2 the hardware main components, 1 the processor subsystem – IBM RS/6000 User Manual
Page 39
The solution to the problem is to use the PCI local bus as the primary system bus
and the ISA bus as an expansion bus. This way, the system can take advantage
of the high-speed data transfer provided by the PCI bus when communicating with
the processor and memory. On the other side, through the PCI-ISA Bridge, the bus
clock can be reduced to match the ISA bus requirements.
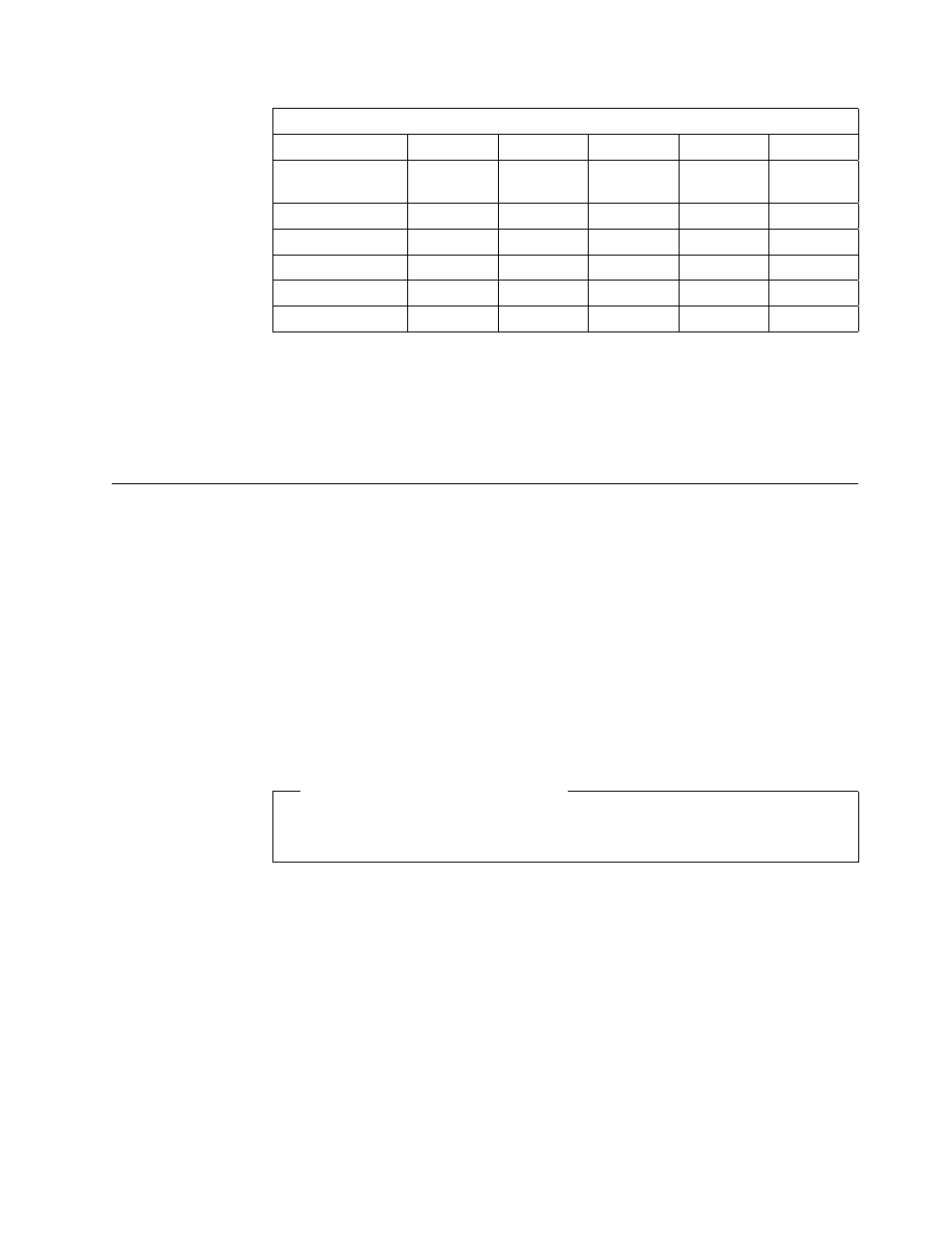
Table 1. PowerPC and Bus Specification
Specification
PowerPC
PCI
ISA(8)
ISA(16)
EISA
Processor Speed
(601-604)
66-132
-
-
-
-
Databus
64
64
8
16
16/32
Address Bus
32
64
20
24
24/32
Bus Clock
66 MHz
33 MHz
4.7 MHz
8.3 MHz
8.3 MHZ
Interrupts
-
4
6
11
11
DMA Channel
-
busmaster
3
7
7
2.2 The Hardware Main Components
The PCI-based RS/6000 servers include the following main hardware components:
Processor Subsystem
L2 Cache
Memory Controller and PCI Bridge
System Memory
Primary PCI Bus
Secondary PCI Bus
EISA Bus
X-bus
No Power Management Controller
Note that the currently available PCI-based RS/6000 servers (E20 and F30) do
not include a power-management controller.
2.2.1 The Processor Subsystem
The PCI-based RS/6000 servers feature the PowerPC 604 microprocessor. The
superscalar multiprocessor-enabled chip issues up to four instructions in parallel
every clock cycle. Its three-stage, double-precision floating point unit provides
tremendous performance capabilities that were previously available only through
expensive add-on hardware.
Figure 6 on page 16 shows the PowerPC 604 microprocessor architecture which is
defined by the following specifications:
PowerPC 604 microprocessor running at:
– 100 MHz on RS/6000 Model E20
– 133 MHz on RS/6000 Model F30
Chapter 2. PCI-Based RS/6000 Server Hardware
15
