NORD Drivesystems BU0260 User Manual
Page 82
Supplementary Manual CANopen for NORDAC SK 20E
82
Subject to technical amendments
BU 0260 GB
Example: Excerpt from the object dictionary of an SK 200E.
Object dictionary
Index
Sub-index
Data
Comments
…
2102
-
200
Parameter (P102), setting 2.00s)
2103
-
200
Parameter (P103), setting 2.00s)
…
Structure of an SDO
Control byte
Index
Sub-index
Data
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
E.g.:
"Download"
E.g.:
"Parameter number"
E.g.:
"Array"
E.g.:
"Parameter values"
SDOs (Service Data Objects) enable access to all device parameters from the object dictionary. They enable
these to be changes and are used for status queries. An SDO consists of eight bytes, of which the first four are
occupied with protocol information (e.g.: data request / parameter number). The remaining four bytes define
the associated data content (e.g.: setting values)
If the length of four bytes is not sufficient, the data contents is divided over several SDOs (segmented). Here,
for all "data SDOs" which follow the first SDO, seven of the eight bytes are available for data transfer. The last
segment contains an "End code".
The exchange of SDOs is carried out by means of a handshake process, i.e. queries are always confirmed
with a response. However, segmented messages are only confirmed once, after receipt of the last associated
SDO. Exchange of new messages is only possible after confirmation of or response to the previous message.
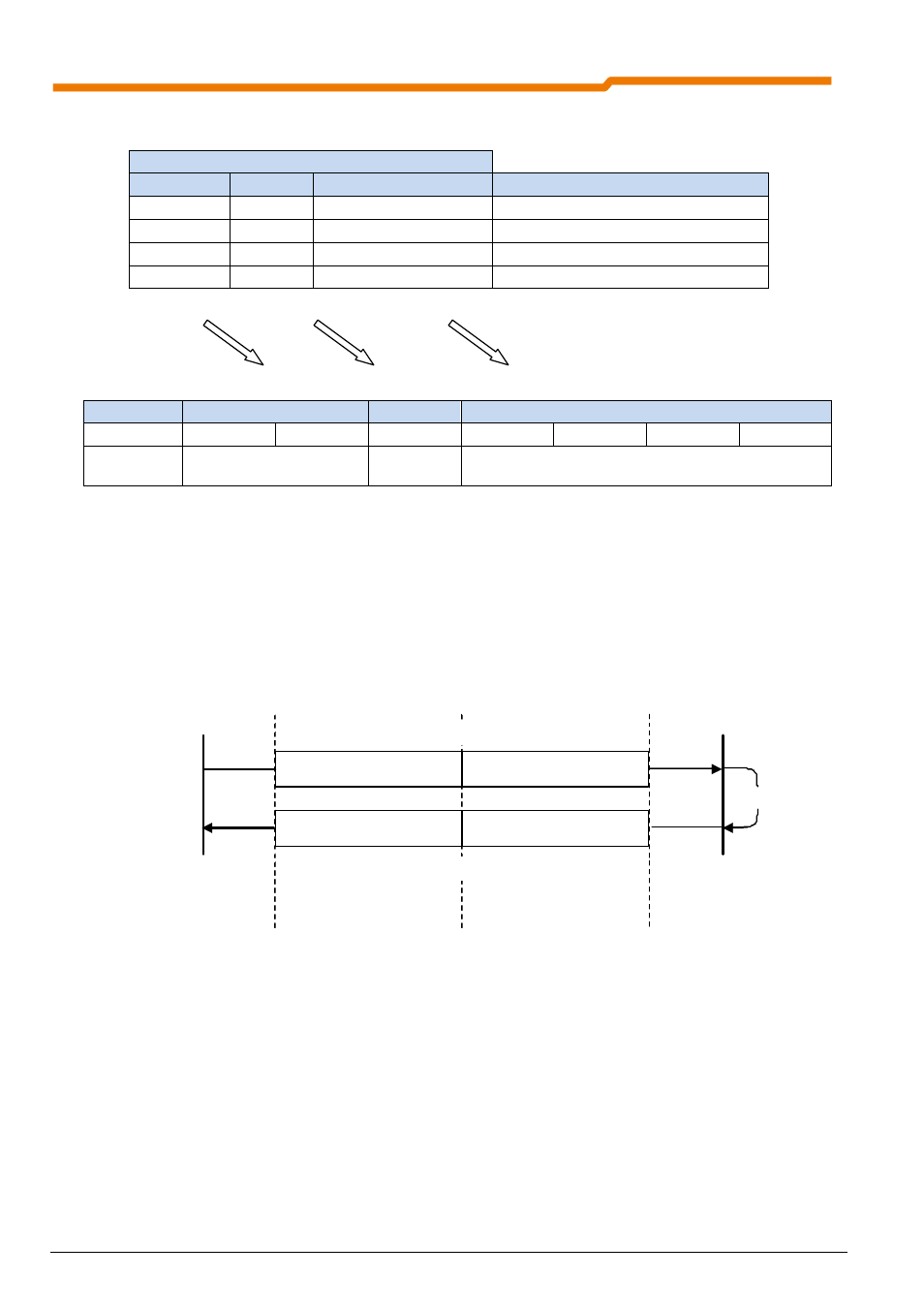
Node 1
Node 2
Protocol information
Object data
Protocol information
Object data
Object definition
Object content
Order telegram
Response telegram
Processing
Diagram: Telegram traffic / structure of reference data area
On the other hand, PDOs (Process Data Objects) serve exclusively for the exchange of process data. A PDO
sent by a node is received by all connected bus subscribers. Each subscriber, which recognises that the
message is relevant on the basis of the identifier, processes it accordingly, however without acknowledgement.
Therefore a message can also be accessed by several subscribers simultaneously (multicast).
The most important advantage of a PDO in comparison with an SDO is that due to the lack of protocol
information, all 8 bytes are available for the exchange of process data. The associated increase in bandwidth
increases the flow of process data by a large factor, which is an advantage for time-critical applications.
