Source options, Source options -6 – HP Storage Mirroring Software User Manual
Page 232
14
-
6
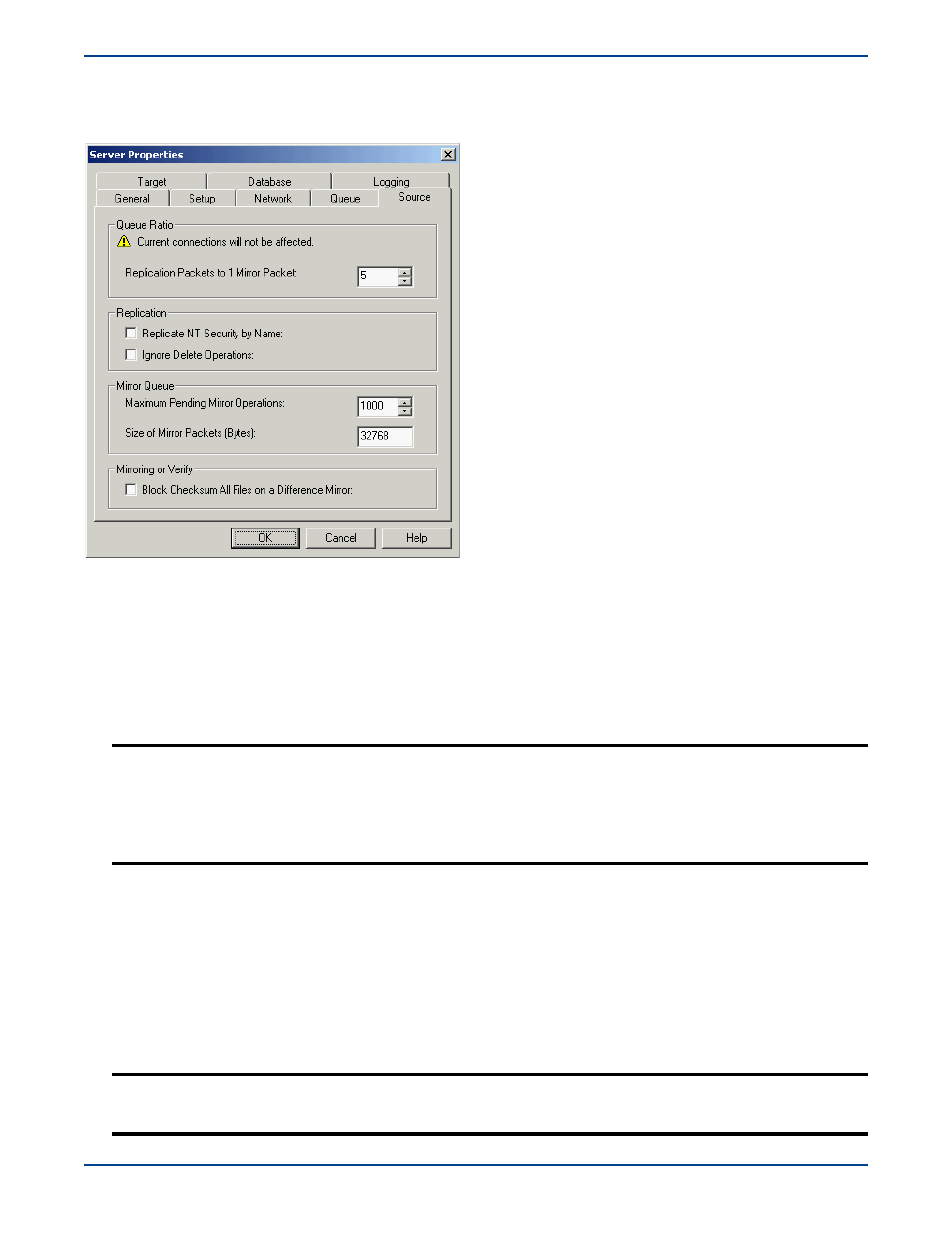
Source options
The
Source
tab consists of settings specific to the source module of Storage Mirroring.
!
Replication Packets to 1 Mirror Packet—This option allows you to specify the ratio of replication packets to mirror
packets that are placed in the source queue. Specify a larger number if you have a busy network that has heavy replication.
Also, if you anticipate increased network activity during a mirror, increase this number so that the replication queue does
not get too large.
!
Replicate NT Security by Name
—This option allows you to replicate permissions and attributes assigned to local
(non-domain) users and groups. For detailed information, see
Windows Permissions
on page 8-2.
!
Ignore Delete Operations—This option allows you to keep files on the target machine after they are deleted on the
source. When a file is deleted on the source, that delete operation is ignored on the target. (All edits to files on the source
are still replicated to the target; only deletions of whole files are ignored.)
!
Mirror Queue
!
Maximum Pending Mirror Operations—This option is the number of mirror operations that are queued on the
source. The default setting is
1000
. If, during mirroring, the mirror queued statistic regularly shows low numbers,
for example, less than
50
, this value can be increased to allow Storage Mirroring to queue more data for transfer.
!
Size of Mirror Packets—The size of the mirror packets that Storage Mirroring transmits. The default setting is
32768
bytes.
!
Block Checksum All Files on a Difference Mirror
—This option allows a file difference mirror to check each block of
data, regardless of the file attributes. If this option is not marked, Storage Mirroring will assume files are synchronized if
their attributes match. For complete details on how this option interacts with the other mirror options, see
File
Differences Mirror Options
on page 7-2.
NOTE:
If a file is deleted using Windows Explorer or My Computer, the file is not actually deleted, from the file
system perspective, but is moved to the Recycle Bin. Because Storage Mirroring sees this as a move to
outside of the replication set and not as a delete, the file will still be deleted from the target even if you
have
Ignore Delete Operations
selected.
If delete operations are ignored long enough, the potential exists for the target to run out of space. In that
case, you can manually delete files from the target to free space for further replication.
NOTE:
Database applications may update files without changing the date, time, or file size. Therefore, if you are
using database applications, you should use the Block Checksum All option to ensure proper file
comparisons.
