HP Insight Management-Software User Manual
Page 14
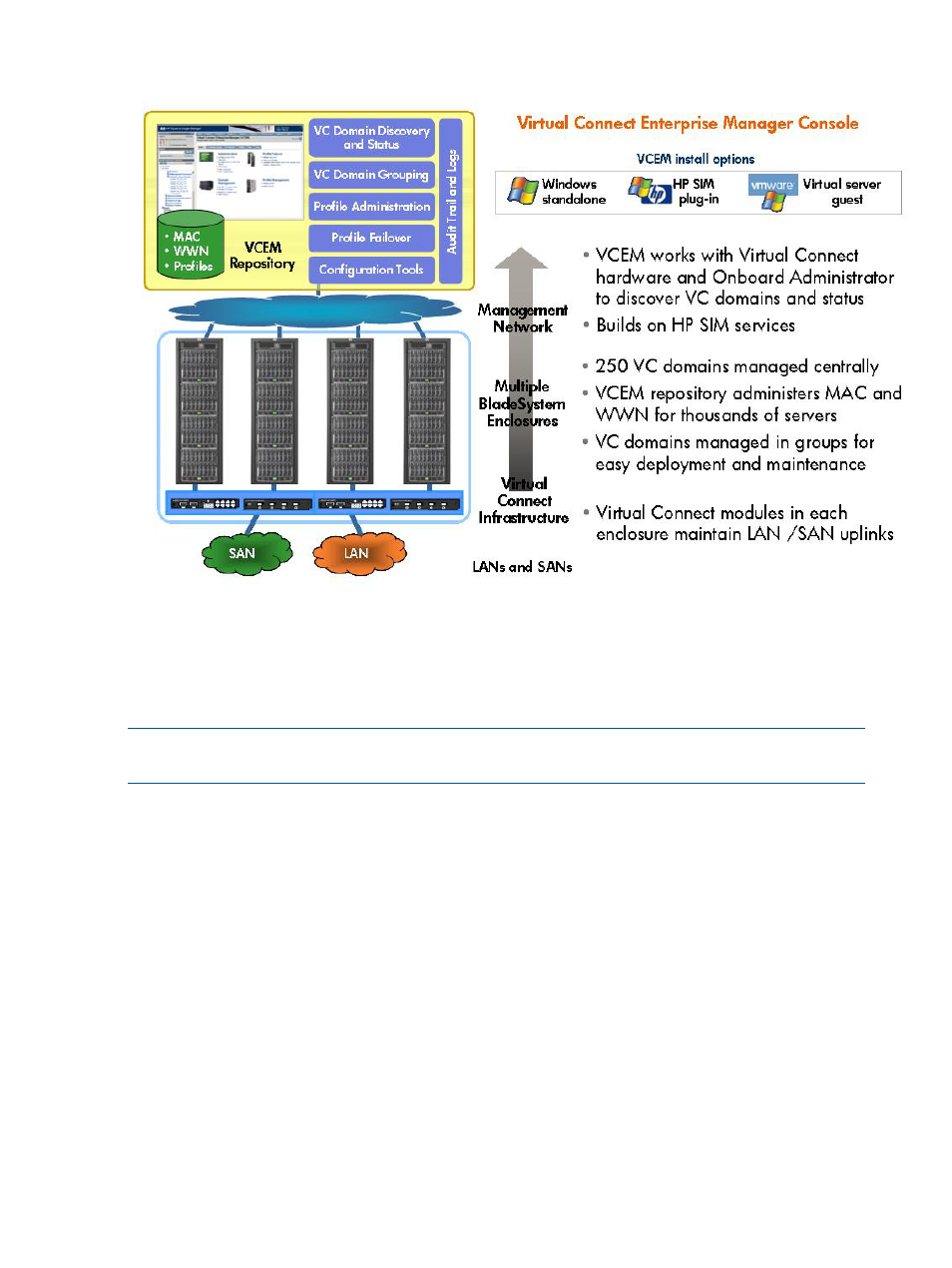
Figure 3 Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager architecture overview
Using VCEM, system administrators can quickly deploy, replace and recover servers and their
associated workloads by simply assigning or reassigning the Virtual Connect server connection
profile to an enclosure bay. The example in
illustrates a server profile movement operation
from “Server A” to “Server C” using VCEM.
NOTE:
The LANs associated with each uplink port and the attributes of the Virtual Connect server
profile remain exactly the same; only the location of the server profile has changed.
When a Virtual Connect server connection profile is moved, the associated MAC, WWN, boot
from SAN parameters and related workload always move with the server profile.
From the VCEM GUI, server profiles can be moved to a user-defined spare server. A server profile
can be moved manually within the same VC Domain, to any other Domain in the same VC Domain
Group, or to a different VC Domain Group, whether it is in the same rack, across the datacenter
or at another location. A server profile move can be scripted within the same VC Domain only,
using the profile failover capability . The profile movement and failover functionality provided by
VCEM can be used to provide cost-effective server blade recovery, perform proactive hardware
maintenance with reduced downtimes, and control rapid server repurposing to meet changing
workload and application priorities. When moving Virtual Connect server profiles, the fastest
completion times are achieved when the corresponding source and target servers are configured
to boot-from-SAN. The automated profile failover functionality delivered in VCEM requires a
boot-from-SAN environment.
14
Introduction
