NORD Drivesystems BU0260 User Manual
Page 106
Supplementary Manual CANopen for NORDAC SK 20E
106
Subject to technical amendments
BU 0260 GB
8.3.2
Overview /Communication possibilities
CANopen provides various possibilities for communication, so that there is always an exchange of telegrams.
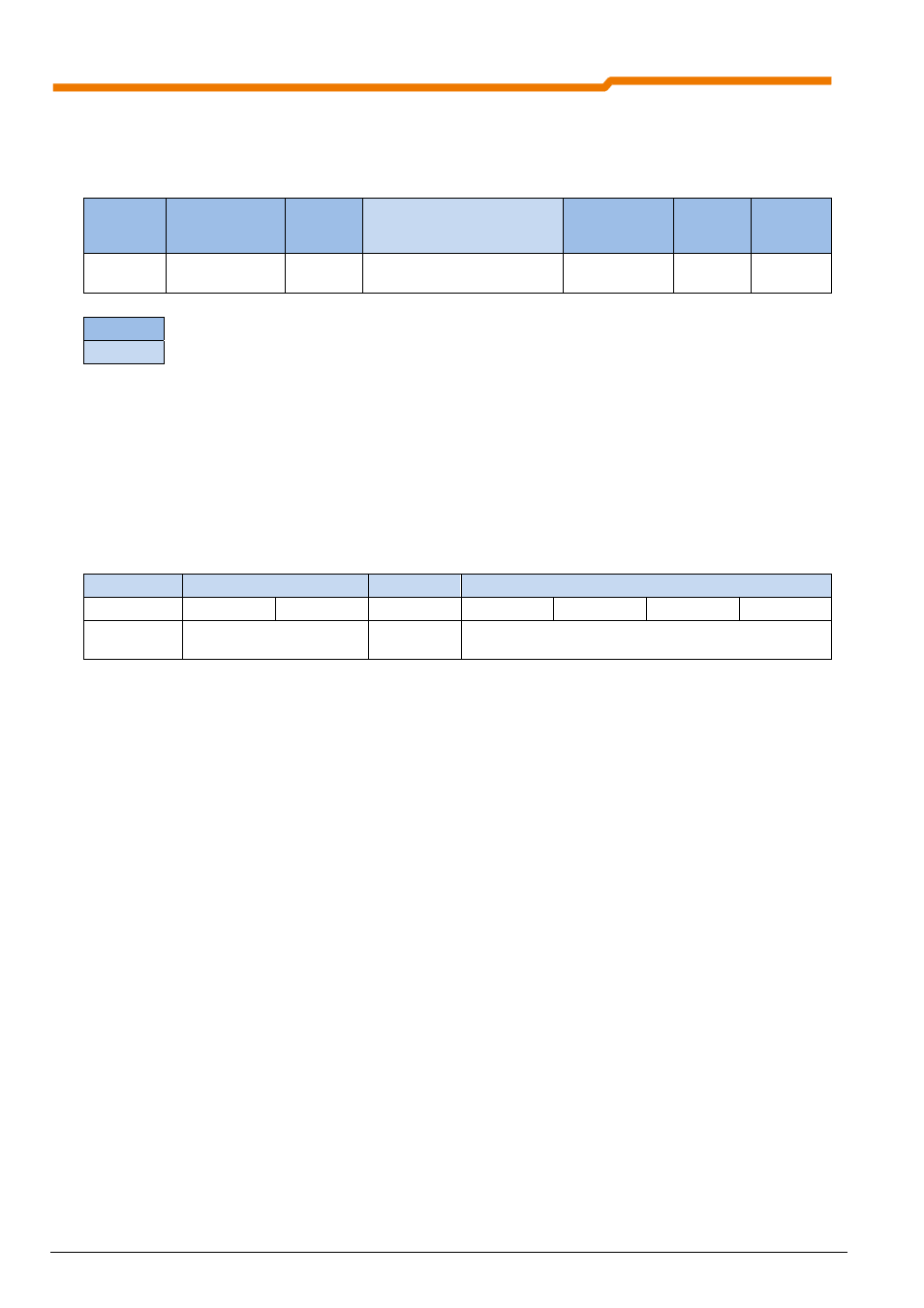
The structure of a telegram complies with the CAN telegram format.
Initial
field
Status field
Control
field
Data field
Security field
Confir-
mation
field
End field
1 bit
12 bit / 32 bit
(identifier)
6 bit
0 - 64 bit
18 bit
2 bit
7 bit
Protocol
information
Reference
data
Due to the different structures of the data field (reference data area) of the CAN protocol, CANopen enables
the exchange of two different types of telegram, the PDO (Process Data Object) and the SDO (Service Data
Object).
A PDO uses the data field exclusively for process data information and is therefore able to transfer 8 bytes of
process data with each telegram.
On the other hand, an SDO divides the data field into a 4 byte configuration area and a 1 - 4 byte data area.
This enables access to the object dictionary and therefore to the function of a subscriber (e.g. frequency
inverter), i.e. enables its parameterisation. However, it restricts the possible size of the data content.
Control byte
Index
Sub-index
Data
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
E.g.:
"Download"
E.g.:
"Parameter number"
E.g.:
"Array"
E.g.:
"Parameter values"
8.3.2.1 PDO (Process Data Object)
A PDO is used for the exchange of data relevant to the process. In addition to the control word (or status word)
it contains up to 3 setpoints (or actual values).
These can be
event-controlled (e.g. after elapse of a time unit),
on request (Polling by Remote Frame) or
synchronous (via a sync telegram (message without data content))
or transmitted (transmission type).
PDOs can only be processed by CANopen subscribers which are in the status "Operational".
PDO messages have comparatively high priorities. This ensures that messages with time-critical process data
are processed with high priority, a fundamental condition for the real-time facility of a system. The fact that
PZD telegrams are transmitted without confirmation plays an important role for this.
The verification of the correct receipt of this data by the relevant subscriber performed by the security
mechanisms of the CANopen protocol on which the exchange of PDO data is based is ensured (bit-stuffing,
CRC, frame-check,...).
