Source display, Network – Extron Electronics VN-Matrix 200 Series User Manual
Page 12
VN-MATRIX
VN-MATRIX
VN-MATRIX
VN-MATRIX
VN-MATRIX
(encoder)
(decoder)
(decoder)
(decoder)
(decoder)
NETWORK
SOURCE
DISPLAY
RTP
RTP
RTP
RTP
RTP
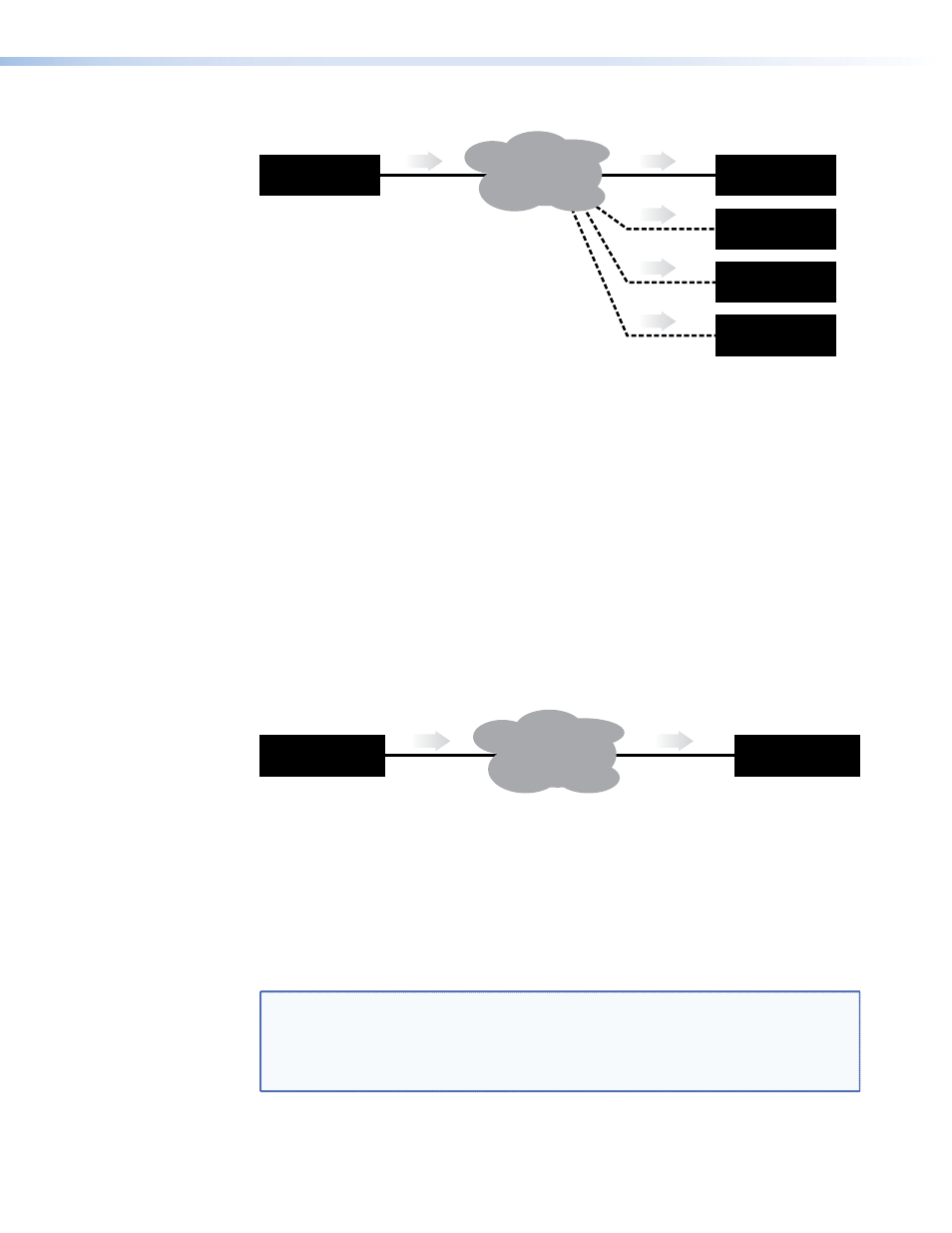
Encoder sends data using RTP
to up to 4 specified decoders
Figure 6.
Unicast RTP
The source encoder defines the display decoder(s) that the source is available to, but the
decoder chooses which source to display.
RTP provides very low latency which is important for video transmission. Unlike other
protocols, RTP packets include a time stamp. Therefore, if packets are received in the
wrong order they can easily be sorted into the correct order for display, or discarded if the
timestamp is out-of-date.
However, because RTP is a connectionless protocol, data delivery is not guaranteed. Where
data packets are lost (for example, due to excessive network traffic) the VNC 200 carefully
manages the data stream to minimize any image disruption.
Unicast TCP
This method transmits data using standard TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and should
only be used for single point-to-point transfer of data.
VN-MATRIX
VN-MATRIX
(encoder)
(decoder)
NETWORK
SOURCE
DISPLAY
TCP
TCP
Decoder makes a TCP connection
with the specified encoder
Figure 7.
Unicast TCP
TCP is a connection-based protocol and, therefore, data is guaranteed to be delivered.
However, in the event of excessive network traffic, delivery may be delayed and will impact
real-time performance.
The decoder defines which source to connect to. Other than defining an IP Address and
source type (if required) no special source encoder setup is required.
NOTE: Multiple decoder connections are theoretically possible using this method but
NOT recommended. Each additional connection will create extra loading on
the encoder CPU which will ultimately result in poor display performance. In
addition, multiple TCP streams carrying the same source data is an inefficient
use of network bandwidth.
VN-Matrix 200 Series • Introduction
7
