2 esp (encapsulating security payload) protocol, 3 my ip address, Table 59 ah and esp – ZyXEL Communications ADSL VoIP IAD with 802.11g Wireless 2602HW Series User Manual
Page 202
Prestige 2602HW Series User’s Guide
202
Chapter 17 VPN Screens
17.2.2 ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) Protocol
The ESP protocol (RFC 2406) provides encryption as well as the services offered by AH. ESP
authenticating properties are limited compared to the AH due to the non-inclusion of the IP
header information during the authentication process. However, ESP is sufficient if only the
upper layer protocols need to be authenticated.
An added feature of the ESP is payload padding, which further protects communications by
concealing the size of the packet being transmitted.
17.3 My IP Address
My IP Address is the WAN IP address of the Prestige. The Prestige has to rebuild the VPN
tunnel if the My IP Address changes after setup.
The following applies if this field is configured as 0.0.0.0:
• The Prestige uses the current Prestige WAN IP address (static or dynamic) to set up the
VPN tunnel.
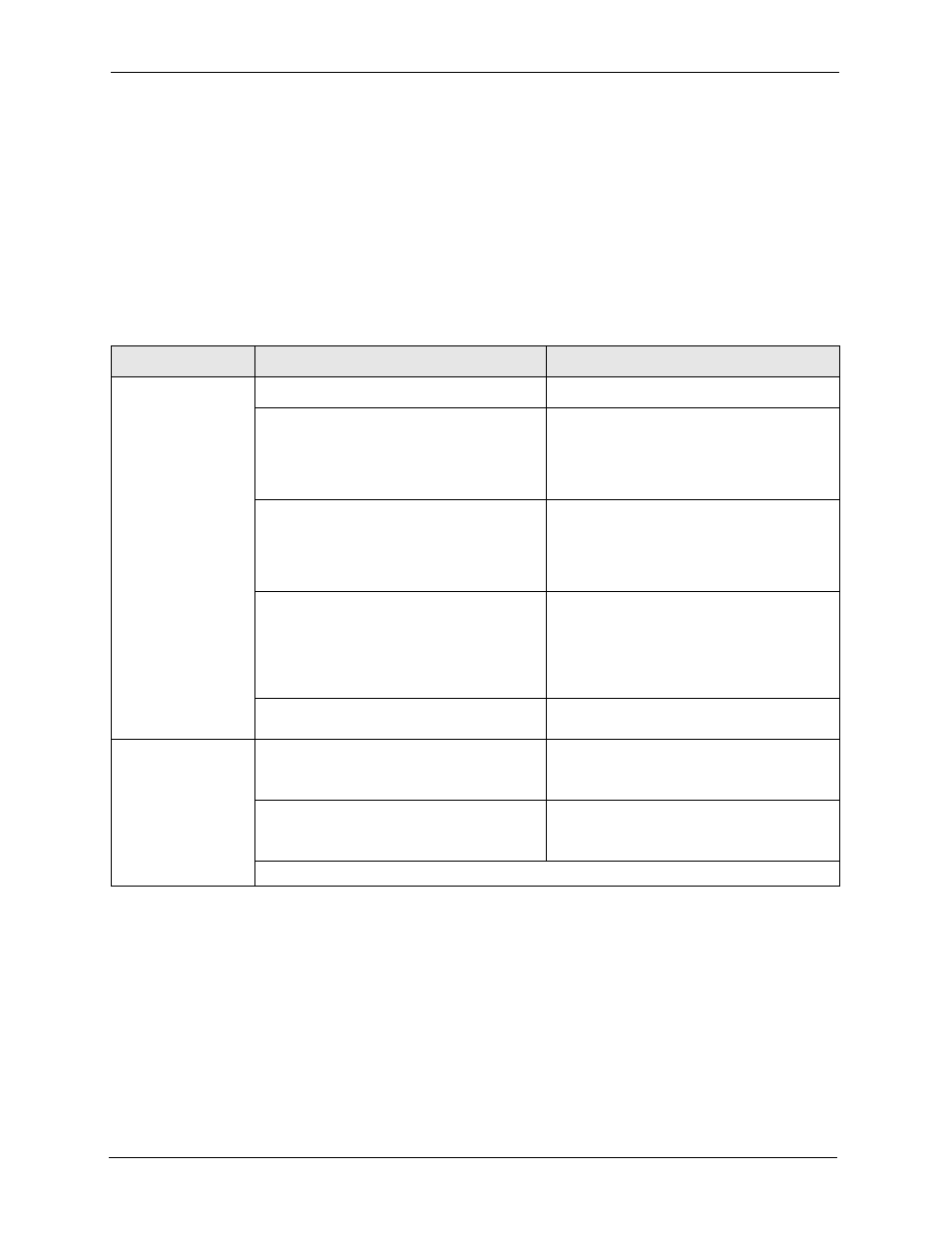
Table 59 AH and ESP
ESP
AH
ENCRYPTION
DES (default)
Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a widely
used method of data encryption using a
private (secret) key. DES applies a 56-bit key
to each 64-bit block of data.
MD5 (default)
MD5 (Message Digest 5) produces a 128-bit
digest to authenticate packet data.
3DES
Triple DES (3DES) is a variant of DES, which
iterates three times with three separate keys
(3 x 56 = 168 bits), effectively doubling the
strength of DES.
SHA1
SHA1 (Secure Hash Algorithm) produces a
160-bit digest to authenticate packet data.
AES
Advanced Encryption Standard is a newer
method of data encryption that also uses a
secret key. This implementation of AES
applies a 128-bit key to 128-bit blocks of data.
AES is faster than 3DES.
Select NULL to set up a phase 2 tunnel
without encryption.
AUTHENTICATION
MD5 (default)
MD5 (Message Digest 5) produces a 128-bit
digest to authenticate packet data.
MD5 (default)
MD5 (Message Digest 5) produces a 128-bit
digest to authenticate packet data.
SHA1
SHA1 (Secure Hash Algorithm) produces a
160-bit digest to authenticate packet data.
SHA1
SHA1 (Secure Hash Algorithm) produces a
160-bit digest to authenticate packet data.
Select MD5 for minimal security and SHA1 for maximum security.
