RAD Data comm LRS-24 User Manual
Page 99
LRS-24 Installation and Operation Manual
Appendix C SNMP Management
IP Environment
C-5
An IP address is logically divided into two main portions:
• Network Portion– assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA). There are five IP address classes: A, B, C, D, and E. However, only the
classes A, B and C are used for IP addressing. Consult your network manager
with respect to the class of IP addresses used on your network.
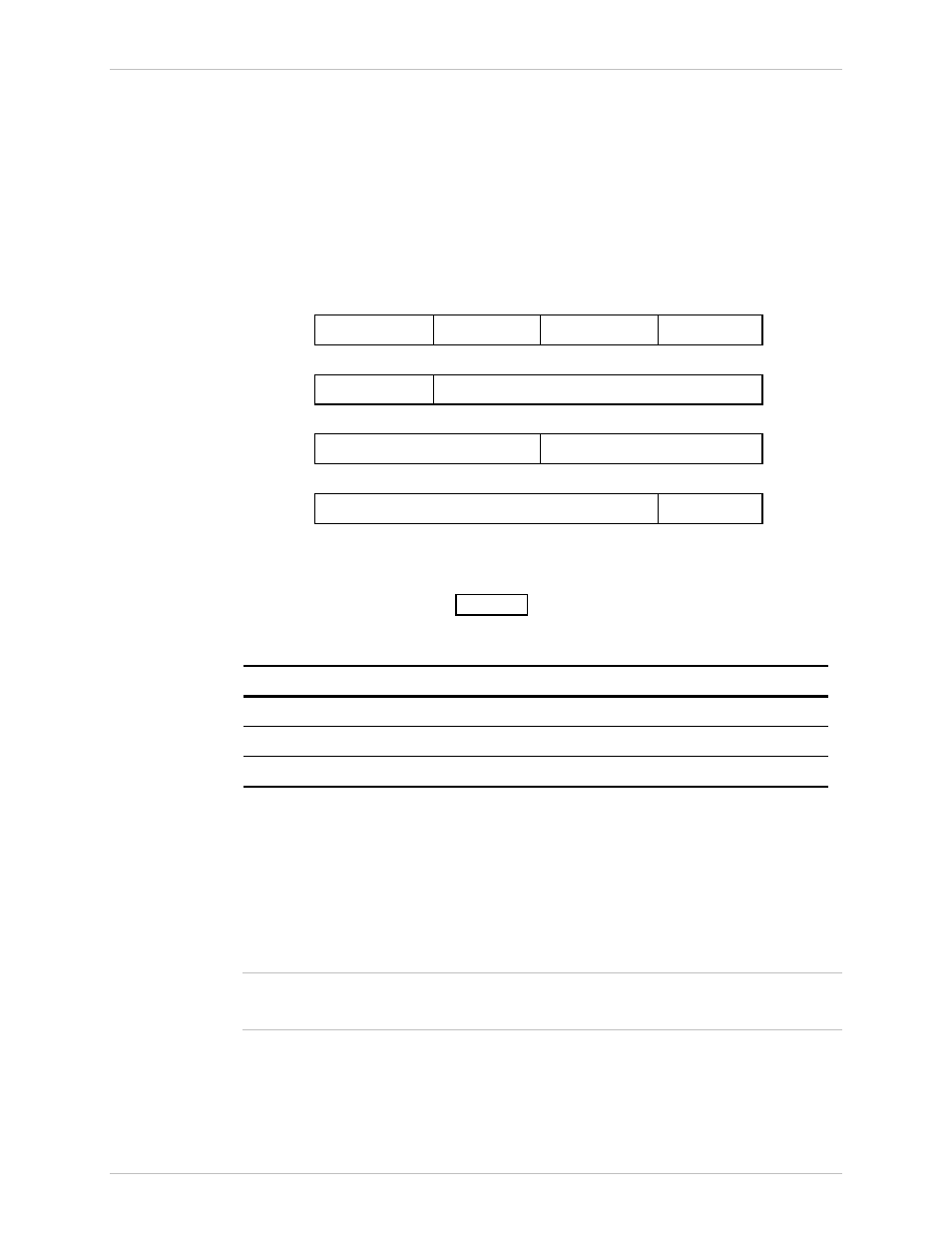
The network portion of an IP address can be one, two or three bytes long, in
accordance with the IP address class. This arrangement is illustrated below:
IP ADDRESS
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Class A
Network Portion Host Portion
Class B
Network Portion
Host Portion
Class C Network Portion
Host Portion
Figure C-1 IP Address
The class of each IP address can be determined from its leftmost byte, in
accordance with the chart in Table C-1.
Table C-1. IP Address Class
Address Class
First Byte
Address Range
Class A
0 thru 127
0.H.H.H through 127.H.H.H
Class B
128 thru 191
128.N.H.H through 191.N.H.H
Class C
192 thru 223
192.N.N.H through 223.N.N.H
N
Bytes that are part of the network portion
H
Bytes that are part of the host portion
• Host Portion–used to identify an individual host connected to the network.
The host identifier is assigned by the using organization, in accordance with its
specific needs.
The all-zero host identifier is always interpreted as a network identifier, and must
not be assigned to an actual host.
Often the host portion is further subdivided into two portions:
Subnet number
Used to identify departmental subnetworks. The subnet number follows
the network identifier.
Host number
Last bits of the IP address.
Note
Order from: Cutter Networks
Ph:727-398-5252/Fax:727-397-9610
www.bestdatasource.com
