Figure52 vlan example – Allied Telesis AT-S20 User Manual
Page 66
Virtual LAN Configuration
5-2
You can group your end stations logically through VLANs.
Information exchange is confined within the members of a given
VLAN. A VLAN constitutes one broadcast domain; therefore,
broadcast packets from an end station only go to other stations
within the same VLAN.
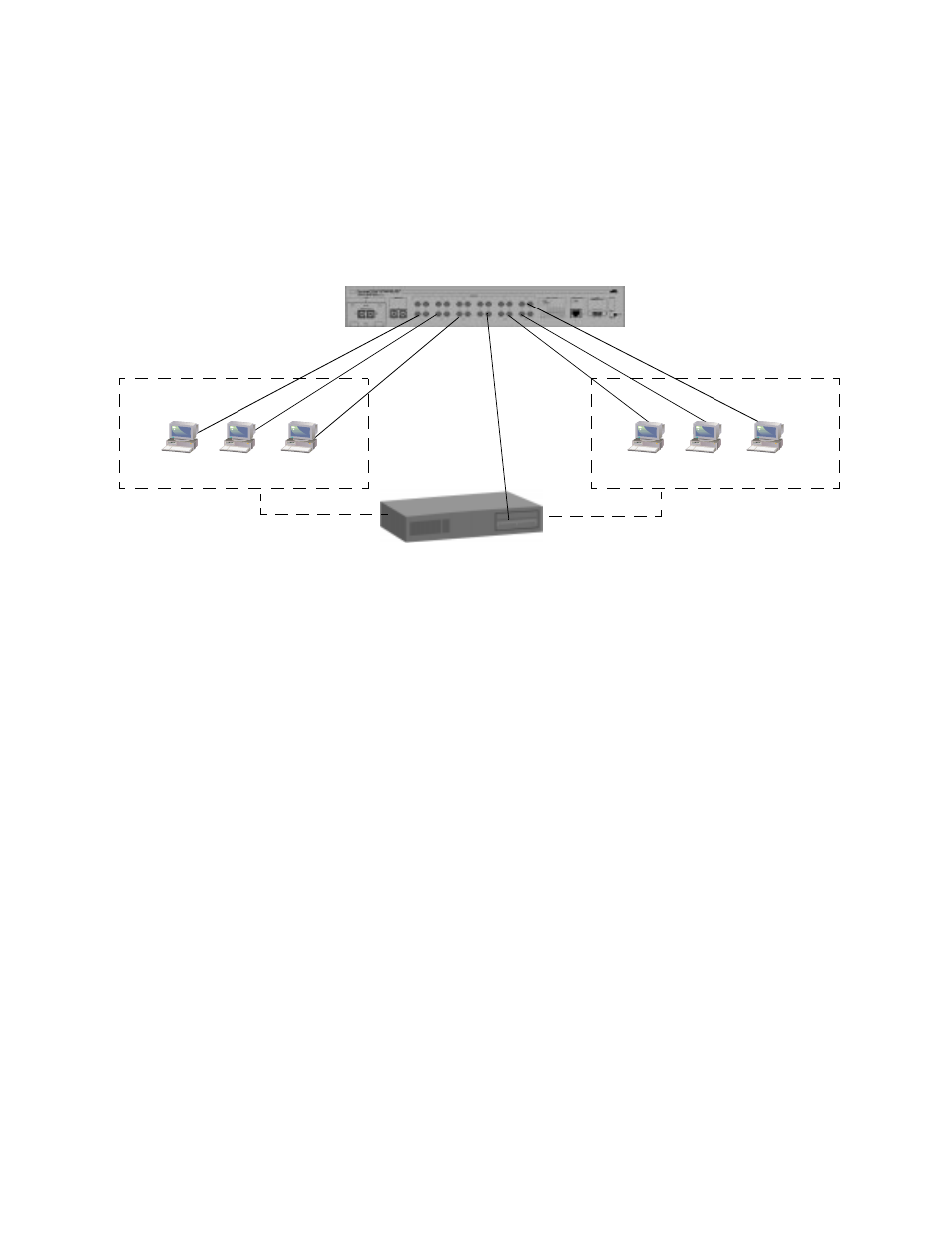
Port-based VLANs cannot communicate with each other through the
switch; they require a router to do this (Figure 5-2).
Figure 5-2 VLAN Example
Advantages of Using VLANs
❑
You have the flexibility of grouping workstations logically or
functionally, regardless of their physical location on the
network.
❑
You can change VLAN memberships anytime by software
configuration without moving the workstations physically, or
change group memberships by simply moving a cable from
one port to another.
❑
With VLAN tagging, the ability to group workstations into
logical work groups is more versatile. You can assign a port to
be an uplink to another 802.1Q-compatible switch and enable
it to carry all VLAN traffic instead of using one uplink port per
each VLAN port configured.
The VLAN ID used to tag incoming packets without a tag is called the
Port Virtual LAN (PVID) for the specified port.
Router
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
AT-3714FXL
#2
#4
#6
#8
#10
#12
#11
