Characteristics of the valve types – Burkert Type 8630 User Manual
Page 17
8630 - 15
S
YSTEM
D
ESCRIPTION
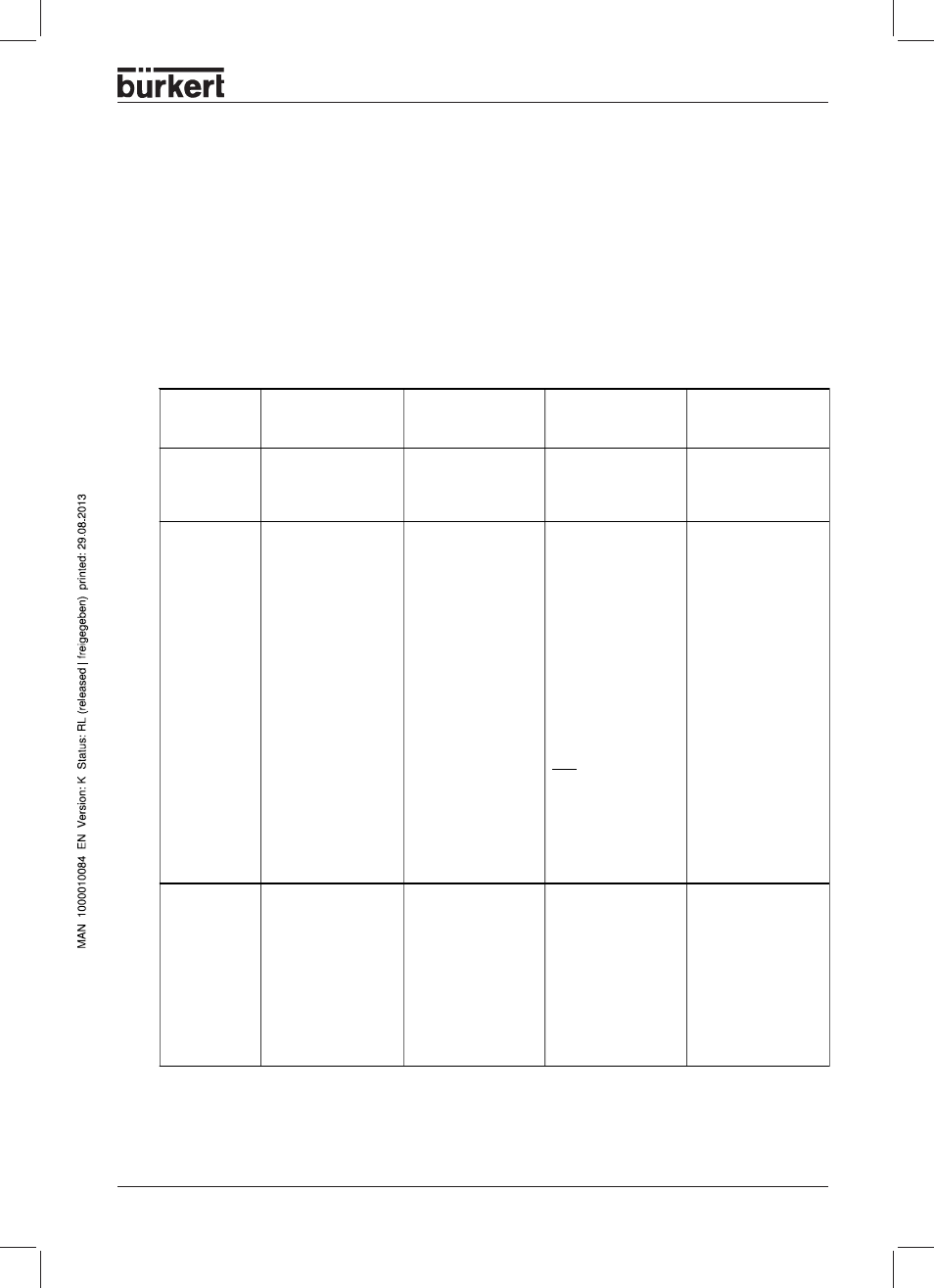
Characteristics of the valve types
Pneumatically driven piston and rotary actuators may be used to operate them. Both single-acting and double-
acting actuators are offered in combination with TOP Control Continuous.
With single-acting actuators, only one chamber in the actuator is pressurized and vented. The pressure
produced works against a spring. The piston moves until an equilibrium is set up between the pressure and the
spring force.
With double-acting actuators, the chambers on both sides of the piston are pressurized. When the one
chamber is pressurized, the other is vented and vice versa. No spring is installed in this actuator version.
Y-valves
Flat seat valves
Diaphram valves
Ball valves
Flap valves
Types
• 2700
• 2712
• 2730 (plastic)
• 2731 (metal)
• 2731K (pipe housing)
• 2652 (2-part,VA)
• 2655 (3-part,VA)
• 2658 (plastic)
• 2672 (metal)
• 2675 (plastic)
Characteristic
• Inlet flow under seat
• Non-impact closure
• Straight flow of
medium
• Self-adjusting packed
gland for very tight seal
• Medium is hermeti-
cally separated from
actuator and the
ambient
• Self-draining housing
design without dead
spaces
• Either flow direction
with low turbulence
flow
• May be steam
sterilized
• CIP compatible
• Non-impact closure
• Actuator and dia-
phragm are de-
tachable with the
housing
• Piggable
• Low and dead space
• insensitive to
contamination
• Lower pressure loss
than with other valve
types
• with 3-part ball valve,
seat and seal can be
exchaged while
installed
Note
Only usable as process
controller.
• insusceptible to dirt
• less pressure loss
compared to other
valve types
• good value for money
• smaller volume
Typical media
• Water, steam and
gases
• Alcohols, oils, fuels,
hydraulic fluides
• Salt solutions, lyes
(organic)
• Organic solvents
• Neutral gases and
liquids
• contaminated, ab-
rasive and aggressive
media
• high purity or sterile
media
• high viscosity media
• Neutral gases and
liquids
• pure water
• slightly aggressive
media
• Neutral gases and
fluides
• slightly aggressive
media
