not wire-wound.
2N2222A,
150pF
10K
22K
560Ω
X1 (see text)
50 or 100Ω
Level
(non-inductive)
RF
OUTPUT
8-14VDC
+
-
.01µF
2N3904, etc.
39pF
Figure 2
Receiver and VFO Signal Tracing
In the following steps you’ll use an RF probe, DMM, and a signal source to
find the stage where the received signal is getting lost or attenuated. You can
then use voltage tables and resistance checks to find the bad component or
connection. Space is provided at each step to record your measurements, which
can vary as much as 25% in most cases and still be acceptable. Test points and
components are on the RF board unless otherwise indicated.
1. Connect the RF probe’s output to your DMM’s +/- DC input jacks. Select a
2 or 3-V DC range.
2. The DMM should read close to 0.000 V DC, and the reading should
increase when you touch the RF probe tip with your finger.
3. Turn on the K1 and switch to the desired band. Use the menu to turn AGC
OFF. Set AF GAIN to minimum.
4. Connect the RF probe’s ground clip to the ground jumper near the VFO
inductor, L1. The probe tip will be touched to the points indicated in the
following steps.
5. VFO: U7, pin 1 (U7 is near the left edge of the RF board). Expected DMM
indication: .02-.04 V (DC). Actual: _______.
6. Premix crystal: U7, pin 7. Expected: .04-.25 V. Actual: _______.
